McDonaldization refers to the process by which the principles of fast-food restaurants, such as efficiency, calculability, predictability, and control, dominate various sectors of society. This concept explains how standardization and automation shape consumer experiences and organizational structures, often leading to the reduction of human creativity and individuality. Discover how McDonaldization influences different aspects of your daily life by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
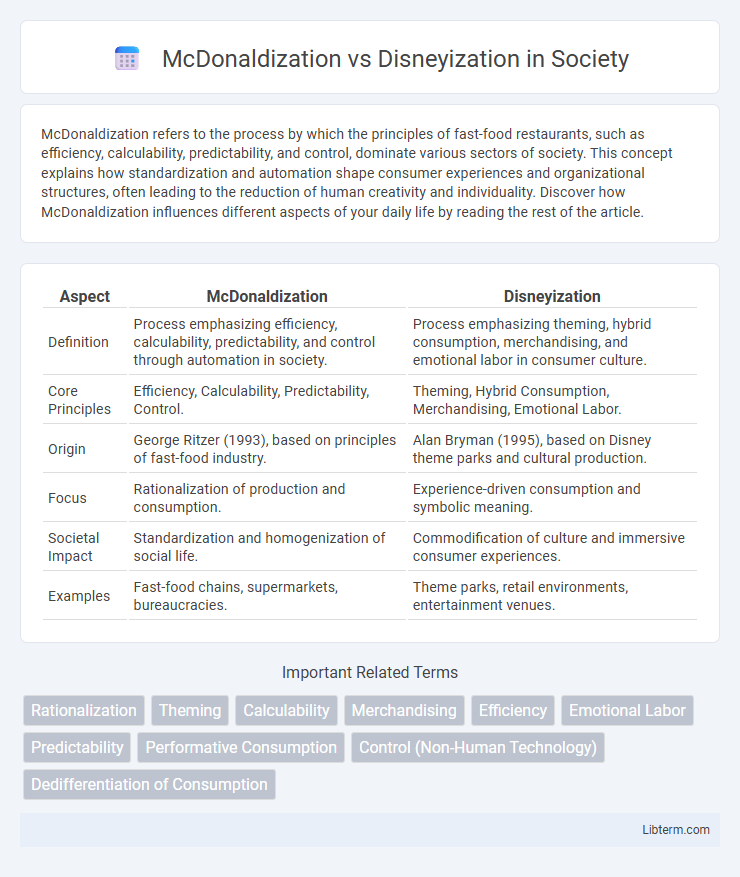
| Aspect | McDonaldization | Disneyization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process emphasizing efficiency, calculability, predictability, and control through automation in society. | Process emphasizing theming, hybrid consumption, merchandising, and emotional labor in consumer culture. |
| Core Principles | Efficiency, Calculability, Predictability, Control. | Theming, Hybrid Consumption, Merchandising, Emotional Labor. |
| Origin | George Ritzer (1993), based on principles of fast-food industry. | Alan Bryman (1995), based on Disney theme parks and cultural production. |
| Focus | Rationalization of production and consumption. | Experience-driven consumption and symbolic meaning. |
| Societal Impact | Standardization and homogenization of social life. | Commodification of culture and immersive consumer experiences. |
| Examples | Fast-food chains, supermarkets, bureaucracies. | Theme parks, retail environments, entertainment venues. |
Defining McDonaldization: Key Characteristics
McDonaldization is defined by four key characteristics: efficiency, calculability, predictability, and control through non-human technology, aimed at streamlining processes and maximizing output. This concept, introduced by sociologist George Ritzer, describes the spread of rationalized systems modeled after fast-food chains like McDonald's. These characteristics prioritize uniformity, standardization, and measurable outcomes, often leading to dehumanization and reduced creativity in service and production.
Understanding Disneyization: Core Elements
Disneyization revolves around the core elements of theming, hybrid consumption, merchandising, and performative labor, each transforming consumer experiences through immersive environments and integrated offerings. Theming creates cohesive narratives that shape spaces, while hybrid consumption blends different types of goods and services, enhancing consumer engagement. Merchandising extends the brand presence through diverse products, and performative labor involves staff acting as entertainers or characters, further enriching the visitor experience.
Historical Origins of McDonaldization and Disneyization
McDonaldization originated from sociologist George Ritzer's 1993 analysis of the fast-food industry's efficiency, calculability, predictability, and control shaping modern social institutions. Disneyization emerged later as a concept describing the transformation of society through theming, hybrid consumption, merchandising, and emotional labor, heavily influenced by The Walt Disney Company's expansion and innovation in entertainment and consumer experiences since the mid-20th century. Both frameworks highlight distinct evolutionary trajectories in the development of cultural and economic practices linked to mass consumption and globalization.
Efficiency vs. Experience: Contrasting Philosophies
McDonaldization emphasizes efficiency, predictability, and calculability, streamlining processes to maximize productivity and reduce time costs in service delivery. Disneyization prioritizes creating immersive, themed experiences that engage customers emotionally and sensorially, focusing on entertainment and storytelling to enhance satisfaction. The contrast lies in McDonaldization's goal of standardizing and speeding up interactions, whereas Disneyization aims to enrich and personalize the consumer's encounter.
Standardization and Control in Modern Society
McDonaldization emphasizes strict standardization and control through uniform procedures, predictable menus, and efficiency-driven workflows, shaping consumer experiences into repeatable and homogeneous encounters. Disneyization, while also using standardization, incorporates theming, storytelling, and emotional engagement to create immersive environments that guide behavior through scripted interactions and controlled atmospheres. Both processes reflect modern society's shift towards rationalized systems that prioritize order, predictability, and consumer compliance within commodified cultural spaces.
The Role of Theming and Spectacle
Theming and spectacle play crucial roles in both McDonaldization and Disneyization, shaping consumer experience through immersive narratives and visually engaging environments. McDonaldization emphasizes efficiency and predictability, often utilizing standardized themes to streamline operations, while Disneyization prioritizes elaborate theming and spectacular design to create emotional connections and memorable experiences. The contrast lies in McDonaldization's functional theming versus Disneyization's focus on entertainment-driven spectacle, enhancing consumer engagement and brand loyalty.
Impact on Consumer Behavior and Culture
McDonaldization encourages efficiency, predictability, and control, leading consumers to value convenience and standardized experiences, which can diminish cultural diversity and uniqueness. Disneyization emphasizes theming, emotional engagement, and consumer participation, fostering immersive experiences that shape consumer expectations towards entertainment and fantasy-based consumption. Together, these models influence modern consumer behavior by blending uniformity with experiential elements, reshaping cultural consumption patterns towards homogenized yet emotionally charged environments.
Globalization: Spreading Influence Worldwide
McDonaldization and Disneyization both illustrate globalization by spreading standardized cultural and consumer experiences worldwide, adapting local markets to global norms. McDonaldization emphasizes efficiency, calculability, predictability, and control through uniform services, while Disneyization expands this by integrating theming, hybrid consumption, merchandising, and performative labor. These processes enable multinational corporations like McDonald's and Disney to dominate global consumer landscapes, influencing lifestyles, consumption patterns, and cultural values across diverse regions.
Criticisms and Societal Implications
McDonaldization, characterized by efficiency, calculability, predictability, and control, faces criticism for promoting homogenization and dehumanization, limiting creativity and authentic social interaction. Disneyization expands this critique by emphasizing theming, hybrid consumption, merchandising, and performative labor, raising concerns about commercialization of culture and consumer manipulation. Both concepts highlight societal implications such as the erosion of local identities, the prioritization of profit over individuality, and the reinforcement of passive consumer behaviors in contemporary capitalist societies.
Future Trends: Blending McDonaldization and Disneyization
Future trends suggest a growing convergence between McDonaldization's efficiency-driven processes and Disneyization's emphasis on thematic experience and emotional engagement. Businesses are increasingly adopting streamlined operations alongside immersive storytelling to enhance customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. This hybrid approach leverages data analytics and automation from McDonaldization with personalized, themed environments characteristic of Disneyization, setting new standards for service innovation.
McDonaldization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com