Coercive tactics involve using force, threats, or intimidation to influence others' behavior, often compromising personal freedom and ethical standards. Recognizing coercive behavior is essential for protecting your rights and maintaining healthy relationships. Explore the rest of the article to understand the signs, impacts, and ways to address coercion effectively.
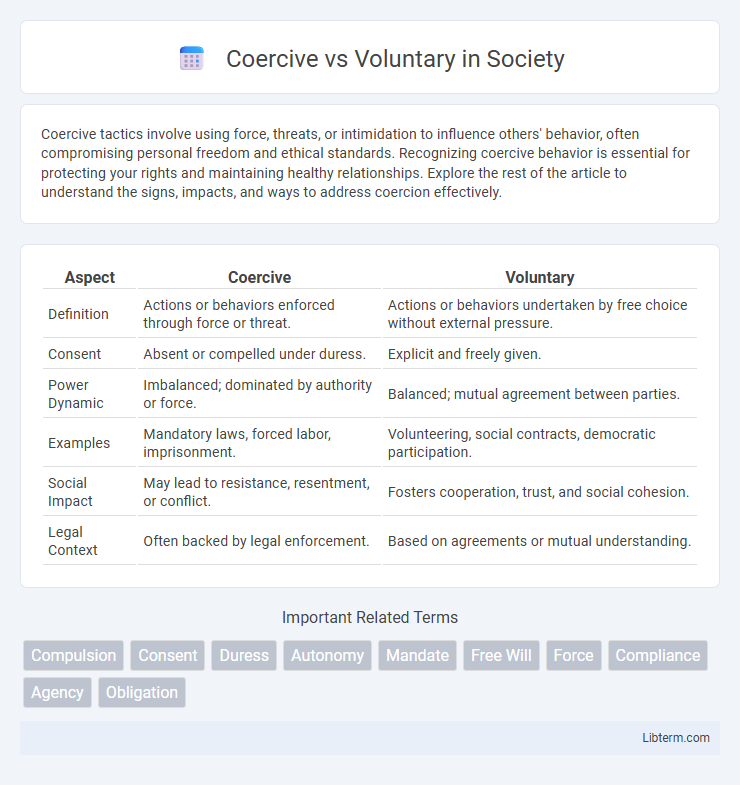
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Coercive | Voluntary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Actions or behaviors enforced through force or threat. | Actions or behaviors undertaken by free choice without external pressure. |
| Consent | Absent or compelled under duress. | Explicit and freely given. |
| Power Dynamic | Imbalanced; dominated by authority or force. | Balanced; mutual agreement between parties. |
| Examples | Mandatory laws, forced labor, imprisonment. | Volunteering, social contracts, democratic participation. |
| Social Impact | May lead to resistance, resentment, or conflict. | Fosters cooperation, trust, and social cohesion. |
| Legal Context | Often backed by legal enforcement. | Based on agreements or mutual understanding. |
Understanding Coercive and Voluntary Approaches
Coercive approaches involve enforcing compliance through threats, penalties, or force, often leading to resistance and ethical concerns, while voluntary approaches rely on mutual agreement, incentives, and collaboration to motivate participation. Understanding these differences is crucial for designing effective policies and organizational strategies that balance authority with individual autonomy. Research shows voluntary methods tend to foster higher engagement and sustainable cooperation compared to coercive tactics.
Defining Coercion in Social and Organizational Contexts
Coercion in social and organizational contexts refers to the use of force, threats, or intimidation to influence an individual's behavior or decisions against their will. This practice undermines autonomy by compelling compliance through fear of negative consequences, contrasting sharply with voluntary actions founded on free choice and consent. Understanding coercion highlights the importance of ethical leadership and organizational policies that promote collaboration without manipulation or undue pressure.
Characteristics of Voluntary Participation
Voluntary participation is characterized by the free choice and willingness of individuals to engage without pressure or threats, ensuring genuine consent and motivation. Participants in voluntary settings often demonstrate higher levels of commitment and satisfaction due to the absence of coercion. This type of engagement fosters trust and autonomy, enhancing the overall effectiveness of programs or activities.
Psychological Impact of Coercion vs Voluntariness
Coercion triggers heightened stress responses, including increased anxiety, feelings of helplessness, and reduced self-esteem, which can lead to long-term psychological trauma. Voluntariness fosters autonomy, intrinsic motivation, and psychological well-being by supporting personal agency and decision-making capacity. The psychological impact of coercion often results in emotional distress and diminished trust, whereas voluntariness promotes resilience and positive mental health outcomes.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Coercive actions in legal contexts often violate principles of consent and can lead to charges of duress, undermining the validity of agreements or confessions. Voluntary actions, by contrast, uphold ethical standards by ensuring informed consent and autonomy, key factors in both criminal law and contract law. The distinction affects court rulings, with voluntariness being critical to the legitimacy of legal transactions and the ethical treatment of individuals.
Real-World Examples: Coercive vs Voluntary Practices
In the workplace, coercive practices such as mandatory unpaid overtime or threats of job loss contrast sharply with voluntary initiatives like flexible hours and optional professional development programs. Political regimes often employ coercive tactics like censorship and forced compliance, whereas democratic governments promote voluntary participation through voting and civic engagement. In marketing, coercive strategies may involve aggressive upselling or deceptive pressure tactics, while voluntary practices rely on transparent information and customer consent.
Measuring Outcomes: Effectiveness of Each Approach
Coercive approaches to measuring outcomes often yield immediate compliance but may result in limited long-term effectiveness due to resistance or lack of intrinsic motivation. Voluntary methods typically encourage genuine engagement and sustained behavior change, leading to more meaningful and lasting results. Data from organizational studies indicate that voluntary participation correlates with higher satisfaction and improved performance metrics compared to coercive tactics.
Influencing Factors: Power Dynamics and Consent
Coercive influence relies on power dynamics where one party exerts control or pressure, often overriding genuine consent, leading to compliance driven by fear or obligation. Voluntary influence emerges from mutual consent and perceived authority without force, fostering engagement through trust and willingness. Understanding the interplay between power imbalance and the presence of consent is crucial in distinguishing coercion from voluntary agreement in social, organizational, and legal contexts.
Benefits of Fostering Voluntary Engagement
Fostering voluntary engagement leads to higher motivation and improved performance, as individuals participate out of genuine interest rather than compulsion. Voluntary involvement enhances creativity and collaboration by creating an environment where people feel valued and empowered. This approach reduces resistance and promotes sustainable commitment, benefiting organizational culture and long-term success.
Choosing the Right Approach: Key Considerations
Choosing between coercive and voluntary approaches hinges on context, objectives, and stakeholder dynamics. Coercive methods often ensure compliance through authority and enforceable rules but risk resistance or reduced morale. Voluntary strategies promote engagement and collaboration, enhancing long-term commitment while requiring clear incentives and effective communication.
Coercive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com