Multiculturalism fosters a rich tapestry of cultural diversity, promoting inclusivity and mutual respect within societies. It empowers individuals to embrace different traditions and perspectives, enhancing social cohesion and innovation. Discover how multiculturalism shapes communities and benefits your everyday life by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
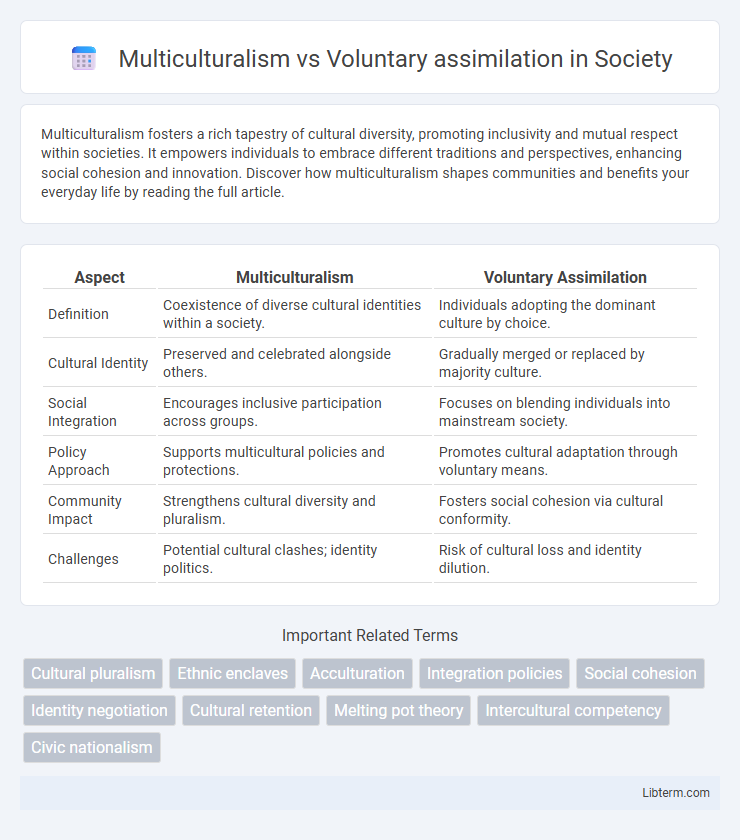
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Voluntary Assimilation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society. | Individuals adopting the dominant culture by choice. |
| Cultural Identity | Preserved and celebrated alongside others. | Gradually merged or replaced by majority culture. |
| Social Integration | Encourages inclusive participation across groups. | Focuses on blending individuals into mainstream society. |
| Policy Approach | Supports multicultural policies and protections. | Promotes cultural adaptation through voluntary means. |
| Community Impact | Strengthens cultural diversity and pluralism. | Fosters social cohesion via cultural conformity. |
| Challenges | Potential cultural clashes; identity politics. | Risk of cultural loss and identity dilution. |
Understanding Multiculturalism: Principles and Practices
Multiculturalism promotes the recognition and celebration of diverse cultural identities within a society, emphasizing equal respect and inclusion for all ethnic and cultural groups. It encourages policies that protect cultural heritage, language rights, and social participation without forcing cultural conformity. Voluntary assimilation contrasts by supporting individuals' choice to integrate into the dominant culture while maintaining personal cultural ties, fostering social cohesion without erasing diversity.
Defining Voluntary Assimilation: Motives and Methods
Voluntary assimilation involves individuals or groups willingly adopting the cultural norms, language, and practices of a dominant society to enhance social integration, economic opportunities, and personal identity alignment. Motives often include improved employment prospects, social acceptance, and educational advancement, while methods range from language acquisition and participation in civic activities to embracing prevailing cultural values. This process contrasts with mandated assimilation by emphasizing personal choice and gradual adaptation over enforced conformity.
Historical Context of Multiculturalism and Assimilation
Multiculturalism emerged in the 1960s as a response to the failure of assimilation policies in countries like Canada and the United States, emphasizing the preservation of distinct cultural identities within a unified society. Assimilation, historically rooted in 19th and early 20th-century nation-building efforts, aimed to integrate immigrants by encouraging conformity to dominant cultural norms, often marginalizing minority groups. The debate between multiculturalism and voluntary assimilation reflects broader historical tensions over cultural pluralism, social cohesion, and national identity formation.
Social Cohesion: Unity or Diversity?
Multiculturalism promotes social cohesion by embracing cultural diversity, allowing various ethnic groups to maintain distinct identities while fostering mutual respect. Voluntary assimilation enhances unity by encouraging individuals to adopt shared societal values and norms, creating a common cultural framework. Balancing these approaches influences the strength of social bonds and collective identity within pluralistic societies.
Identity and Belonging in Diverse Societies
Multiculturalism fosters the preservation of distinct cultural identities within a shared society, promoting a sense of belonging through mutual respect and recognition of diversity. Voluntary assimilation emphasizes individual choice, encouraging integration into the dominant culture while allowing for the retention of personal heritage. Both approaches shape identity formation and social cohesion by balancing cultural maintenance and adaptation in diverse populations.
Policy Approaches: Integration Models Compared
Multiculturalism promotes cultural diversity through policies supporting ethnic preservation, anti-discrimination laws, and minority language rights, highlighting inclusivity within societal frameworks. Voluntary assimilation encourages newcomers to adopt the dominant culture's language, customs, and values, often through incentives like citizenship pathways or social integration programs. Integration models vary globally, with multicultural approaches prevalent in Canada and Australia, while voluntary assimilation policies are more common in France and the United States, reflecting differing national attitudes toward cultural identity and social cohesion.
Economic Impact of Multiculturalism vs Assimilation
Multiculturalism fosters diverse skill sets and global networks, boosting innovation and international trade, which enhances economic growth. Voluntary assimilation may streamline labor markets and reduce transaction costs but risks underutilizing cultural assets critical for competitive advantage. Studies show cities embracing multicultural policies often experience higher entrepreneurial activity and productivity compared to those emphasizing assimilation.
Challenges and Criticisms of Multiculturalism
Multiculturalism faces challenges such as social fragmentation, where diverse cultural groups may coexist without meaningful integration, potentially weakening national unity and shared values. Critics argue it can lead to identity politics, fostering division and resentment rather than cohesion, complicating public policy and social harmony. Resistance to voluntary assimilation is seen as limiting individuals' ability to fully participate in the broader society, creating parallel communities and hindering economic and social mobility.
Advocating for Voluntary Assimilation: Perspectives and Policies
Advocating for voluntary assimilation emphasizes personal choice and cultural integration without coercion, promoting social cohesion and shared values within diverse societies. Policies supporting this approach include language acquisition programs, civic education, and community engagement initiatives that facilitate smoother transitions while respecting individual backgrounds. Critics argue these measures help balance cultural preservation with national unity by encouraging adaptation without erasing distinct identities.
Future Trends: Navigating Diversity in a Globalized World
Future trends in multiculturalism emphasize the integration of diverse cultural identities through policies that promote inclusivity while respecting individual heritage. Voluntary assimilation increasingly centers on personal choice, reflecting a global shift toward hybrid identities in urbanized, interconnected societies. Advances in technology and communication continue to facilitate cultural exchange, reshaping how communities balance unity and diversity in a globalized world.
Multiculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com