Pragmatism emphasizes practical consequences and real-world applications as the key criteria for truth and meaning, focusing on ideas that work effectively in everyday situations. This philosophical approach encourages evaluating beliefs by their tangible outcomes rather than abstract principles. Discover how pragmatism can influence your decision-making and problem-solving by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
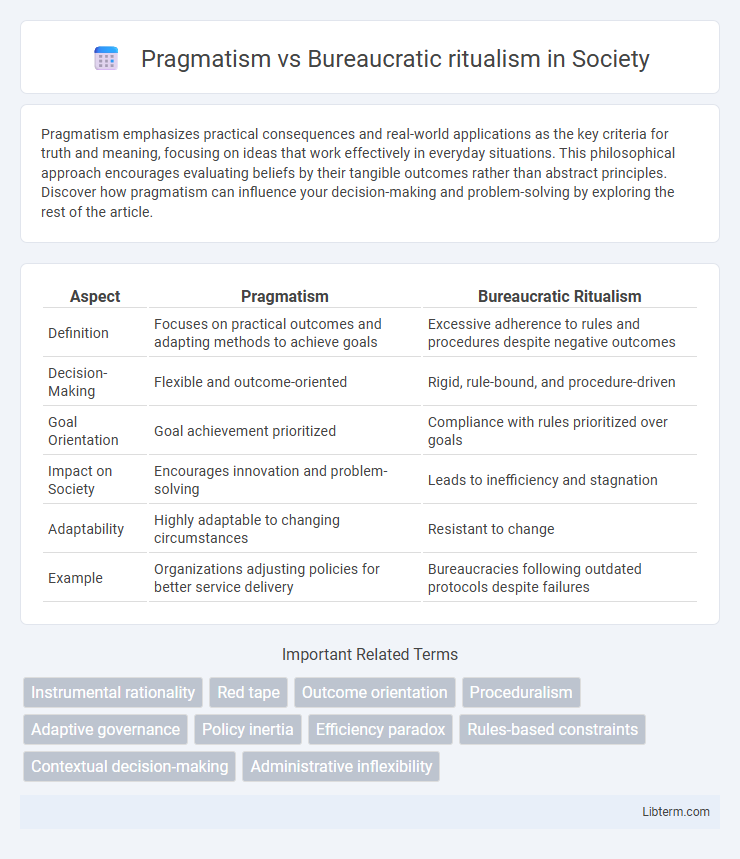
| Aspect | Pragmatism | Bureaucratic Ritualism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on practical outcomes and adapting methods to achieve goals | Excessive adherence to rules and procedures despite negative outcomes |
| Decision-Making | Flexible and outcome-oriented | Rigid, rule-bound, and procedure-driven |
| Goal Orientation | Goal achievement prioritized | Compliance with rules prioritized over goals |
| Impact on Society | Encourages innovation and problem-solving | Leads to inefficiency and stagnation |
| Adaptability | Highly adaptable to changing circumstances | Resistant to change |
| Example | Organizations adjusting policies for better service delivery | Bureaucracies following outdated protocols despite failures |
Understanding Pragmatism: A Practical Approach
Pragmatism emphasizes practical problem-solving and flexible decision-making based on outcomes and real-world effectiveness, contrasting sharply with bureaucratic ritualism's strict adherence to rules regardless of context. This approach values adaptability, encouraging innovation and responsiveness to changing circumstances within organizations. Understanding pragmatism helps managers prioritize functional results over procedural compliance, enhancing efficiency and goal achievement.
Defining Bureaucratic Ritualism: Process Over Purpose
Bureaucratic ritualism refers to a rigid adherence to established procedures and rules, emphasizing process compliance over the actual achievement of organizational goals. This phenomenon prioritizes formalities and routine tasks, often leading to inefficiency and a disconnect from practical outcomes. In contrast to pragmatism, which values flexibility and results-oriented decision-making, bureaucratic ritualism can stifle innovation and hinder adaptive responses in dynamic environments.
Historical Roots of Pragmatism and Bureaucratic Ritualism
Pragmatism originated in the late 19th century through the works of philosophers like Charles Sanders Peirce, William James, and John Dewey, emphasizing practical consequences and adaptive problem-solving as the basis for truth and meaning. Bureaucratic ritualism, rooted in Max Weber's early 20th-century sociological analysis, describes rigid adherence to formal rules and procedures, often leading to inefficiency and resistance to change within hierarchical organizations. The historical development of pragmatism reflects a focus on flexibility and innovation, while bureaucratic ritualism highlights the tensions between order and stagnation in administrative systems.
Core Principles: Pragmatic Flexibility vs. Rigid Protocols
Pragmatism emphasizes adaptive problem-solving and practical outcomes, prioritizing flexibility to respond effectively to changing circumstances. Bureaucratic ritualism adheres strictly to fixed rules and procedures, often valuing protocol compliance over situational effectiveness. This contrast highlights pragmatic flexibility as essential for innovation, while rigid protocols can hinder responsiveness and efficiency.
Decision-Making in Practice: Efficiency vs. Procedure
Pragmatism in decision-making prioritizes efficiency by emphasizing practical solutions and outcomes tailored to specific contexts, often adapting strategies to meet real-world demands. Bureaucratic ritualism, however, centers on strict adherence to established procedures and rules, potentially slowing decision processes despite ensuring consistency and control. This contrast highlights the trade-off between flexible, outcome-driven choices and rigid, process-oriented governance in organizational practice.
Impact on Organizational Effectiveness
Pragmatism in organizations fosters adaptability and innovation, enhancing problem-solving capabilities and promoting efficient decision-making processes that directly improve organizational effectiveness. Bureaucratic ritualism, characterized by rigid adherence to rules and procedures regardless of outcomes, often leads to decreased flexibility, slowed response times, and reduced employee motivation, ultimately hampering organizational performance. Balancing pragmatic approaches with necessary bureaucratic controls is essential to optimize operational efficiency and sustain long-term success.
Real-World Examples: Successes and Failures
Pragmatism in organizational management emphasizes practical solutions and flexibility, exemplified by Tesla's adaptive production strategies that enabled rapid innovation and market responsiveness. In contrast, bureaucratic ritualism, seen in government agencies like the DMV, often leads to inefficiencies due to rigid adherence to procedures, causing delays and customer dissatisfaction. The success of pragmatic approaches in companies like Amazon contrasts sharply with the failures of bureaucratic rigidity in public sector contexts, highlighting the impact of adaptability versus procedural inertia.
Challenges of Balancing Pragmatism and Bureaucratic Ritualism
Balancing pragmatism and bureaucratic ritualism presents challenges such as inefficiency caused by rigid adherence to established procedures, which can stifle innovation and slow decision-making in dynamic environments. Organizations struggle to maintain compliance with regulatory frameworks while adapting to practical solutions that address real-world problems effectively. This tension often results in conflicts between frontline employees seeking flexible approaches and management enforcing standardized protocols, hindering overall organizational performance.
Strategies to Foster Practical Solutions in Bureaucracies
Pragmatism in bureaucracies emphasizes flexible problem-solving and adaptive decision-making to enhance operational efficiency and responsiveness. Implementing outcome-oriented performance metrics and encouraging decentralized authority enables practical solutions by reducing rigid adherence to procedural formalities. Training programs that promote critical thinking and innovation among employees also help overcome bureaucratic ritualism, fostering a culture focused on results rather than mere rule compliance.
The Future of Policy: Integrating Pragmatic Thinking
Integrating pragmatic thinking into future policy development emphasizes flexibility, evidence-based solutions, and responsiveness to real-world challenges, contrasting sharply with bureaucratic ritualism's rigid adherence to rules and procedures. Policies shaped by pragmatism prioritize outcomes and adaptability, fostering innovation and effective governance in dynamic social and economic contexts. This approach encourages continuous evaluation and revision, ensuring that policy frameworks remain relevant and practical amid evolving public needs and complex global issues.
Pragmatism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com