Suburbanization transforms urban landscapes by shifting populations from city centers to surrounding suburbs, influencing housing demand, transportation patterns, and local economies. This migration impacts community development and environmental sustainability while reshaping social dynamics. Discover how suburbanization affects your living environment and urban growth in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
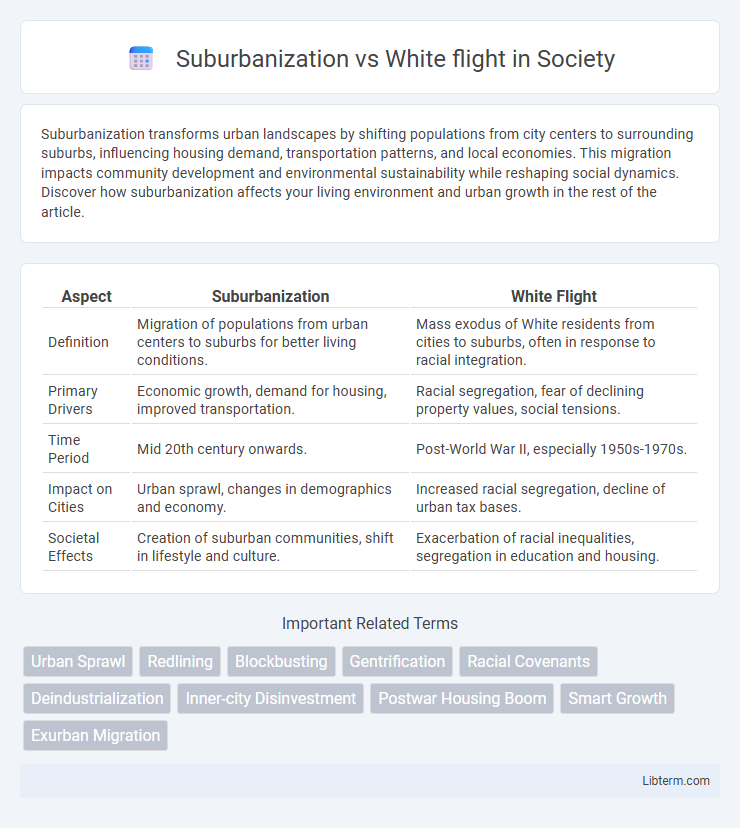
| Aspect | Suburbanization | White Flight |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Migration of populations from urban centers to suburbs for better living conditions. | Mass exodus of White residents from cities to suburbs, often in response to racial integration. |
| Primary Drivers | Economic growth, demand for housing, improved transportation. | Racial segregation, fear of declining property values, social tensions. |
| Time Period | Mid 20th century onwards. | Post-World War II, especially 1950s-1970s. |
| Impact on Cities | Urban sprawl, changes in demographics and economy. | Increased racial segregation, decline of urban tax bases. |
| Societal Effects | Creation of suburban communities, shift in lifestyle and culture. | Exacerbation of racial inequalities, segregation in education and housing. |
Understanding Suburbanization: Definition and Key Drivers
Suburbanization refers to the population shift from central urban areas to the suburbs, driven primarily by factors such as affordable housing, improved transportation infrastructure, and the desire for better living conditions. Key drivers include the expansion of highway systems, economic opportunities in suburban areas, and government policies favoring homeownership and suburban development. This trend shapes demographic patterns and urban sprawl, influencing social, economic, and environmental dynamics.
White Flight: Origins, Meaning, and Social Context
White flight describes the mass migration of White populations from urban centers to suburban areas primarily during the mid-20th century, driven by racial integration, economic factors, and housing policies. Originating in response to desegregation efforts and changing urban demographics, this movement reshaped metropolitan social geography and contributed to increased racial segregation in American cities. Socially, white flight accelerated disparities in public services, education funding, and economic opportunities between inner cities and suburbs, reinforcing systemic inequality.
Historical Overview: Suburbanization and White Flight in the United States
Suburbanization in the United States accelerated post-World War II, driven by economic prosperity, the GI Bill, and highway expansion, facilitating mass migration from urban centers to newly developed suburbs. Concurrently, white flight emerged as white residents moved to suburban areas to escape increasing racial integration and urban decay in cities, significantly altering demographic patterns. This exodus contributed to urban decline, socioeconomic segregation, and long-lasting disparities in housing, education, and municipal resources.
Demographic Shifts: Patterns of Population Movement
Suburbanization refers to the demographic shift where populations move from urban centers to suburban areas, driven by factors such as affordable housing, better schools, and increased living space. White flight specifically describes the mass migration of white residents from racially diversifying cities to predominantly white suburbs, often in response to racial integration and changing socio-economic conditions. These intertwined patterns have reshaped metropolitan demographics, leading to increased suburban growth and urban population declines, influencing housing markets, school demographics, and local economies.
Economic Impacts of Suburbanization Versus White Flight
Suburbanization drives economic growth by increasing demand for housing, retail, and infrastructure development in suburban areas, often expanding the tax base and creating jobs. White flight results in economic decline in urban centers due to reduced investment, lower property values, and shrinking tax revenues, which hampers public services and economic opportunities. The contrasting economic impacts highlight suburbanization as a catalyst for regional economic expansion, while white flight exacerbates urban decay and economic disparity.
Racial Segregation and Urban Transformation
Suburbanization and white flight profoundly shaped racial segregation and urban transformation in American cities during the mid-20th century. White flight accelerated the migration of white populations from racially diverse urban centers to homogeneous suburban areas, intensifying segregation and contributing to economic disinvestment in inner cities. This demographic shift restructured urban landscapes, reinforcing racial divides and influencing patterns of housing, education, and public services access.
Policy Influence: Housing, Zoning, and Federal Legislation
Housing policies such as redlining and restrictive zoning laws historically reinforced white flight by limiting minority access to suburban areas, shaping demographic patterns. Federal legislation like the GI Bill and Federal Housing Administration loans disproportionately favored white families, enabling suburbanization while exacerbating racial segregation. Local zoning ordinances often restricted affordable housing development, maintaining economic and racial homogeneity in suburbs and perpetuating systemic disparities in urban planning.
Urban Decline and the Growth of Suburbs
Suburbanization and white flight significantly contributed to urban decline by accelerating the migration of predominantly white middle-class families from city centers to suburbs, resulting in reduced tax revenues and deteriorating urban infrastructure. This demographic shift led to increased economic segregation and disinvestment in inner-city neighborhoods, amplifying poverty and social challenges. Suburban growth expanded metropolitan regions, promoting residential development and new commercial hubs while reshaping urban landscapes and regional economies.
Contemporary Perspectives: Diversity and Suburban Trends
Contemporary suburbanization reflects increasing racial and ethnic diversity, challenging traditional associations with white flight that linked suburban growth to white populations leaving urban centers. Current suburban trends reveal a more complex pattern, with minority groups significantly contributing to suburban population growth and reshaping cultural landscapes. This shift underscores evolving demographic dynamics and calls for nuanced policy approaches addressing diversity, housing, and transportation in suburban areas.
Future Outlook: Suburbanization, Integration, and Urban Renewal
Suburbanization continues to shape metropolitan growth with increased emphasis on sustainable urban planning and mixed-use developments that promote integration across diverse populations. Future urban renewal projects prioritize affordable housing, green spaces, and enhanced public transportation to counteract segregation trends historically linked to white flight. Emerging policies encourage inclusive community development to balance economic opportunity and social cohesion in expanding suburban areas.
Suburbanization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com