Legal sanctions impose penalties or corrective measures to enforce compliance with laws and regulations, safeguarding public order and individual rights. These sanctions range from fines and community service to imprisonment and license revocation, depending on the severity of the offense. Explore the rest of the article to understand how legal sanctions impact various aspects of society and your rights.
Table of Comparison
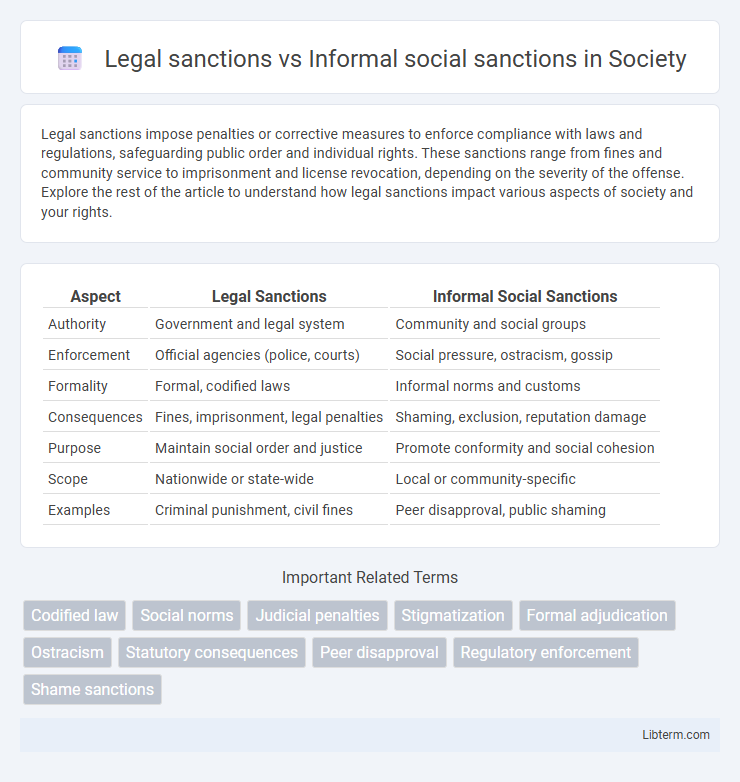
| Aspect | Legal Sanctions | Informal Social Sanctions |
|---|---|---|
| Authority | Government and legal system | Community and social groups |
| Enforcement | Official agencies (police, courts) | Social pressure, ostracism, gossip |
| Formality | Formal, codified laws | Informal norms and customs |
| Consequences | Fines, imprisonment, legal penalties | Shaming, exclusion, reputation damage |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and justice | Promote conformity and social cohesion |
| Scope | Nationwide or state-wide | Local or community-specific |
| Examples | Criminal punishment, civil fines | Peer disapproval, public shaming |
Understanding Legal Sanctions: Definition and Scope
Legal sanctions are formal penalties imposed by authorized institutions such as courts or government agencies to enforce laws and regulations, typically including fines, imprisonment, or community service. They are defined by statutory law and have a clear legal framework and documentation process that ensures consistency and accountability. The scope of legal sanctions covers criminal offenses, civil wrongs, and administrative violations, aiming to maintain public order and protect individual rights within a structured judicial system.
Informal Social Sanctions: Nature and Characteristics
Informal social sanctions are unwritten, culturally driven responses such as praise, ridicule, or ostracism that enforce community norms without formal legal authority. These sanctions operate through social interactions and collective expectations, often varying widely across different groups and contexts. Their effectiveness relies on social cohesion and the internalization of shared values rather than official enforcement mechanisms.
Key Differences Between Legal and Informal Sanctions
Legal sanctions are formal penalties imposed by authorized institutions such as courts or law enforcement agencies, including fines, imprisonment, or community service. Informal social sanctions arise from community or peer groups and may include social disapproval, ostracism, or verbal reprimands, functioning without official enforcement. Key differences lie in their source of authority, formalization, and enforcement mechanisms; legal sanctions rely on codified laws and official procedures, whereas informal sanctions depend on social norms and collective approval.
Historical Evolution of Sanctioning Mechanisms
Legal sanctions have evolved through codified laws and formal judicial systems, tracing back to ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia's Code of Hammurabi, emphasizing state-enforced penalties for rule violations. Informal social sanctions developed earlier as communal responses to behavior, using mechanisms such as shaming, ostracism, and social approval to maintain order within small-scale societies. Over time, formal legal sanctions increasingly institutionalized, yet informal social sanctions continue to operate alongside, influencing behavior through social norms and cultural enforcement.
Functions and Purposes of Legal Sanctions
Legal sanctions function primarily to enforce compliance with laws, deter unlawful behavior, and maintain social order through officially mandated penalties such as fines, imprisonment, or community service. These sanctions serve to uphold justice by providing clear consequences for violations, thereby supporting the rule of law and protecting individual rights. In contrast, informal social sanctions rely on societal reactions like gossip, ostracism, or praise to regulate behavior informally within communities.
The Role of Informal Social Sanctions in Society
Informal social sanctions play a crucial role in maintaining societal norms by encouraging compliance through social approval, disapproval, or ostracism, which often proves more immediate and psychologically impactful than legal sanctions. These sanctions operate within communities, relying on shared values and interpersonal relationships to regulate behavior without formal legal intervention. They complement legal sanctions by addressing minor infractions and promoting social cohesion through subtle reinforcement mechanisms.
Case Studies: Application of Legal vs Informal Sanctions
Case studies highlight that legal sanctions, such as fines or imprisonment, enforce formal compliance and maintain societal order through codified laws, exemplified by traffic violation penalties or corporate fraud prosecutions. Informal social sanctions, including social ostracism or verbal reprimands, influence behavior by leveraging community norms and peer pressure, as seen in tight-knit communities responding to ethical breaches without legal intervention. Comparative analysis reveals legal sanctions provide uniform deterrence with documented consequences, whereas informal sanctions yield flexible, context-specific behavioral corrections often faster but less predictable.
Effectiveness: Legal Sanctions Compared to Informal Sanctions
Legal sanctions enforce compliance through formal authority, imposing penalties such as fines or imprisonment, which ensures standardized consequences for violations. Informal social sanctions operate through community approval or disapproval, leveraging social pressure and reputation to influence behavior effectively in close-knit groups. While legal sanctions guarantee legal consistency, informal sanctions often achieve quicker behavioral adjustments by targeting social identity and interpersonal relationships.
Interplay Between Law and Social Norms
Legal sanctions enforce compliance through formal penalties such as fines, imprisonment, or community service, ensuring adherence to codified laws. Informal social sanctions operate through societal mechanisms like ostracism, disapproval, or praise, shaping behavior by reinforcing cultural norms and values. The interplay between law and social norms creates a dynamic regulatory environment where legal frameworks legitimize social expectations while societal attitudes influence the creation and enforcement of laws, promoting social cohesion and order.
The Future of Sanctions: Legal Systems and Social Dynamics
Legal sanctions are officially imposed penalties enforced by governmental institutions to maintain public order and deter criminal behavior, often involving fines, imprisonment, or other formal punishments. Informal social sanctions operate through societal norms and community pressures, such as ostracism, ridicule, or social disapproval, influencing behavior without legal authority. The future of sanctions will likely involve an integrated approach where evolving legal systems adapt to dynamic social values and leverage informal community mechanisms to enhance compliance and social cohesion.
Legal sanctions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com