Cultural integration enriches communities by blending diverse traditions, values, and customs to foster mutual understanding and respect. Successful integration enhances social cohesion and creates opportunities for innovative collaboration across different cultural backgrounds. Explore the rest of this article to discover how cultural integration can transform your environment and promote unity.
Table of Comparison
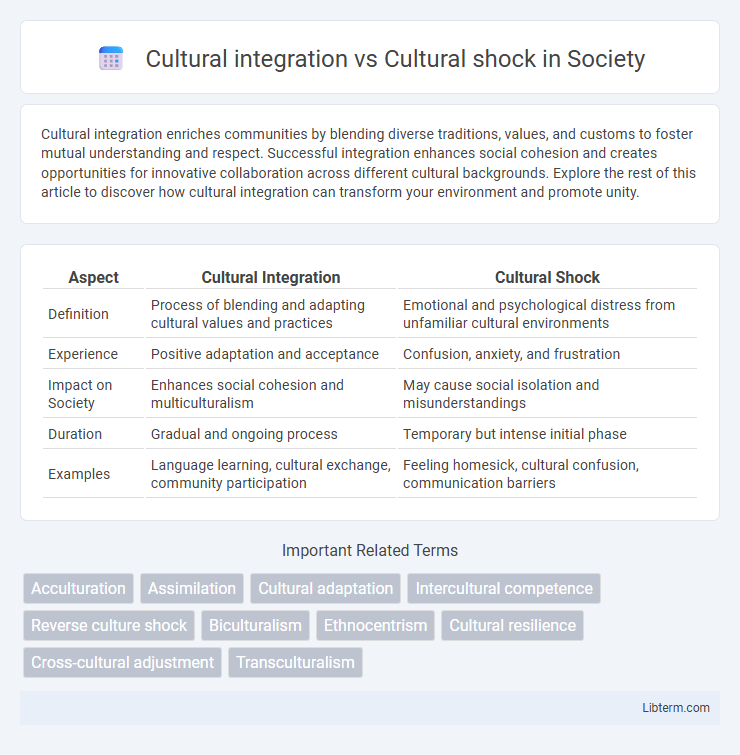
| Aspect | Cultural Integration | Cultural Shock |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of blending and adapting cultural values and practices | Emotional and psychological distress from unfamiliar cultural environments |
| Experience | Positive adaptation and acceptance | Confusion, anxiety, and frustration |
| Impact on Society | Enhances social cohesion and multiculturalism | May cause social isolation and misunderstandings |
| Duration | Gradual and ongoing process | Temporary but intense initial phase |
| Examples | Language learning, cultural exchange, community participation | Feeling homesick, cultural confusion, communication barriers |
Understanding Cultural Integration
Cultural integration involves the process by which individuals or groups adopt and adapt to the cultural norms, values, and practices of a new society while maintaining aspects of their original culture. This blend enhances social cohesion and fosters mutual respect, facilitating smoother transitions in multicultural environments. Understanding cultural integration is essential for promoting inclusivity, reducing conflicts, and supporting immigrant adaptation in diverse communities.
Defining Cultural Shock
Cultural shock refers to the feeling of disorientation and stress experienced when encountering an unfamiliar culture, marked by confusion, anxiety, and homesickness. It typically occurs during the initial exposure to a new cultural environment and can impact individuals' ability to adapt and communicate effectively. Understanding cultural shock is essential for successful cultural integration, which involves gradually adapting to and embracing the new cultural norms and values.
Key Differences Between Integration and Shock
Cultural integration involves adapting and blending into a new culture by understanding and respecting its norms, values, and practices, leading to smoother social interactions and personal growth. Cultural shock, on the other hand, refers to the initial feelings of confusion, anxiety, and disorientation experienced when encountering unfamiliar cultural environments. Key differences include the time frame--cultural shock is usually temporary, whereas integration is a gradual, ongoing process--and the psychological impact, with shock often causing stress and integration fostering acceptance and belonging.
Stages of Cultural Integration
Cultural integration involves progressive stages such as initial contact, adaptation, and eventual blending of cultural traits, enabling individuals or groups to function effectively within a new cultural environment. This process contrasts with cultural shock, which typically encompasses phases of honeymoon, frustration, adjustment, and acceptance, reflecting emotional and psychological responses to unfamiliar cultural settings. Understanding these stages aids in managing transitions and fostering successful intercultural interactions.
Phases of Cultural Shock
Cultural shock unfolds in distinct phases: the honeymoon phase, where individuals feel excitement and fascination with the new culture; the frustration phase, marked by confusion and frustration due to language barriers and cultural differences; the adjustment phase, where people begin to develop coping mechanisms and understanding; and the mastery phase, characterized by acceptance and effective navigation of the new cultural environment. Cultural integration involves progressing through these phases to achieve emotional and social adaptation, resulting in a harmonious blend between one's original and the host culture. Understanding these phases is critical for successful intercultural adaptation and fostering cross-cultural competence.
Factors Influencing Cultural Adaptation
Factors influencing cultural adaptation include individual personality traits, such as openness and resilience, which facilitate smoother cultural integration. Social support systems, including family, friends, and community networks, play a crucial role in mitigating cultural shock by providing emotional and informational resources. Language proficiency and prior intercultural experiences significantly impact the ease of adapting to new cultural environments, enhancing understanding and reducing misunderstandings.
Psychological Impacts of Cultural Experiences
Cultural integration fosters psychological resilience by promoting adaptability and a sense of belonging, which reduces anxiety and stress in new environments. In contrast, cultural shock often triggers feelings of confusion, frustration, and isolation, potentially leading to depression or emotional distress. Understanding these psychological impacts is crucial for developing effective support systems that facilitate smoother transitions in multicultural settings.
Strategies to Overcome Cultural Shock
Effective strategies to overcome cultural shock include developing cultural awareness by learning about local customs, language, and social norms to ease adjustment. Building a supportive social network through engaging with locals and other expatriates fosters a sense of belonging and reduces feelings of isolation. Practicing patience and maintaining an open mindset helps individuals adapt gradually to cultural differences, promoting smoother integration into the new environment.
Benefits of Successful Cultural Integration
Successful cultural integration enhances workplace collaboration by fostering mutual respect and understanding among diverse teams. It improves employee satisfaction and retention by creating an inclusive environment where individuals feel valued and supported. Organizations benefit from increased innovation and competitive advantage through the diverse perspectives and ideas brought by integrated cultural groups.
Real-world Examples of Integration and Shock
Cultural integration occurs when immigrants in Canada, such as Vietnamese refugees in Toronto, adopt local customs while maintaining their heritage, leading to multicultural communities and economic contributions. Conversely, cultural shock is evident in refugees from Syria relocating to Germany, facing initial disorientation due to language barriers, unfamiliar social norms, and climate differences. These real-world examples underscore how successful integration fosters social cohesion, whereas cultural shock can impede adaptation and mental health.
Cultural integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com