Social norms shape behavior by establishing unwritten rules that govern acceptable conduct within a community. They influence Your interactions, guiding decisions and fostering social cohesion. Explore the rest of this article to understand how social norms impact everyday life and cultural dynamics.
Table of Comparison
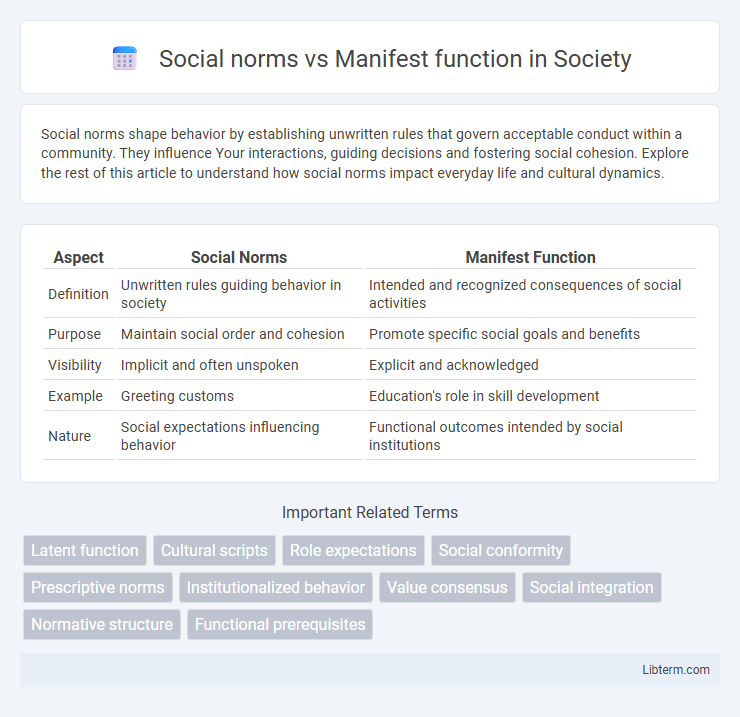
| Aspect | Social Norms | Manifest Function |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unwritten rules guiding behavior in society | Intended and recognized consequences of social activities |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and cohesion | Promote specific social goals and benefits |
| Visibility | Implicit and often unspoken | Explicit and acknowledged |
| Example | Greeting customs | Education's role in skill development |
| Nature | Social expectations influencing behavior | Functional outcomes intended by social institutions |
Understanding Social Norms: Definition and Examples
Social norms are the unwritten rules and expectations that guide individual behavior within a society, helping maintain order and predictability. These norms differ from manifest functions, which are the explicit, intended purposes of social institutions, such as schools aiming to educate. Examples of social norms include waiting in line, dressing appropriately for occasions, and greeting others politely, demonstrating the implicit social mechanisms shaping daily interactions.
Manifest Function: Meaning in Sociology
Manifest function in sociology refers to the explicit, intended, and recognized consequences of social institutions or actions. Social norms serve to maintain order and predictability by prescribing acceptable behavior, directly contributing to the manifest functions of societal structures like education, family, and religion. Understanding manifest functions helps reveal how social norms support the stability and functionality of complex social systems.
Historical Evolution of Social Norms
Social norms have historically evolved as informal rules guiding behavior to maintain societal order, closely related to the manifest function of institutions, which are intended consequences explicitly recognized by society. Over time, these norms have adapted through cultural shifts, technological advancements, and changing social structures, reflecting the dynamic nature of societal expectations. Understanding this evolution highlights the interplay between prescribed social roles and the intended purposes of social institutions in shaping collective behavior.
Key Differences Between Social Norms and Manifest Functions
Social norms are unwritten rules and expectations guiding individual behavior within a society, shaping everyday interactions and social order. Manifest functions refer to the intended and recognized consequences of social institutions or activities, explicitly designed to fulfill specific societal needs. The key difference lies in social norms being informal behavioral standards, while manifest functions are deliberate, objective purposes identified by sociologists.
How Social Norms Influence Behavior
Social norms serve as unwritten rules that guide individual behavior within a society, creating predictable patterns that facilitate social cohesion and cooperation. These norms shape expectations and influence actions by establishing what is considered acceptable or unacceptable in various contexts. Manifest functions, meanwhile, are the intended and recognized consequences of social norms, such as promoting conformity and social order, which directly impact behavior regulation.
Manifest Function in Social Institutions
Manifest functions in social institutions refer to the explicit, intended purposes these structures serve, such as education imparting knowledge and cultural values to students. These functions maintain social order and contribute to the stability and continuity of society by clearly defining roles and expectations. Understanding manifest functions helps reveal how institutions like family, government, and religion actively shape behavior and fulfill societal needs.
Social Norms and Manifest Functions: Interactions and Overlaps
Social norms guide individual behavior by establishing expected standards within societies, while manifest functions represent the explicit, intended outcomes of social structures. These concepts interact as social norms often reinforce and sustain manifest functions, ensuring societal stability and predictable social roles. Overlaps occur when the adherence to norms facilitates the realization of institutional goals, highlighting their intertwined role in maintaining social order.
Real-World Examples Illustrating Both Concepts
Social norms guide everyday behavior by setting expectations such as queuing in public places, while manifest functions represent the intended, recognized outcomes of social institutions, such as education providing knowledge and skills. In schools, social norms include punctuality and respect toward teachers, whereas the manifest function is student learning and credentialing. Traffic laws embody social norms that promote orderly driving, with the manifest function being road safety and accident reduction.
Implications for Social Policy and Change
Social norms shape everyday behavior by establishing unwritten rules that maintain societal order, while manifest functions represent the intended and recognized consequences of social institutions. Understanding the distinction allows policymakers to design social policies that address both observable outcomes and underlying behavioral expectations, facilitating more effective social change. Targeting manifest functions ensures clear goals for reform, whereas integrating social norms promotes sustainable acceptance and long-term adaptation within communities.
Future Directions in the Study of Social Norms and Manifest Functions
Future research on social norms and manifest functions emphasizes integrating interdisciplinary approaches to better understand how evolving societal values shape collective behaviors and institutional roles. Advances in data analytics and computational modeling offer new tools to predict norm shifts and their explicit functions within complex social systems. Emphasizing the interplay between technological innovation and cultural adaptation will provide deeper insights into how norms generate intended outcomes in rapidly changing environments.
Social norms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com