Acceptance fosters emotional well-being by encouraging you to embrace situations without resistance, reducing stress and increasing resilience. It promotes a balanced mindset that allows for growth, self-awareness, and improved relationships. Dive into the rest of the article to explore practical strategies for cultivating acceptance in your daily life.
Table of Comparison
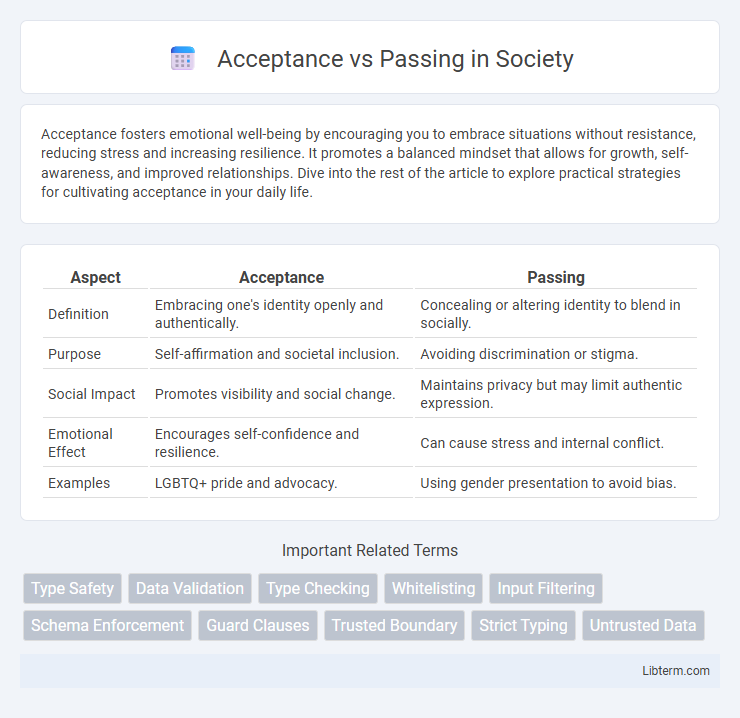
| Aspect | Acceptance | Passing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Embracing one's identity openly and authentically. | Concealing or altering identity to blend in socially. |
| Purpose | Self-affirmation and societal inclusion. | Avoiding discrimination or stigma. |
| Social Impact | Promotes visibility and social change. | Maintains privacy but may limit authentic expression. |
| Emotional Effect | Encourages self-confidence and resilience. | Can cause stress and internal conflict. |
| Examples | LGBTQ+ pride and advocacy. | Using gender presentation to avoid bias. |
Understanding Acceptance vs Passing
Understanding acceptance versus passing involves recognizing acceptance as embracing reality and emotions without resistance, fostering emotional resilience and mental well-being. Passing refers to concealing or suppressing true feelings or identity to conform or avoid judgment, often leading to internal conflict and stress. Differentiating these concepts is crucial for personal growth, as acceptance promotes authenticity, while passing prioritizes social approval.
Definitions and Key Differences
Acceptance refers to the willingness to acknowledge and embrace a situation or reality without resistance, often leading to emotional peace and adaptability. Passing involves presenting oneself as belonging to a different group or identity, typically to gain social acceptance or avoid discrimination, which can involve concealment or deception. The key difference lies in acceptance being an internal process of acknowledgment, while passing is an external act of altering perception to fit societal expectations.
Historical Context and Evolution
Acceptance and Passing have evolved distinctly within social and psychological discourse, originally rooted in identity politics and minority experiences. Acceptance refers to the conscious embrace of one's authentic self by both the individual and society, gaining prominence during Civil Rights movements and LGBTQ+ activism in the 20th century. Passing, historically linked to racial and gender identity, involves presenting oneself as part of a dominant group to avoid discrimination, with critical examination emerging alongside expanding dialogues on authenticity and self-representation.
Societal Perceptions and Expectations
Societal perceptions of acceptance emphasize embracing differences and fostering inclusivity, while passing often reflects pressure to conform to dominant cultural norms to gain social approval. Acceptance promotes genuine self-expression and validation of diverse identities, contrasting with passing, which can lead to internal conflict and erasure of authentic experiences. These differing expectations shape individual identity and influence social dynamics within communities and broader society.
Psychological Impact on Individuals
Acceptance involves acknowledging reality and emotions, leading to reduced stress and improved mental resilience. Passing, or concealing true identity, often results in anxiety, emotional exhaustion, and diminished self-esteem due to internalized conflict. Research in psychology highlights that acceptance fosters healthier coping mechanisms and long-term well-being compared to the psychological strain caused by passing.
Cultural and Identity Considerations
Acceptance involves embracing and integrating cultural identity as a source of strength, fostering self-awareness and community belonging. Passing often requires concealing or altering cultural traits to fit dominant societal norms, which can lead to internal conflict and identity fragmentation. Navigating between acceptance and passing impacts mental health, social relationships, and the preservation of cultural heritage.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Acceptance involves acknowledging a situation or emotion without resistance, as demonstrated in mindfulness-based stress reduction programs that improve mental health outcomes. Passing, commonly observed in social contexts, refers to presenting oneself as part of a different identity group, such as in racial passing during the Harlem Renaissance or gender passing in transgender experiences. Real-world case studies reveal that acceptance strategies foster resilience and emotional well-being, while passing often involves complex identity negotiations with both psychological and social implications.
Challenges and Controversies
Acceptance involves embracing realities or emotions without resistance, yet it faces challenges such as misinterpretation as passivity or weakness, causing internal conflict and societal misunderstanding. Passing, often related to identity concealment or assimilation, raises controversies around authenticity, psychological stress, and erasure of marginalized experiences. Both concepts generate debate about their implications in mental health, social dynamics, and ethical considerations, highlighting the complexity of navigating personal and collective identity.
Strategies for Navigating Acceptance and Passing
Navigating the strategies for acceptance versus passing involves understanding personal identity and societal expectations while prioritizing mental health and authenticity. Embracing acceptance centers on self-compassion and aligning actions with core values, whereas passing requires adaptive techniques to blend into dominant social norms without compromising one's sense of self. Cultivating supportive networks and setting clear boundaries facilitates resilience, enabling individuals to navigate social environments with confidence and integrity.
Looking Forward: Embracing Authenticity
Acceptance involves acknowledging one's true self with compassion and understanding, allowing emotional healing and growth. Passing, often driven by external pressures, may lead to concealment and internal conflict, hindering genuine self-expression. Embracing authenticity fosters empowerment, resilience, and a hopeful outlook toward a future where individuality is celebrated.
Acceptance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com