Collectivism emphasizes the importance of group goals and social cohesion over individual desires, fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility. This philosophy shapes various cultural, social, and political systems by prioritizing cooperation and collective well-being. Discover how collectivism influences your society and personal interactions by exploring the full article.
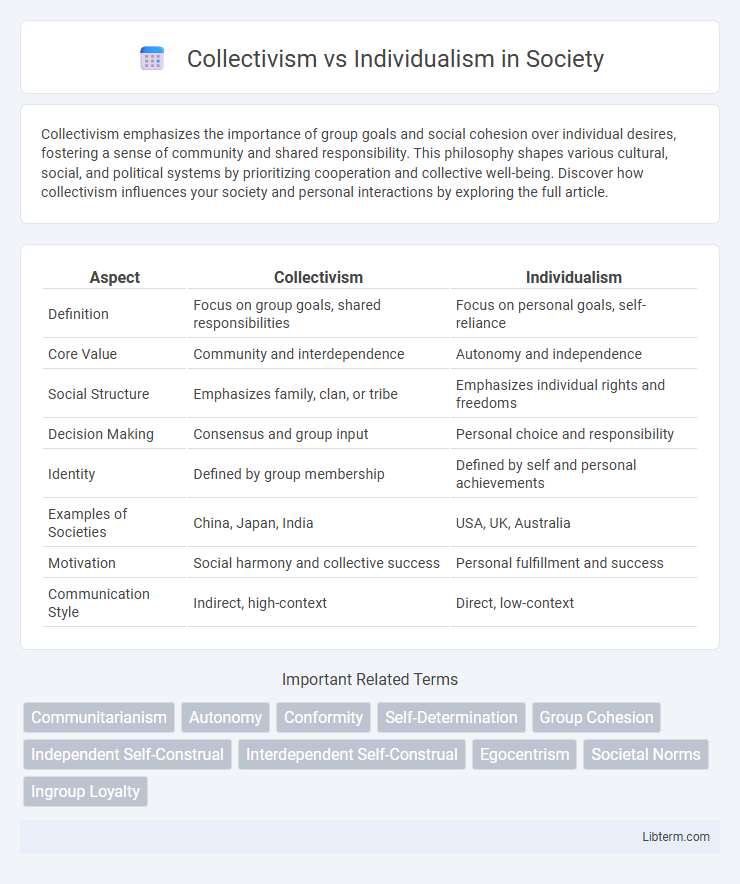
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Collectivism | Individualism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focus on group goals, shared responsibilities | Focus on personal goals, self-reliance |
| Core Value | Community and interdependence | Autonomy and independence |
| Social Structure | Emphasizes family, clan, or tribe | Emphasizes individual rights and freedoms |
| Decision Making | Consensus and group input | Personal choice and responsibility |
| Identity | Defined by group membership | Defined by self and personal achievements |
| Examples of Societies | China, Japan, India | USA, UK, Australia |
| Motivation | Social harmony and collective success | Personal fulfillment and success |
| Communication Style | Indirect, high-context | Direct, low-context |
Defining Collectivism and Individualism
Collectivism is a social framework emphasizing the group's needs, goals, and interdependence over individual desires, promoting community cohesion and shared responsibility. Individualism values personal autonomy, self-expression, and independence, prioritizing individual rights and freedoms above collective obligations. These contrasting ideologies shape cultural, political, and economic systems by influencing societal behaviors and decision-making processes.
Historical Roots and Evolution
Collectivism finds its historical roots in agrarian societies and communal cultures where survival depended on group cooperation and shared responsibilities, evident in early civilizations like Mesopotamia and Indigenous tribes worldwide. Individualism emerged prominently during the Renaissance and Enlightenment periods, emphasizing personal autonomy, self-expression, and the pursuit of individual rights, which shaped modern Western political and economic systems. Over time, the evolution of these ideologies reflects a dynamic tension between community-oriented values and personal freedoms, influencing contemporary debates in social structures, governance, and cultural identity.
Key Characteristics and Values
Collectivism emphasizes group goals, social cohesion, and interdependence, prioritizing the welfare of the community over individual desires, with values rooted in loyalty, cooperation, and shared responsibility. Individualism centers on personal autonomy, self-expression, and individual rights, valuing independence, personal achievement, and self-reliance. These contrasting cultural frameworks influence social behavior, decision-making, and identity formation across societies.
Influence on Social Structures
Collectivism emphasizes interconnectedness and prioritizes group harmony, shaping social structures that foster cooperation, community-oriented decision-making, and shared responsibilities. Individualism promotes personal autonomy and self-expression, influencing social systems to value independence, individual rights, and personal achievements. These contrasting cultural paradigms impact governance models, workplace dynamics, and educational approaches by defining the balance between collective welfare and individual freedom.
Impact on Education Systems
Collectivism shapes education systems to emphasize group harmony, cooperation, and social responsibility, fostering collaborative learning environments and shared success. Individualism promotes personalized education, encouraging critical thinking, self-expression, and independent problem-solving to develop autonomous learners. These contrasting cultural values influence curriculum design, assessment methods, and teacher-student dynamics, ultimately affecting student engagement and achievement outcomes.
Workplace Dynamics and Productivity
Collectivism in workplace dynamics emphasizes group cohesion, shared goals, and collaborative problem-solving, often leading to higher team morale and consistency in productivity across members. Individualism prioritizes personal achievement, autonomy, and innovation, which can drive competitive performance and foster unique contributions but may challenge team integration. Balancing these cultural orientations influences employee motivation, conflict resolution, and overall organizational effectiveness in diverse business environments.
Personal Identity and Community
Personal identity in collectivist cultures is deeply intertwined with the community, emphasizing social roles and group harmony over individual desires. Individualism prioritizes self-expression and autonomy, encouraging personal goals and unique traits as central to identity formation. The balance between these perspectives shapes social behavior, influencing how people define themselves within or apart from their communities.
Economic Implications and Models
Collectivism emphasizes shared ownership and cooperative economic models, often leading to planned economies where resources are allocated based on communal goals and social welfare. Individualism promotes market-driven economies that prioritize personal entrepreneurship, private property, and competitive innovation, resulting in diverse wealth distribution and economic dynamism. Economic implications of collectivism typically include reduced income inequality and increased social safety nets, while individualism fosters higher economic growth rates but can exacerbate wealth disparities.
Political Systems and Governance
Collectivism emphasizes the role of the state and community in decision-making, promoting policies that prioritize social welfare, equality, and shared resource management typically seen in socialist or communist political systems. Individualism advocates for personal freedom, limited government intervention, and protection of individual rights, which align closely with democratic and libertarian governance models. The balance between these ideologies impacts policy formulation, civil liberties, and the distribution of political power within diverse political frameworks.
Challenges and Future Trends
Collectivism faces challenges in balancing group cohesion with individual rights, often struggling to foster innovation and personal freedom. Individualism encounters difficulties in addressing social inequality and building community support systems amid rising self-reliance. Future trends suggest hybrid models blending collective welfare with personal autonomy, leveraging technology to create inclusive yet flexible social frameworks.
Collectivism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com