Inclusion fosters a sense of belonging by embracing diversity and ensuring equal opportunities for everyone. Creating an inclusive environment enhances collaboration, innovation, and overall well-being in any community or workplace. Discover how you can promote inclusion effectively by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
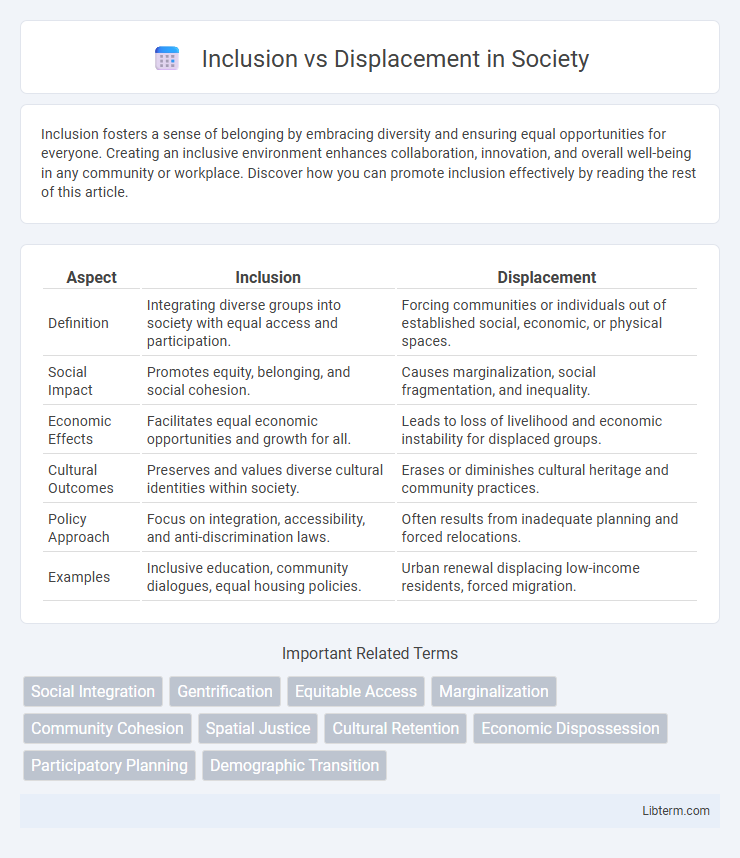
| Aspect | Inclusion | Displacement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrating diverse groups into society with equal access and participation. | Forcing communities or individuals out of established social, economic, or physical spaces. |
| Social Impact | Promotes equity, belonging, and social cohesion. | Causes marginalization, social fragmentation, and inequality. |
| Economic Effects | Facilitates equal economic opportunities and growth for all. | Leads to loss of livelihood and economic instability for displaced groups. |
| Cultural Outcomes | Preserves and values diverse cultural identities within society. | Erases or diminishes cultural heritage and community practices. |
| Policy Approach | Focus on integration, accessibility, and anti-discrimination laws. | Often results from inadequate planning and forced relocations. |
| Examples | Inclusive education, community dialogues, equal housing policies. | Urban renewal displacing low-income residents, forced migration. |
Understanding Inclusion and Displacement
Inclusion involves integrating diverse individuals or groups into existing social, educational, or workplace environments, ensuring equal access and participation. Displacement occurs when one group or individuals are removed or replaced within a community or system, often leading to marginalization or loss of resources. Understanding inclusion versus displacement requires recognizing the impact on equity, social cohesion, and access to opportunities for marginalized populations.
Historical Context of Inclusion and Displacement
The historical context of inclusion and displacement reveals patterns of demographic shifts shaped by policies such as colonial land seizures, forced relocations of Indigenous populations, and immigration laws favoring certain groups. Inclusion efforts emerged during the civil rights movements and post-colonial reforms, aiming to integrate marginalized communities into political, social, and economic systems. Displacement often resulted from urban renewal projects, gentrification, and economic development strategies that prioritized dominant groups, perpetuating cycles of exclusion despite emerging inclusion discourses.
Key Differences Between Inclusion and Displacement
Inclusion integrates individuals with disabilities into general education settings, promoting accessibility and equal participation alongside peers, while displacement involves removing or segregating individuals from mainstream environments, often to separate settings. Inclusion emphasizes support services and accommodations tailored to diverse needs within the same space, whereas displacement relies on relocating individuals to specialized environments that may limit social interaction and access to typical resources. The key differences lie in the approach to participation, with inclusion fostering shared experiences and displacement resulting in isolation or separation.
Social Impacts of Inclusion
Inclusion fosters social cohesion by promoting equal participation of diverse groups, leading to enhanced community well-being and reduced social isolation. It empowers marginalized individuals, improving access to education, employment, and health services, which drives economic growth and social stability. Research shows inclusive policies significantly decrease inequality and increase collective resilience in multicultural societies.
Negative Effects of Displacement
Displacement often causes significant negative effects such as loss of community, cultural erosion, and economic instability for displaced populations. Forced relocation disrupts social networks and access to essential resources, leading to increased poverty and mental health issues. Unlike inclusion, displacement marginalizes vulnerable groups, exacerbating inequality and social exclusion.
Economic Implications: Inclusion vs Displacement
Inclusion fosters economic growth by integrating marginalized groups into the workforce, thereby expanding consumer markets and increasing productivity. Displacement often leads to higher unemployment rates and social welfare costs, reducing overall economic stability. Inclusive policies promote sustainable development by leveraging diverse talents and reducing economic inequality.
Policy Approaches to Promote Inclusion
Policy approaches to promote inclusion focus on creating equitable access to education, employment, and social services for marginalized groups, emphasizing the removal of physical, social, and economic barriers. Inclusive policies prioritize representation, participation, and tailored support mechanisms such as affirmative action, inclusive curricula, and accessibility standards. Governments and organizations implement monitoring frameworks and community engagement strategies to ensure sustainable inclusion while preventing displacement of vulnerable populations.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Case studies reveal that inclusion strategies often lead to improved social cohesion and economic opportunities by integrating marginalized groups into existing systems. In contrast, displacement cases frequently result in loss of community, cultural erosion, and long-term socio-economic instability. For example, successful inclusion in urban redevelopment projects in Curitiba, Brazil, contrasts sharply with displacement failures in Johannesburg's informal settlement clearances, highlighting the critical role of participatory planning and equitable resource allocation.
Barriers to Achieving True Inclusion
Barriers to achieving true inclusion often stem from systemic biases, lack of accessible infrastructure, and insufficient representation of marginalized groups in decision-making roles. Cultural misconceptions and stereotypes perpetuate exclusion by limiting opportunities for diverse individuals to fully participate in social, educational, and professional environments. Overcoming these obstacles requires targeted policies that promote equity, continuous education on diversity, and adaptive frameworks that address both visible and invisible forms of exclusion.
Future Directions: Balancing Inclusion and Displacement
Future directions in balancing inclusion and displacement emphasize creating equitable urban development policies that protect vulnerable communities. Leveraging data-driven approaches and community engagement fosters inclusive growth while minimizing displacement risks. Sustainable models integrate affordable housing strategies with economic opportunities to ensure long-term social stability.
Inclusion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com