Mutual aid fosters community resilience by encouraging individuals to share resources and support each other in times of need. This cooperative approach enhances social bonds and builds stronger networks, enabling everyone to face challenges more effectively. Learn how mutual aid can transform your community and improve collective well-being in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
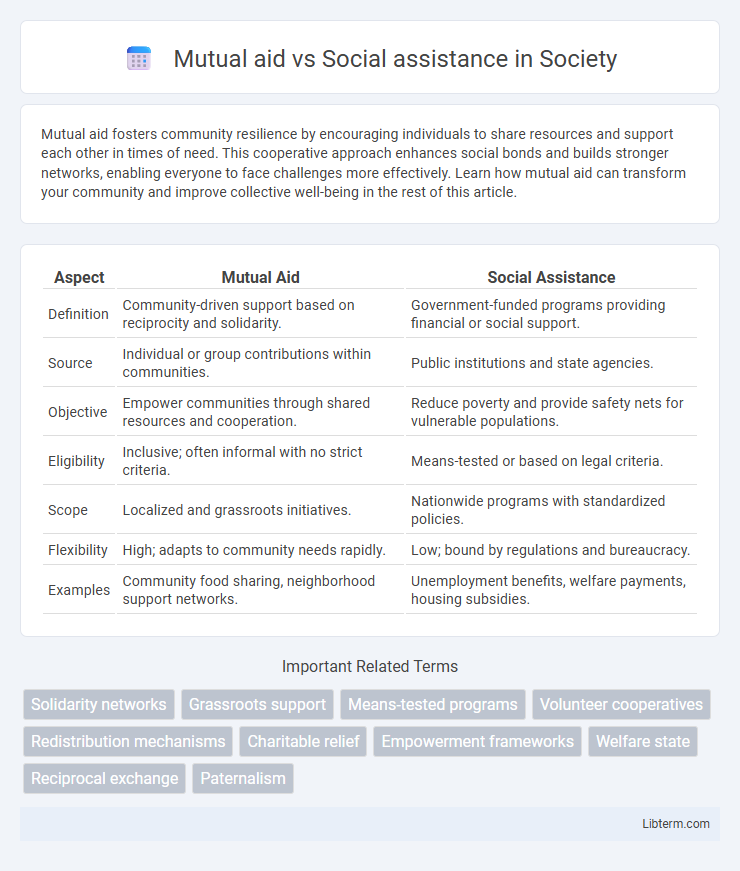
| Aspect | Mutual Aid | Social Assistance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Community-driven support based on reciprocity and solidarity. | Government-funded programs providing financial or social support. |
| Source | Individual or group contributions within communities. | Public institutions and state agencies. |
| Objective | Empower communities through shared resources and cooperation. | Reduce poverty and provide safety nets for vulnerable populations. |
| Eligibility | Inclusive; often informal with no strict criteria. | Means-tested or based on legal criteria. |
| Scope | Localized and grassroots initiatives. | Nationwide programs with standardized policies. |
| Flexibility | High; adapts to community needs rapidly. | Low; bound by regulations and bureaucracy. |
| Examples | Community food sharing, neighborhood support networks. | Unemployment benefits, welfare payments, housing subsidies. |
Understanding Mutual Aid and Social Assistance
Mutual aid involves reciprocal support systems where community members voluntarily help each other based on shared needs and solidarity. Social assistance refers to government or institutional programs designed to provide financial or material support to individuals facing economic hardship. Understanding the distinction highlights that mutual aid centers on collective, non-hierarchical exchanges, while social assistance relies on formal, often means-tested interventions.
Historical Background of Mutual Aid
Mutual aid has deep historical roots tracing back to ancient communities where social cooperation ensured survival, predating formal social assistance systems developed by modern states. Early mutual aid societies emerged during the 19th century industrialization era, as working-class groups pooled resources to support members facing illness, unemployment, or death. Unlike state-sponsored social assistance programs, mutual aid emphasizes voluntary, reciprocal support networks driven by communal solidarity.
The Evolution of Social Assistance Programs
Social assistance programs have evolved from informal mutual aid practices rooted in community solidarity to structured, government-administered systems designed to provide standardized support for vulnerable populations. Historically, mutual aid emphasized reciprocal support within families or local groups, while modern social assistance integrates policy frameworks, eligibility criteria, and formal funding mechanisms. This transition reflects broader societal changes, including urbanization, welfare state development, and increased recognition of social rights.
Key Differences Between Mutual Aid and Social Assistance
Mutual aid involves community-driven support where individuals collaborate directly to address shared needs, emphasizing reciprocity and solidarity without government intervention. Social assistance refers to government-provided programs designed to offer financial aid or services to vulnerable populations, relying on formal eligibility criteria and institutional structures. The key difference lies in mutual aid's grassroots, voluntary nature versus social assistance's institutionalized, policy-driven approach.
Motivations and Underlying Philosophies
Mutual aid is driven by principles of solidarity, reciprocity, and community empowerment, emphasizing collective self-help and shared responsibility among members. Social assistance is motivated by governmental or institutional goals to alleviate poverty and provide a safety net for vulnerable populations, often through formal, top-down mechanisms. While mutual aid fosters grassroots support based on equality, social assistance typically operates within bureaucratic frameworks prioritizing resource allocation and social welfare policies.
Community Engagement in Mutual Aid
Mutual aid exemplifies community engagement by fostering grassroots cooperation where members actively participate in resource sharing and problem-solving, unlike social assistance, which typically involves top-down support from government or organizations. The collective involvement in mutual aid enhances social bonds, encourages local empowerment, and builds resilience within communities. This participatory approach ensures that aid is tailored to specific needs, promoting sustained community well-being and solidarity.
Government Involvement in Social Assistance
Social assistance involves direct government involvement through public programs aimed at providing financial aid and services to vulnerable populations, ensuring a safety net funded by taxpayers. Mutual aid operates through community-driven, voluntary support systems without formal government administration, relying on collective resource sharing and solidarity. Government involvement in social assistance allows for standardized eligibility criteria, regulatory oversight, and predictable funding, which contrasts with the decentralized, organic nature of mutual aid networks.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations
Mutual aid fosters community-driven support by enabling vulnerable populations to access resources through collective solidarity, reducing reliance on formal systems and promoting empowerment. Social assistance programs provide structured financial aid and services administered by governments or organizations, targeting poverty alleviation and social protection for at-risk groups. The impact of mutual aid lies in building resilience and social cohesion, while social assistance offers immediate relief and long-term stability for marginalized individuals.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Mutual aid faces challenges such as limited scalability and reliance on community cohesion, which can restrict the reach and sustainability of support during widespread crises. Social assistance programs often struggle with bureaucratic inefficiencies, inadequate funding, and exclusion errors that prevent timely and sufficient aid to vulnerable populations. Both approaches encounter limitations in addressing systemic inequalities, requiring integrated strategies to enhance effectiveness and inclusivity.
Future Trends: Integrating Mutual Aid and Social Assistance
Future trends in social support emphasize integrating mutual aid with formal social assistance systems to enhance community resilience and resource efficiency. Leveraging technology platforms facilitates real-time collaboration between grassroots networks and government agencies, boosting responsiveness to crises. Data-driven approaches empower tailored interventions that address localized needs, fostering sustainable and inclusive support ecosystems.
Mutual aid Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com