Normativity refers to the principles and standards that guide behavior, determining what is considered right or wrong within a society. These norms shape ethical frameworks, influence legal systems, and govern social interactions to maintain order and cohesion. Explore the rest of the article to understand how normativity impacts your daily decisions and societal dynamics.
Table of Comparison
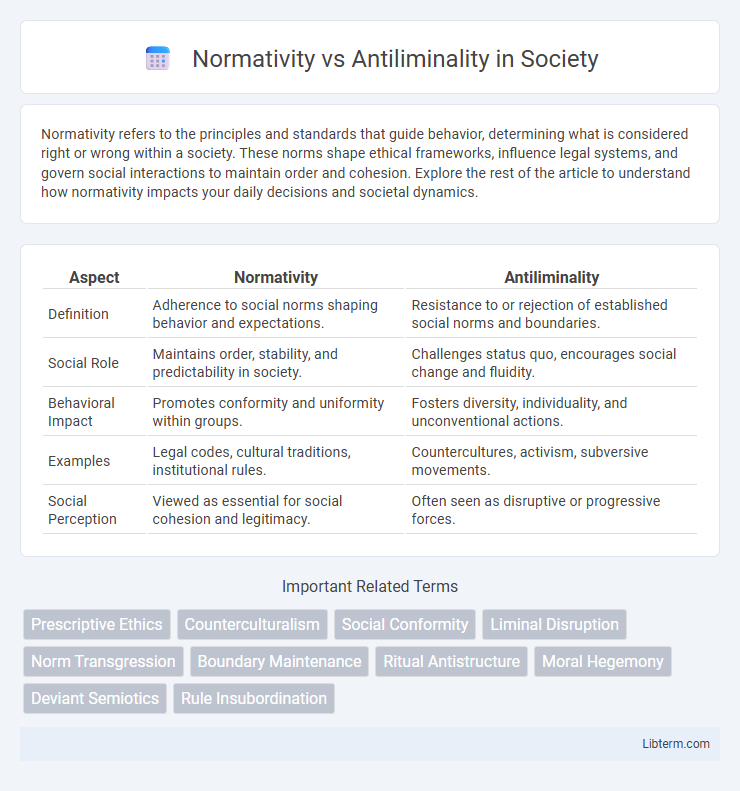
| Aspect | Normativity | Antiliminality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adherence to social norms shaping behavior and expectations. | Resistance to or rejection of established social norms and boundaries. |
| Social Role | Maintains order, stability, and predictability in society. | Challenges status quo, encourages social change and fluidity. |
| Behavioral Impact | Promotes conformity and uniformity within groups. | Fosters diversity, individuality, and unconventional actions. |
| Examples | Legal codes, cultural traditions, institutional rules. | Countercultures, activism, subversive movements. |
| Social Perception | Viewed as essential for social cohesion and legitimacy. | Often seen as disruptive or progressive forces. |
Understanding Normativity: Definition and Scope
Normativity refers to the system of norms, standards, and principles that guide behavior, beliefs, and practices within a society or community. It encompasses moral, legal, and social rules that establish what is considered acceptable or unacceptable, shaping individuals' decision-making processes and interactions. Understanding normativity involves examining the origin, justification, and enforceability of these norms to comprehend their influence on social cohesion and individual conduct.
Defining Antiliminality: Origins and Meaning
Antiliminality, originating from sociological and psychological discourse, challenges normativity by opposing established social norms and expectations. It refers to behaviors or attitudes that resist or invert the liminal state, which is a transitional phase where social norms are temporarily suspended. This concept highlights how certain groups or individuals maintain a permanent state outside normative structures, emphasizing alternative identities and social orders.
Historical Evolution of Normative Frameworks
The historical evolution of normative frameworks reveals a progression from rigid, prescriptive rules to more flexible and context-sensitive standards, reflecting shifts in social, cultural, and legal understandings. Early normative systems were often rooted in religious or authoritarian mandates, while modern frameworks incorporate pluralistic perspectives and emphasize human rights, justice, and equity. This transition highlights the dynamic tension between normativity, which enforces conformity, and antiliminality, which challenges boundaries and promotes transformative change.
Antiliminality in Contemporary Thought
Antiliminality in contemporary thought challenges traditional normativity by rejecting established boundaries and fixed moral frameworks. Emphasizing fluidity and multiplicity, it advocates for disruptive perspectives that undermine dominant cultural narratives and power structures. This concept resonates strongly within postmodern philosophy, queer theory, and critical social movements that prioritize heterogeneity and resistance to normative constraints.
Key Differences Between Normativity and Antiliminality
Normativity refers to the establishment of standards or norms that guide behavior, beliefs, and practices within a society or group, emphasizing what is considered acceptable or ideal. Antiliminality, by contrast, challenges or rejects these established norms, promoting alternative perspectives that resist conventional boundaries and thresholds. The key differences between normativity and antiliminality lie in their roles as enforcers versus disruptors of social or cultural standards, with normativity fostering conformity and antiliminality encouraging resistance and transformation.
Examples of Normativity in Society
Normativity in society is exemplified by laws that define acceptable behavior, such as traffic regulations mandating speed limits to ensure public safety. Social norms like dress codes in professional settings establish expectations for appropriate appearance and conduct. Educational systems impose curricular standards to shape knowledge acquisition and socialization processes.
Manifestations of Antiliminality in Culture
Manifestations of antiliminality in culture appear through the rejection of traditional norms, embracing ambiguity and fluidity in identity, art, and social roles. This cultural shift challenges conventional structures by promoting counter-normative behaviors, experimental aesthetics, and nonconformist values. Examples include avant-garde movements, subcultures that resist mainstream conformity, and media that question established narratives and moral frameworks.
Impacts on Identity and Social Structure
Normativity establishes social norms and expectations that shape individual identity and group cohesion by promoting conformity and shared values, reinforcing existing power structures. Antiliminality challenges these norms by encouraging resistance to dominant cultural narratives, fostering alternative identities and subcultures that disrupt traditional social hierarchies. The tension between normativity and antiliminality influences social dynamics, identity formation, and the evolution of societal organization.
Navigating the Tension: Normativity vs Antiliminality
Navigating the tension between normativity and antiliminality involves balancing established social norms with the resistance to crossing traditional boundaries. Normativity enforces expected behaviors that maintain social order, while antiliminality challenges these standards by rejecting transitions or threshold experiences that disrupt conventional identities. Understanding this dynamic aids in addressing conflicts arising in cultural, psychological, and organizational contexts where stability and change are in constant negotiation.
Future Perspectives and Theoretical Implications
Future perspectives in normativity versus antiliminality explore evolving frameworks of moral and social standards, emphasizing adaptive ethical models that respond to emerging digital and globalized contexts. Theoretical implications challenge traditional boundaries of norm construction, advocating for fluidity in ethical paradigms and highlighting the role of context-dependent interpretation in shaping collective behavior. Research trends suggest integrating interdisciplinary approaches, including cognitive science and cultural theory, to refine normative theories and address antiliminal resistance in dynamic sociopolitical environments.
Normativity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com