Equality ensures that every individual receives fair treatment and equal opportunities regardless of their background, gender, race, or beliefs. It fosters inclusivity and social justice, creating environments where diverse perspectives thrive and collective progress is achieved. Discover how embracing equality can transform your community and empower you by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
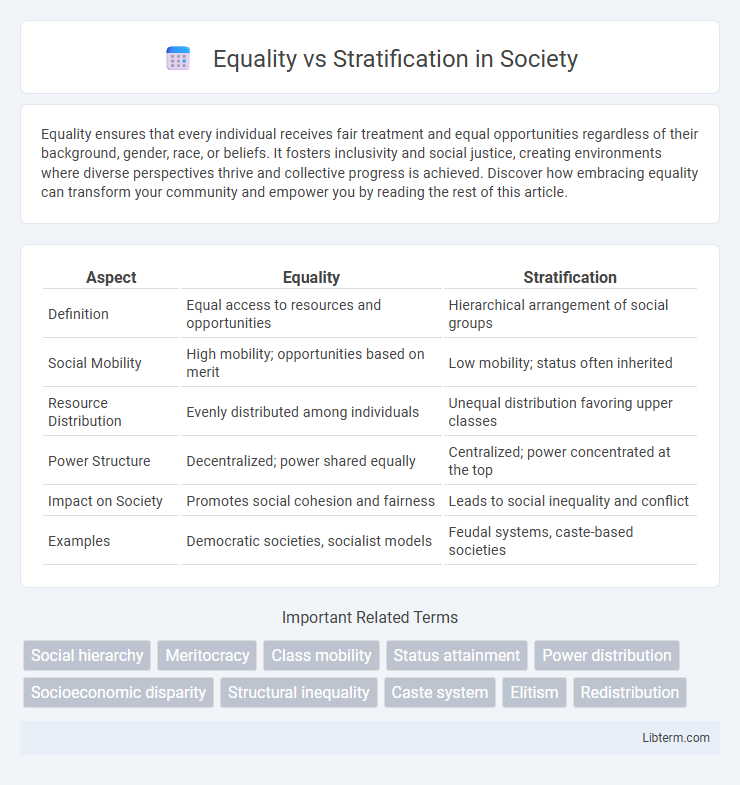
| Aspect | Equality | Stratification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Equal access to resources and opportunities | Hierarchical arrangement of social groups |
| Social Mobility | High mobility; opportunities based on merit | Low mobility; status often inherited |
| Resource Distribution | Evenly distributed among individuals | Unequal distribution favoring upper classes |
| Power Structure | Decentralized; power shared equally | Centralized; power concentrated at the top |
| Impact on Society | Promotes social cohesion and fairness | Leads to social inequality and conflict |
| Examples | Democratic societies, socialist models | Feudal systems, caste-based societies |
Understanding Equality and Stratification
Equality refers to the state where individuals or groups have the same rights, opportunities, and resources, ensuring fair treatment and access across society. Stratification involves the hierarchical classification of people into different social layers based on factors like wealth, power, education, or status. Understanding equality and stratification requires analyzing how social systems distribute resources and opportunities, influencing individuals' life chances and social mobility.
Historical Perspectives on Social Stratification
Historical perspectives on social stratification reveal deeply entrenched hierarchies that have structured societies through class, caste, and status distinctions. Ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and Egypt institutionalized stratification with rigid social orders, where power and resources were concentrated among elites. Over time, scholars such as Karl Marx and Max Weber analyzed class relations, emphasizing economic factors and social status as central to understanding persistent inequality and social mobility barriers.
Foundations of Equality in Society
Foundations of equality in society revolve around the principles of equal rights, access to resources, and equitable opportunities for all individuals regardless of socioeconomic status, race, or gender. Social institutions such as education, legal systems, and economic policies play pivotal roles in reducing disparities and promoting inclusivity. Empirical studies show that societies with robust equality foundations experience higher social cohesion, improved health outcomes, and greater economic stability.
Types and Levels of Social Stratification
Social stratification manifests through distinct types such as caste, class, estate, and status stratification, each characterized by varying degrees of social mobility and criteria for ranking individuals. Levels of social stratification range from micro-level interactions, such as interpersonal status distinctions, to macro-level structures encompassing vast social hierarchies based on wealth, power, and prestige. Understanding these types and levels reveals how equality is challenged by entrenched systems that allocate resources and opportunities unevenly across different social groups.
Causes and Consequences of Inequality
Economic disparities, social class distinctions, and unequal access to education are primary causes of inequality, leading to systemic stratification within societies. This stratification results in limited social mobility, unequal opportunities, and persistent poverty for marginalized groups. Consequences include heightened social tensions, reduced economic growth, and entrenched cycles of disadvantage across generations.
Social Mobility: Bridging Equality and Stratification
Social mobility serves as a critical mechanism bridging the gap between equality and stratification by enabling individuals to move upward or downward within a societal hierarchy based on merit and opportunity rather than fixed social classes. Access to quality education, equitable economic resources, and inclusive policies enhances upward mobility, mitigating the rigid effects of stratification and promoting a more egalitarian society. Persistent barriers such as discrimination, unequal wealth distribution, and limited access to social networks continue to challenge social mobility, thereby sustaining structural inequalities.
Equality vs Stratification in Modern Societies
Modern societies exhibit complex dynamics between equality and stratification, where economic status, education, and social networks create layered social hierarchies. Social equality promotes inclusive access to resources and opportunities, striving to reduce disparities rooted in class, race, and gender. Stratification persists through institutional mechanisms and cultural norms, shaping individuals' life chances and reinforcing systemic inequality.
Policy Approaches to Addressing Stratification
Policy approaches to addressing stratification prioritize equitable access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities to reduce systemic disparities. Affirmative action programs and progressive taxation aim to redistribute resources and promote social mobility among marginalized groups. Inclusive social policies target income inequality and structural barriers, fostering a more balanced and equitable society.
The Role of Education in Promoting Equality
Education serves as a critical vehicle for promoting equality by providing equal access to knowledge, skills, and opportunities regardless of social background. By fostering inclusive curricula and equitable resource distribution, education helps mitigate social stratification and enables upward mobility for marginalized groups. Effective policies targeting disparities in educational quality and access can significantly reduce systemic inequalities and promote a more just society.
Future Directions: Towards a More Equitable Society
Future directions towards a more equitable society emphasize dismantling systemic barriers by promoting inclusive policies and equitable access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. Leveraging data-driven approaches and technology can help identify and address disparities in social stratification, fostering social mobility and reducing inequality. Collaborative efforts between governments, organizations, and communities are essential to implement sustainable frameworks that prioritize equity over hierarchical divisions.
Equality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com