Administrative law governs the activities of government agencies, ensuring they act within their legal authority and follow fair procedures. It plays a critical role in protecting individual rights and maintaining a balance between public power and private interests. Explore the full article to understand how administrative law impacts your daily interactions with government entities.
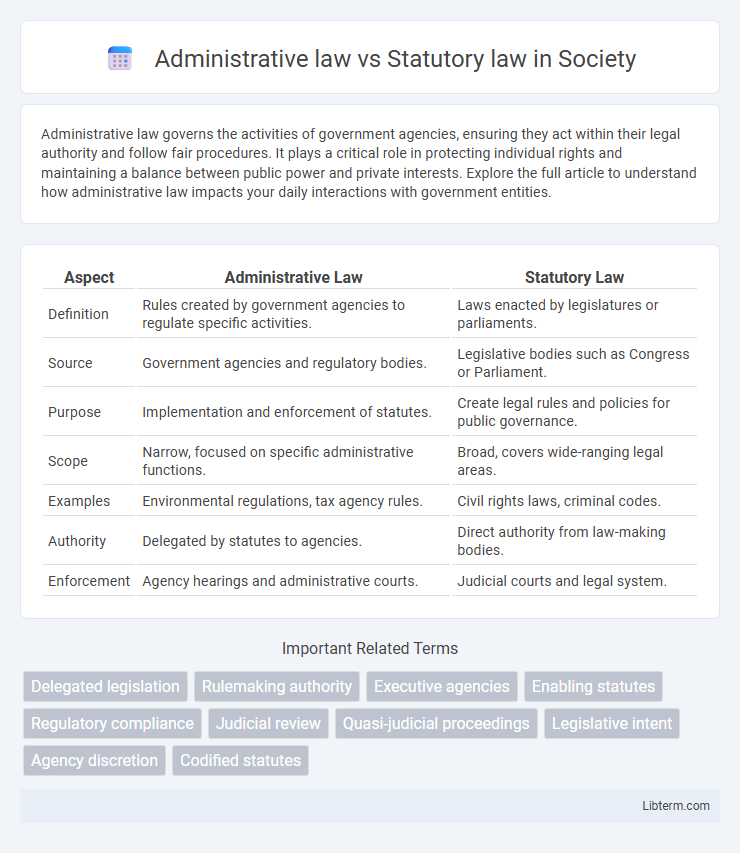
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Administrative Law | Statutory Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rules created by government agencies to regulate specific activities. | Laws enacted by legislatures or parliaments. |
| Source | Government agencies and regulatory bodies. | Legislative bodies such as Congress or Parliament. |
| Purpose | Implementation and enforcement of statutes. | Create legal rules and policies for public governance. |
| Scope | Narrow, focused on specific administrative functions. | Broad, covers wide-ranging legal areas. |
| Examples | Environmental regulations, tax agency rules. | Civil rights laws, criminal codes. |
| Authority | Delegated by statutes to agencies. | Direct authority from law-making bodies. |
| Enforcement | Agency hearings and administrative courts. | Judicial courts and legal system. |
Introduction: Defining Administrative Law and Statutory Law
Administrative law governs the rules and regulations created by government agencies to implement and enforce statutory laws passed by legislatures. Statutory law consists of formal written laws enacted by legislative bodies, providing the legal foundation for government policies and citizen conduct. Understanding the distinction clarifies how agencies interpret statutes versus how laws are originally established.
Historical Evolution of Both Legal Concepts
Administrative law emerged in the early 20th century as governments expanded their regulatory functions, creating specialized agencies to enforce statutes and implement public policy. Statutory law dates back to ancient codified laws, such as Hammurabi's Code and Roman law, evolving through legislative bodies to establish formal legal frameworks. The historical evolution of administrative law reflects modern governance's complexity, while statutory law represents the foundational legislative authority governing societies.
Sources and Foundations of Administrative Law
Administrative law derives from the delegation of legislative authority to government agencies, establishing rules and regulations based on statutes enacted by legislative bodies, primarily reflected in statutory law. It is grounded in statutes that empower administrative agencies, giving administrative law a foundation rooted in statutory law but extended through agency rulemaking, enforcement, and adjudication. Key sources include enabling statutes, administrative rules, executive orders, and judicial decisions interpreting agency authority and procedural requirements.
Origins and Basis of Statutory Law
Statutory law originates from formal legislative enactments created by governing bodies such as parliaments or congresses, providing a written framework of rules and regulations. It is grounded in the authority granted to legislators by constitutions, ensuring laws reflect the collective will and legal standards of the state. Administrative law, by contrast, derives from statutes delegated to government agencies, emphasizing the implementation and enforcement of these legislative mandates.
Key Differences Between Administrative Law and Statutory Law
Administrative law governs the activities and rule-making of government agencies, focusing on the implementation and enforcement of regulations, whereas statutory law consists of laws formally enacted by legislative bodies such as Congress or Parliament. Administrative law involves procedures for agency decisions, hearings, and enforcement actions, while statutory law provides the legal framework and specific statutes that agencies must follow. Key differences include the source of authority--administrative law derives from delegated power within statutes, while statutory law originates directly from legislative enactments.
Roles of Government Agencies in Administrative Law
Government agencies play a central role in administrative law by creating and enforcing regulations that implement statutory laws passed by legislatures. These agencies have the authority to issue rules, adjudicate disputes, and ensure compliance within specific sectors such as environmental protection, labor, and public health. Unlike statutory law, which is established by legislative bodies, administrative law derives its rules and procedures from the powers delegated to these agencies by statutes.
Legislative Process in Statutory Law Creation
The legislative process in statutory law creation involves drafting, proposal, committee review, and voting by legislative bodies to enact laws that govern public and private conduct. Administrative law, however, is established by agencies through rulemaking and enforcement based on authority granted by statutes. Statutory law serves as the foundational legal framework, while administrative law interprets and implements these laws through regulations and administrative procedures.
Enforcement Mechanisms: Administrative vs. Statutory Law
Administrative law relies on specialized agencies to enforce regulations through administrative procedures, including investigations, hearings, and penalties. Statutory law is enforced primarily by courts and law enforcement agencies through judicial proceedings and criminal or civil sanctions. The distinction in enforcement mechanisms highlights administrative law's focus on regulatory compliance versus statutory law's emphasis on formal legal adjudication.
Impact on Citizens and Legal Rights
Administrative law governs the actions and decisions of government agencies, directly affecting citizens' interactions with public services and regulatory compliance, thus ensuring accountability and protection of individual rights in bureaucratic processes. Statutory law, enacted by legislative bodies, establishes clear legal standards and obligations that define citizens' rights and duties across various aspects of daily life, providing a concrete framework for resolving disputes. The interplay between administrative and statutory law shapes the legal landscape by balancing regulatory flexibility with statutory mandates, ultimately influencing how effectively citizens' legal rights are upheld and enforced.
Conclusion: Comparative Significance in Modern Legal Systems
Administrative law governs the actions and decisions of government agencies, ensuring regulatory compliance and protecting public interests, while statutory law consists of formal written laws enacted by legislative bodies. Both legal frameworks are essential in modern legal systems for maintaining order and accountability, with administrative law providing mechanisms for oversight and enforcement of statutory mandates. Their comparative significance lies in statutory law setting the legal foundation, whereas administrative law operationalizes and interprets these statutes within complex governmental functions.
Administrative law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com