Positive thinking enhances mental well-being by reducing stress and promoting resilience through a constructive outlook on challenges. Embracing optimism can improve your physical health, boost creativity, and strengthen relationships by fostering a supportive environment. Discover how cultivating a positive mindset can transform your life by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
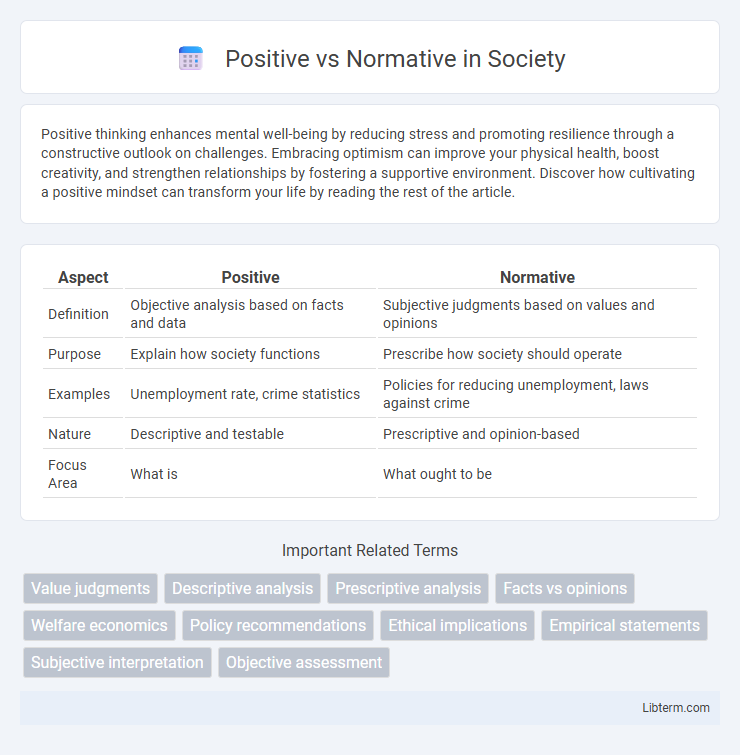
| Aspect | Positive | Normative |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Objective analysis based on facts and data | Subjective judgments based on values and opinions |
| Purpose | Explain how society functions | Prescribe how society should operate |
| Examples | Unemployment rate, crime statistics | Policies for reducing unemployment, laws against crime |
| Nature | Descriptive and testable | Prescriptive and opinion-based |
| Focus Area | What is | What ought to be |
Introduction to Positive and Normative Economics
Positive economics analyzes factual and objective statements about economic phenomena, relying on data, empirical evidence, and testable hypotheses to explain how economies function. Normative economics involves value-based judgments and subjective opinions about what economic policies or outcomes should be, often guiding decisions based on ethical considerations and societal goals. Understanding the distinction between positive and normative economics is essential for interpreting economic analyses and policymaking effectively.
Defining Positive Economics
Positive economics involves the objective analysis and description of economic phenomena based on factual data and empirical evidence, focusing on what is or what will be rather than what ought to be. It deals with cause-and-effect relationships, using models and statistics to predict outcomes without incorporating value judgments. This branch of economics distinguishes itself from normative economics by its commitment to scientific inquiry and verifiable statements.
Defining Normative Economics
Normative economics involves value-based judgments and prescribes economic policies based on what ought to be rather than what is. It contrasts with positive economics, which relies on objective analysis and factual data to describe and predict economic phenomena. Defining normative economics requires emphasizing ethical considerations and subjective opinions about economic outcomes and priorities.
Key Differences Between Positive and Normative Statements
Positive statements describe facts and can be tested or validated through evidence, focusing on objective analysis without personal judgments. Normative statements express opinions or value-based judgments about what ought to be, reflecting subjective beliefs and ethical considerations. The key difference lies in positive statements being fact-driven and descriptive, whereas normative statements are prescriptive and rooted in ideology or preferences.
Examples of Positive Statements
Positive statements describe facts or cause-and-effect relationships that can be tested or validated, such as "The unemployment rate in the United States was 3.7% in 2023" or "Increasing the minimum wage led to higher consumer spending in some studies." These statements are objective and rely on empirical evidence, differentiating them from normative statements that express opinions or value judgments. Examples include "Inflation rose by 2% last year" and "Higher taxes on cigarettes reduce smoking rates," all based on observable data.
Examples of Normative Statements
Normative statements express subjective opinions or value judgments rather than objective facts, such as "The government should increase the minimum wage to reduce poverty" or "Healthcare access must be free for all citizens." These statements often reflect ethical beliefs and policy preferences, contrasting with positive statements that describe facts or cause-and-effect relationships. Policymakers rely on normative statements to advocate for laws based on what ought to be rather than what is.
Importance of Distinguishing Positive and Normative
Distinguishing positive and normative statements is crucial for clear economic analysis and policy-making, as positive statements rely on objective data and facts while normative statements incorporate subjective values and opinions. This differentiation helps prevent bias in economic research by ensuring that empirical evidence is separated from personal beliefs or policy preferences. Understanding the distinction enables economists and policymakers to communicate effectively and make informed decisions based on evidence rather than ideology.
Role of Positive vs Normative in Policy Making
Positive analysis in policy making provides objective, data-driven insights by describing and predicting economic and social outcomes without judgment. Normative analysis evaluates policies based on value judgments and societal goals, guiding decision-makers on what ought to be done to achieve desired objectives. Combining positive facts with normative considerations ensures policies are both feasible and aligned with public values, enhancing effective governance and social welfare.
Common Misconceptions and Challenges
Positive economics deals with objective analysis based on empirical data, describing what is, whereas normative economics involves subjective judgments about what ought to be. A common misconception is that positive statements are always true and normative statements are purely opinion, overlooking that positive statements can be false if facts are incorrect, while normative statements are influenced by values and cultural context. Challenges arise in distinguishing factual analysis from value-based recommendations, especially in policymaking where separating objective evidence from personal or societal biases is difficult.
Conclusion: Balancing Positive and Normative Approaches
Balancing positive and normative approaches requires integrating empirical data with value-based judgments to create well-rounded economic policies. Positive analysis offers objective insights grounded in facts, while normative perspectives ensure that ethical considerations and societal goals guide decision-making. Effective policymaking hinges on harmonizing these methods to address both what is and what ought to be.
Positive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com