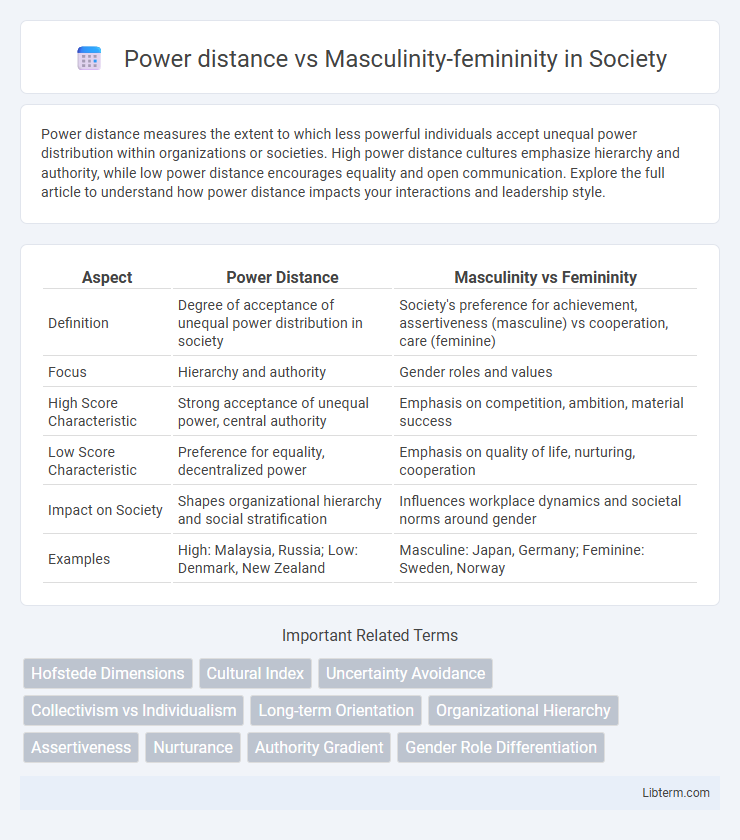
Power distance measures the extent to which less powerful individuals accept unequal power distribution within organizations or societies. High power distance cultures emphasize hierarchy and authority, while low power distance encourages equality and open communication. Explore the full article to understand how power distance impacts your interactions and leadership style.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Power Distance | Masculinity vs Femininity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Degree of acceptance of unequal power distribution in society | Society's preference for achievement, assertiveness (masculine) vs cooperation, care (feminine) |
| Focus | Hierarchy and authority | Gender roles and values |
| High Score Characteristic | Strong acceptance of unequal power, central authority | Emphasis on competition, ambition, material success |
| Low Score Characteristic | Preference for equality, decentralized power | Emphasis on quality of life, nurturing, cooperation |
| Impact on Society | Shapes organizational hierarchy and social stratification | Influences workplace dynamics and societal norms around gender |
| Examples | High: Malaysia, Russia; Low: Denmark, New Zealand | Masculine: Japan, Germany; Feminine: Sweden, Norway |
Understanding Power Distance in Cultural Contexts
Power distance measures how much less powerful members of society accept unequal power distribution, influencing workplace hierarchy and communication styles. Masculinity-femininity reflects cultural values on competitiveness versus cooperation, shaping social roles and organizational behavior. Understanding power distance in cultural contexts helps predict authority dynamics and employee expectations across diverse global environments.
Exploring Masculinity-Femininity as a Cultural Dimension
Masculinity-Femininity as a cultural dimension reflects the distribution of emotional roles between genders, emphasizing traits like competitiveness and achievement in masculine societies versus care and quality of life in feminine ones. This dimension influences workplace dynamics, communication styles, and organizational priorities, with masculine cultures valuing assertiveness and success while feminine cultures prioritize collaboration and consensus. Understanding this dimension aids businesses in navigating cultural expectations and improving intercultural interactions by aligning strategies with societal values.
Key Differences Between Power Distance and Masculinity-Femininity
Power distance measures the acceptance of unequal power distribution within a society, while masculinity-femininity reflects the preference for assertiveness and competitiveness versus cooperation and care. Power distance impacts hierarchical structures and authority dynamics, whereas masculinity-femininity influences gender roles, values, and societal priorities. Understanding these dimensions aids in cross-cultural communication by highlighting differences in organizational behavior and social interactions.
Historical Roots of Power Distance and Masculinity-Femininity
Power distance and masculinity-femininity dimensions in cultural studies originate from Hofstede's research on societal values and workplace behaviors. Power distance reflects historical roots in hierarchical structures and centralized authority in societies, often influenced by feudal systems and colonial legacies. Masculinity-femininity emerges from gender role distinctions shaped by traditional economic roles and social expectations, where masculine cultures emphasize competitiveness and achievement while feminine cultures prioritize care and cooperation.
Impact on Workplace Dynamics and Leadership
Power distance influences hierarchical relationships and communication flow in the workplace, with high power distance cultures emphasizing authority and centralized decision-making. Masculinity-femininity affects workplace dynamics by shaping values around competition, achievement, and collaboration, where masculine cultures prioritize assertiveness and performance, while feminine cultures emphasize empathy and work-life balance. Leadership styles adapt accordingly, with high power distance and masculine cultures favoring directive, task-oriented leaders, whereas low power distance and feminine cultures encourage participative and relational leadership approaches.
Effects on Communication Styles and Social Interactions
High power distance cultures emphasize hierarchical communication where subordinates expect clear directives, leading to formal and respectful interactions, while low power distance cultures encourage open dialogue and equality in conversations. Masculinity-focused societies prioritize assertiveness and competition, often resulting in direct and task-oriented communication, whereas femininity-oriented cultures value empathy and cooperation, promoting nurturing and relationship-centered interactions. These cultural dimensions shape social behaviors by influencing how individuals express respect, resolve conflicts, and build rapport within various social and professional settings.
Influence on Gender Roles and Organizational Hierarchies
Power distance significantly shapes organizational hierarchies by determining the acceptance of unequal power distribution, often reinforcing traditional gender roles where masculine traits are associated with authority and leadership. Masculinity-femininity dimensions influence workplace culture and gender expectations, with masculine societies valuing competitiveness and assertiveness, while feminine cultures emphasize collaboration and care, impacting gender role flexibility. The interplay between power distance and masculinity-femininity affects how organizations assign roles and responsibilities, potentially perpetuating gender disparities or fostering inclusive leadership structures.
Cross-Cultural Examples and Comparisons
Power distance measures how less powerful members of organizations or societies accept unequal power distribution, while masculinity-femininity reflects a cultural preference for achievement and assertiveness versus cooperation and quality of life. In high power distance and masculine societies like Japan, hierarchy is respected and competition thrives, contrasting with feminine, low power distance countries such as Sweden, where equality and consensus are prioritized. Cross-cultural comparisons reveal that understanding these dimensions helps multinational organizations tailor leadership styles and communication strategies for better global collaboration.
Practical Implications for Multinational Organizations
Power distance influences hierarchical decision-making structures in multinational organizations, affecting communication flow and authority distribution across offices. Masculinity-femininity impacts organizational culture by shaping competitiveness versus cooperation preferences, influencing employee motivation and conflict resolution strategies. Understanding these cultural dimensions enables multinational corporations to tailor leadership approaches and human resource practices for enhanced cross-cultural collaboration and productivity.
Navigating Cultural Differences: Strategies for Global Success
Understanding the dynamics of power distance and masculinity-femininity is crucial for navigating cultural differences in global business environments. High power distance cultures often emphasize hierarchy and authority, requiring leaders to adopt clear, top-down communication, while masculinity-oriented societies prioritize competitiveness and achievement, influencing negotiation styles and decision-making processes. Adapting strategies to respect these cultural dimensions fosters effective collaboration, minimizes misunderstandings, and enhances global success.
Power distance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com