Master status is a sociological concept referring to a social position that dominates all other statuses an individual holds, profoundly shaping their identity and interactions. This status influences how others perceive and treat you, often overshadowing other roles in various social contexts. Discover how master status impacts your social life and the dynamics of power by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
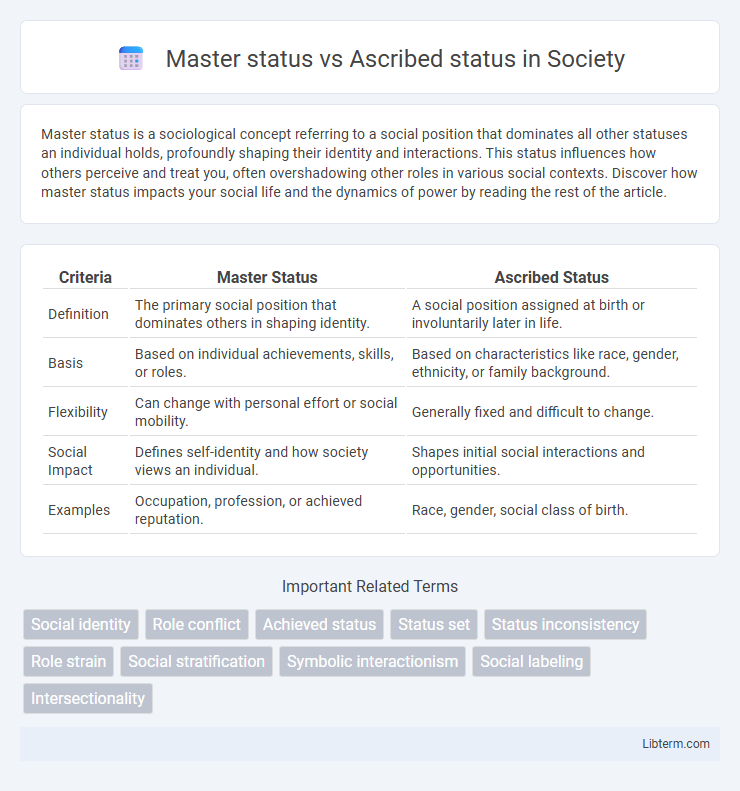
| Criteria | Master Status | Ascribed Status |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The primary social position that dominates others in shaping identity. | A social position assigned at birth or involuntarily later in life. |
| Basis | Based on individual achievements, skills, or roles. | Based on characteristics like race, gender, ethnicity, or family background. |
| Flexibility | Can change with personal effort or social mobility. | Generally fixed and difficult to change. |
| Social Impact | Defines self-identity and how society views an individual. | Shapes initial social interactions and opportunities. |
| Examples | Occupation, profession, or achieved reputation. | Race, gender, social class of birth. |
Understanding Social Status: Key Definitions
Master status refers to a social position that dominates other statuses and shapes a person's identity and interactions, such as occupation or gender. Ascribed status is assigned at birth or involuntarily, based on factors like race, ethnicity, or family background, without personal choice. Understanding social status involves recognizing how master and ascribed statuses influence social behavior, opportunities, and societal expectations.
What is Master Status?
Master status is a social position that dominates other statuses an individual holds and significantly influences their identity and social interactions. It can be either achieved, such as a career or accomplishment, or ascribed, like race or gender, shaping how others perceive and respond to the person. Master status often determines social roles and power dynamics within various societal contexts.
Exploring Ascribed Status: An Overview
Ascribed status refers to the social position assigned at birth or involuntarily later in life, such as race, gender, ethnicity, and family heritage, which significantly influences an individual's opportunities and interactions. This status often shapes social identity and affects access to resources regardless of personal achievements or efforts. Understanding ascribed status is crucial in sociological analysis to detect social stratification and inequality patterns across societies.
Differences Between Master and Ascribed Status
Master status refers to a social position that dominates other statuses and significantly shapes an individual's identity and interactions, often earned or chosen. Ascribed status is assigned at birth or involuntarily later in life, such as race, gender, or family heritage. The primary difference lies in master status's influence on personal identity and decision-making versus ascribed status being predetermined and less subject to personal control.
Examples of Master Status in Society
Master status represents the dominant social identity that shapes an individual's interactions and self-perception, such as being a celebrity, CEO, or Olympic athlete. Examples include a doctor whose professional role defines their social standing or an individual known primarily for their disability, which influences how others perceive and interact with them. These statuses often overshadow other aspects of identity, highlighting the significance of societal roles in social dynamics.
Common Ascribed Status Categories
Common ascribed status categories include age, gender, ethnicity, and family heritage, which individuals are born into and cannot change. Master status, often influenced by either ascribed or achieved statuses, is the primary identifying characteristic that shapes a person's social identity and interactions. Understanding the dynamics between ascribed status and master status is crucial for analyzing social roles and power structures within society.
How Status Influences Social Identity
Master status, often the most significant social position a person holds, profoundly shapes social identity by defining how individuals are perceived and how they interact within society. Ascribed status, assigned at birth or involuntarily later in life, influences social identity by setting expectations and social roles that limit or enable social mobility. The interplay between master and ascribed status determines social experiences, access to resources, and the formation of self-concept within social structures.
Status Shifts: From Ascribed to Achieved
Master status often evolves from an ascribed status through personal accomplishments, reflecting shifts in social identity and influence. Ascribed statuses, such as race or family background, provide an initial social position, but achieved statuses gained through education, career, or skills frequently redefine an individual's master status over time. This transition highlights the dynamic nature of social hierarchies and the potential for upward mobility within societal structures.
Impact of Master and Ascribed Status on Life Opportunities
Master status significantly shapes life opportunities by influencing social identity, access to resources, and power dynamics within various social contexts. Ascribed status, often determined by factors such as race, gender, and family background, can limit or expand opportunities regardless of individual achievements. The interplay between master and ascribed statuses determines social mobility and the ability to navigate institutional structures effectively.
Contemporary Debates on Social Status and Mobility
Master status represents a dominant social identity that shapes an individual's interactions and self-perception, whereas ascribed status refers to traits assigned at birth, such as race or gender. Contemporary debates on social status and mobility critically examine how master status can either reinforce or challenge structural inequalities linked to ascribed characteristics. Research highlights that while ascribed status often restricts upward mobility, the emergence of new master statuses in multicultural and digital societies reshapes pathways to social influence and economic success.
Master status Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com