Educational disparity creates significant barriers to equal opportunity by limiting access to quality resources, experienced teachers, and advanced curriculum for underprivileged communities. This gap not only affects academic performance but also hinders lifelong economic and social mobility. Discover how understanding the root causes of educational disparity can help you contribute to meaningful change in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
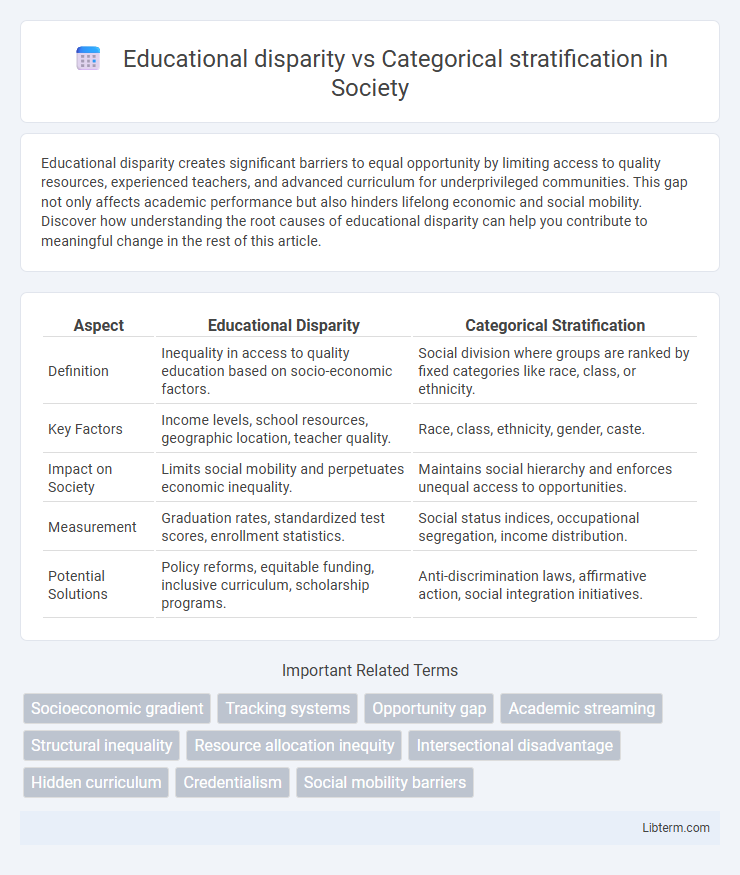
| Aspect | Educational Disparity | Categorical Stratification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inequality in access to quality education based on socio-economic factors. | Social division where groups are ranked by fixed categories like race, class, or ethnicity. |
| Key Factors | Income levels, school resources, geographic location, teacher quality. | Race, class, ethnicity, gender, caste. |
| Impact on Society | Limits social mobility and perpetuates economic inequality. | Maintains social hierarchy and enforces unequal access to opportunities. |
| Measurement | Graduation rates, standardized test scores, enrollment statistics. | Social status indices, occupational segregation, income distribution. |
| Potential Solutions | Policy reforms, equitable funding, inclusive curriculum, scholarship programs. | Anti-discrimination laws, affirmative action, social integration initiatives. |
Understanding Educational Disparity
Educational disparity refers to the unequal access to quality education and resources experienced by students from different socioeconomic, racial, or geographic backgrounds. It results in significant achievement gaps and limits opportunities for marginalized groups. Understanding educational disparity involves analyzing factors such as funding inequalities, teacher quality, and systemic barriers that perpetuate these differences.
Defining Categorical Stratification
Categorical stratification refers to the systematic division of populations into distinct groups based on specific attributes such as race, socioeconomic status, or educational attainment, leading to unequal access to resources and opportunities. Unlike educational disparity, which highlights gaps in academic achievement and access, categorical stratification emphasizes the structural and institutional mechanisms that perpetuate social hierarchies. Understanding categorical stratification is crucial for addressing the root causes of inequality and designing policies that promote equity across diverse demographic categories.
Historical Roots of Educational Inequality
Historical roots of educational inequality reveal a persistent divide where educational disparity arises from unequal access to resources, while categorical stratification organizes students based on socio-economic, racial, or ethnic categories. Segregation policies, discriminatory laws, and economic disenfranchisement have embedded systemic barriers that perpetuate unequal schooling opportunities. These historical inequities create long-lasting effects, reinforcing the cycle of disadvantage and limiting social mobility for marginalized groups.
Socioeconomic Factors Shaping Access to Education
Socioeconomic factors such as family income, parental education, and neighborhood resources play a crucial role in educational disparity by limiting access to quality schooling and academic support. These economic constraints reinforce categorical stratification, where students from lower-income or marginalized groups face systemic barriers in achieving educational advancement. Addressing these disparities requires targeted policies that allocate resources equitably and dismantle structural inequalities in the education system.
Race, Ethnicity, and Stratified Educational Outcomes
Educational disparity manifests in unequal access and achievement among racial and ethnic groups, driven by systemic factors such as resource allocation and cultural biases. Categorical stratification reinforces these disparities by sorting students into educational tracks based on race and ethnicity, perpetuating segregated outcomes and limiting social mobility. Research consistently links stratified educational outcomes to long-term socioeconomic inequalities, underscoring the need for policies addressing race-based educational barriers.
The Role of Policy in Perpetuating Stratification
Education policies that allocate resources unevenly often reinforce existing educational disparities by limiting opportunities for marginalized groups. Categorical stratification is perpetuated through tracking systems and standardized testing that disproportionately affect students based on race, socioeconomic status, and ability. Policy reforms aimed at equitable funding and inclusive curricula are essential to disrupt these systemic mechanisms sustaining stratification.
Intersectionality: Where Disparity Meets Stratification
Educational disparity highlights unequal access to learning opportunities based on socioeconomic status, race, or gender, while categorical stratification organizes individuals into hierarchical groups within institutions. Intersectionality reveals how these inequalities overlap, intensifying barriers for marginalized students who face multiple layers of disadvantage simultaneously. Understanding this overlap is crucial for developing policies that address complex systemic inequities rather than isolated factors.
Educational Disparity Across Urban and Rural Divides
Educational disparity across urban and rural divides reveals significant gaps in access to quality schooling, resources, and experienced teachers, contributing to uneven academic outcomes. Rural areas often face challenges such as limited infrastructure, fewer extracurricular opportunities, and inadequate funding compared to urban counterparts. Addressing these disparities requires targeted policy interventions to ensure equitable educational opportunities regardless of geographic location.
Consequences of Stratification for Social Mobility
Educational disparity and categorical stratification significantly hinder social mobility by limiting access to quality resources and opportunities for marginalized groups. Stratification entrenches socioeconomic inequalities through segregated schooling systems, which perpetuate disparities in academic achievement, skill development, and future employment prospects. This systemic division reduces the likelihood of upward mobility by reinforcing existing social hierarchies and restricting intergenerational economic advancement.
Strategies for Bridging Educational and Categorical Gaps
Targeted interventions such as equitable resource allocation and inclusive curriculum design effectively reduce educational disparity by addressing diverse student needs across categorical stratifications like socioeconomic status, race, and disability. Implementing mentorship programs and culturally responsive teaching fosters engagement and academic success, bridging gaps between marginalized groups and their peers. Policy reforms promoting equal access to advanced coursework and extracurricular opportunities further dismantle structural barriers perpetuating categorical stratification in education.
Educational disparity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com