Destigmatization plays a crucial role in promoting mental health awareness and fostering inclusive communities where individuals feel safe to seek help. By challenging harmful stereotypes and misinformation, societies can create supportive environments that empower people to openly discuss their experiences. Discover how destigmatization can transform perspectives and improve your well-being in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
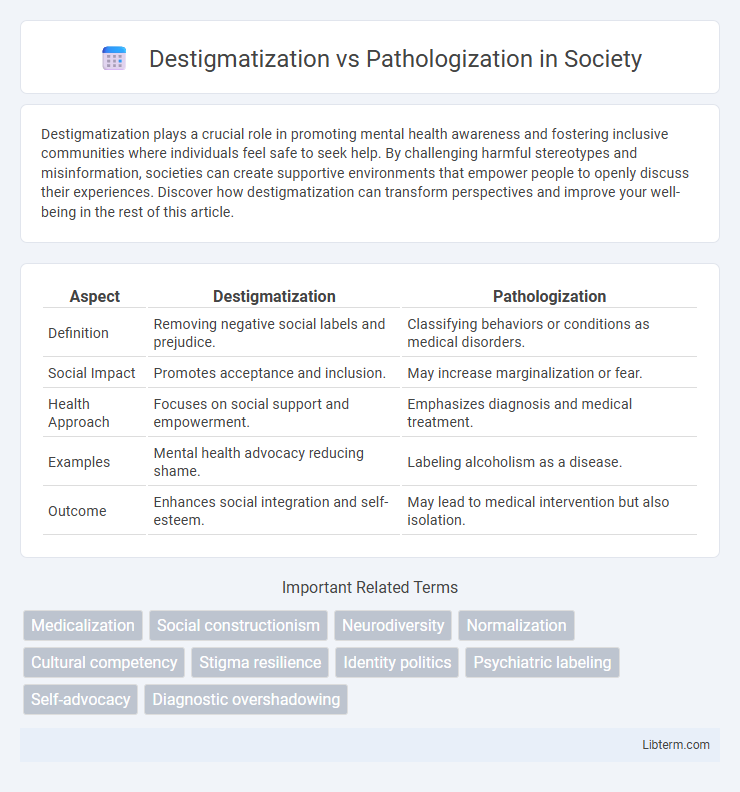
| Aspect | Destigmatization | Pathologization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removing negative social labels and prejudice. | Classifying behaviors or conditions as medical disorders. |
| Social Impact | Promotes acceptance and inclusion. | May increase marginalization or fear. |
| Health Approach | Focuses on social support and empowerment. | Emphasizes diagnosis and medical treatment. |
| Examples | Mental health advocacy reducing shame. | Labeling alcoholism as a disease. |
| Outcome | Enhances social integration and self-esteem. | May lead to medical intervention but also isolation. |
Understanding Destigmatization: A Brief Overview
Destigmatization involves reducing negative stereotypes and social prejudices associated with mental health conditions to promote acceptance and support. It emphasizes viewing mental health issues as common human experiences rather than moral failings or signs of weakness. Understanding destigmatization is crucial for fostering inclusive environments that encourage individuals to seek help without fear of judgment.
Pathologization: Defining the Concept
Pathologization refers to the process of identifying and labeling certain behaviors, emotions, or experiences as medical or psychological disorders. This concept involves classifying normal variations of human experience as symptoms requiring diagnosis and treatment within clinical frameworks. Pathologization can influence healthcare approaches, societal attitudes, and policy decisions by framing diverse conditions under medical categorizations.
Historical Perspectives on Mental Health Stigma
Historical perspectives on mental health stigma reveal a complex relationship between destigmatization and pathologization, where earlier societies often viewed mental illness through supernatural or moral lenses, leading to severe discrimination and exclusion. The shift during the 19th and early 20th centuries toward pathologization framed mental health conditions as medical disorders, which improved understanding but also entrenched labels that could perpetuate stigma. Contemporary movements emphasize destigmatization by promoting mental health awareness and humanizing affected individuals, challenging outdated pathologizing narratives rooted in historical prejudices.
The Impact of Destigmatization in Society
Destigmatization promotes social acceptance by challenging negative stereotypes associated with mental health, leading to increased willingness to seek help and better access to care. This cultural shift reduces discrimination and supports inclusive policies that prioritize mental well-being. Improved public understanding fosters empathy, diminishing barriers and driving systemic changes in education, healthcare, and the workplace.
Risks and Consequences of Pathologization
Pathologization risks reinforcing stigma by labeling natural variations in human behavior as disorders, leading to unnecessary medicalization and psychological harm. It can contribute to social exclusion, discrimination, and reduce individuals' autonomy, often resulting in inappropriate treatments and increased mental health burden. Misdiagnosis and overdiagnosis driven by pathologization also strain healthcare systems and divert resources from those with genuine clinical needs.
Destigmatization vs. Pathologization: Key Differences
Destigmatization involves reducing negative stereotypes and social shame associated with mental health conditions, promoting acceptance and understanding, while pathologization refers to labeling normal variations in behavior as medical disorders, often leading to overdiagnosis and unnecessary treatment. Destigmatization emphasizes humanizing individuals and encouraging help-seeking behaviors, whereas pathologization risks reinforcing stigma by framing differences as abnormalities. Key differences lie in their impact on public perception, treatment approaches, and mental health policy development.
Role of Media in Shaping Public Perception
Media plays a crucial role in shaping public perception by either promoting destigmatization or reinforcing pathologization of mental health issues. Positive and accurate portrayals in news outlets, movies, and social platforms contribute to reducing stigma and encouraging acceptance, whereas sensationalized or inaccurate representations perpetuate misconceptions and fear. Studies show that media framing significantly influences societal attitudes, impacting policy decisions and the willingness of individuals to seek help.
Social and Cultural Drivers Behind Each Approach
Social norms and cultural beliefs significantly influence whether behaviors are viewed through the lens of destigmatization or pathologization. Communities emphasizing acceptance and diversity tend to promote destigmatization, recognizing individual variations as normal rather than pathological. In contrast, cultures with rigid conformity standards often pathologize differences, framing them as disorders requiring treatment or correction.
Consequences for Individuals: Empowerment or Marginalization
Destigmatization fosters empowerment by promoting acceptance and reducing social barriers for individuals with mental health conditions, enabling better access to support and opportunities. Pathologization often leads to marginalization as it emphasizes illness and abnormality, which can result in discrimination, social exclusion, and reduced self-esteem. The balance between these approaches significantly impacts personal identity and societal integration for affected individuals.
Striking a Balance: Toward Compassionate Mental Health Care
Striking a balance between destigmatization and pathologization is crucial for compassionate mental health care, promoting understanding without overmedicalizing normal experiences. Emphasizing empathy and individualized treatment supports recovery while avoiding unnecessary labeling that can exacerbate stigma. This approach fosters a culture where mental health challenges are acknowledged with respect and appropriate clinical attention.
Destigmatization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com