Nature offers a diverse range of ecosystems that support countless species and maintain ecological balance essential for human survival. Experiencing natural environments can improve mental health, boost creativity, and foster a deeper connection with the planet. Explore the rest of this article to discover how embracing nature can enhance your well-being and contribute to a sustainable future.
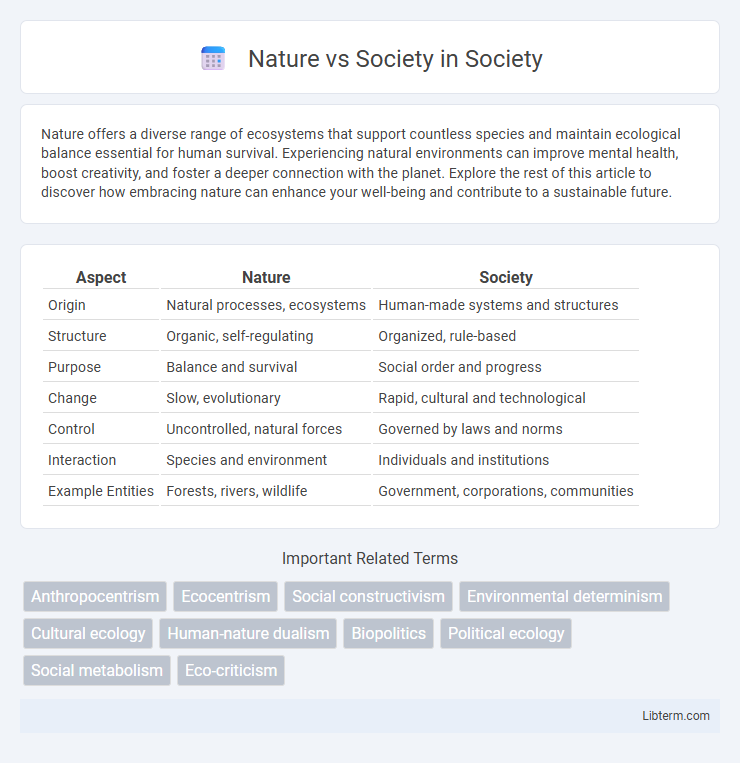
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nature | Society |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural processes, ecosystems | Human-made systems and structures |
| Structure | Organic, self-regulating | Organized, rule-based |
| Purpose | Balance and survival | Social order and progress |
| Change | Slow, evolutionary | Rapid, cultural and technological |
| Control | Uncontrolled, natural forces | Governed by laws and norms |
| Interaction | Species and environment | Individuals and institutions |
| Example Entities | Forests, rivers, wildlife | Government, corporations, communities |
Defining Nature and Society
Nature encompasses the physical world and its ecosystems, including flora, fauna, climate, and geological features, operating independently of human intervention. Society refers to the structured communities of humans characterized by cultural norms, institutions, social relationships, and shared values. The interaction between nature and society highlights the dynamic balance between environmental processes and human development.
Historical Perspectives on Nature vs Society
Historical perspectives on the conflict between nature and society trace back to ancient civilizations, where natural forces were often revered but also feared as obstacles to human progress. During the Enlightenment, philosophers like Rousseau emphasized the corrupting influence of society on natural human goodness, contrasting with Hobbes' view of nature as a brutal state requiring social order. Industrialization intensified debates by highlighting human capacity to dominate nature through technology, raising early concerns about environmental degradation and the sustainability of societal growth.
The Human-Nature Relationship
The human-nature relationship is a complex interplay where society relies on natural ecosystems for resources, climate regulation, and spiritual well-being. Human activities, including urbanization and industrialization, impact biodiversity and ecosystem services, creating challenges for sustainable development. Understanding this dynamic fosters environmental stewardship and policies that balance economic growth with conservation efforts.
Cultural Influences on Environment
Cultural influences shape environmental perceptions and practices, impacting natural resource management and conservation efforts. Indigenous knowledge systems often promote sustainable interactions with ecosystems, contrasting with industrialized societies that prioritize economic growth. These cultural frameworks determine how communities value biodiversity, regulate land use, and respond to environmental challenges.
Urbanization and Its Impact on Nature
Urbanization significantly transforms natural landscapes by replacing forests, wetlands, and agricultural areas with concrete and infrastructure, leading to habitat loss and fragmentation. Increased pollution from vehicles, industries, and construction activities degrades air and water quality, threatening biodiversity and ecosystem health. The expansion of cities also alters local climates through the urban heat island effect, disrupting natural processes and increasing energy consumption.
Environmental Ethics in Society
Environmental ethics in society critically examines humanity's moral obligations toward the natural world, emphasizing the intrinsic value of ecosystems beyond human utility. It challenges anthropocentric views by advocating for sustainable practices, biodiversity preservation, and equitable resource distribution to mitigate ecological degradation. This ethical framework influences policy-making, promoting environmental justice and fostering a responsible coexistence between society and nature.
Nature Conservation vs Societal Development
Balancing nature conservation with societal development requires sustainable urban planning that integrates green spaces to preserve biodiversity while accommodating population growth. Implementing eco-friendly technologies and renewable energy sources reduces environmental impact and supports economic progress. Effective environmental policies incentivize conservation efforts without hindering social infrastructure and industrial expansion.
Technology Bridging Nature and Society
Technology serves as a crucial bridge between nature and society by enabling sustainable resource management and environmental monitoring through advanced sensors, satellite imaging, and data analytics. Innovations such as renewable energy systems and smart agriculture integrate natural processes with societal needs, promoting ecological balance and enhancing the quality of life. These technological advancements foster a symbiotic relationship where human development supports conservation efforts and natural ecosystems contribute to technological progress.
Balancing Progress and Sustainability
Balancing progress and sustainability requires integrating innovative technologies with ecological preservation to minimize environmental impact while advancing human development. Sustainable practices emphasize renewable energy, resource efficiency, and biodiversity conservation to ensure long-term planetary health. Aligning societal growth with nature's limits fosters resilience and equitable prosperity for future generations.
Future Trends in Nature-Society Interactions
Emerging technologies such as AI and IoT are driving smarter urban planning and sustainable resource management, reshaping the dynamic between nature and society. Climate change mitigation efforts prioritize integrating natural systems with human infrastructure to enhance resilience and biodiversity. Increasing emphasis on circular economies and green innovation signals a future where society adapts to ecological limits while fostering environmental restoration.
Nature Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com