Cultural societies play a vital role in preserving traditions, promoting arts, and fostering community identity. They create opportunities for cultural exchange, education, and social connection, enriching the lives of members and the broader public. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your involvement can strengthen cultural heritage and community bonds.
Table of Comparison
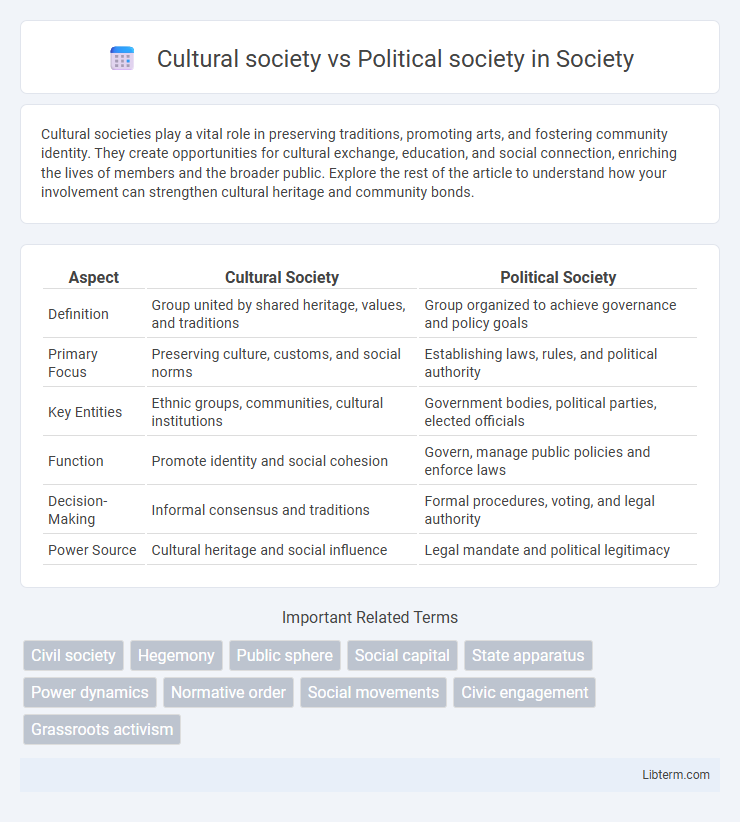
| Aspect | Cultural Society | Political Society |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group united by shared heritage, values, and traditions | Group organized to achieve governance and policy goals |
| Primary Focus | Preserving culture, customs, and social norms | Establishing laws, rules, and political authority |
| Key Entities | Ethnic groups, communities, cultural institutions | Government bodies, political parties, elected officials |
| Function | Promote identity and social cohesion | Govern, manage public policies and enforce laws |
| Decision-Making | Informal consensus and traditions | Formal procedures, voting, and legal authority |
| Power Source | Cultural heritage and social influence | Legal mandate and political legitimacy |
Defining Cultural Society
Cultural society refers to a community unified by shared customs, traditions, language, and artistic expressions that shape its collective identity and social values. Unlike political society, which centers on governance, laws, and institutional authority, cultural society emphasizes social cohesion through common heritage and cultural norms. This collective cultural framework influences individuals' beliefs, behaviors, and social interactions within the group.
Understanding Political Society
Political society is a structured organization where power dynamics and governance mechanisms regulate social order through laws, institutions, and authority. Unlike cultural society, which centers on shared beliefs, traditions, and values, political society exercises formal control to maintain stability and enforce collective decisions. Understanding political society involves analyzing the role of governments, legal systems, and political actors in shaping public policies and societal norms.
Historical Roots of Cultural and Political Societies
Cultural societies trace their roots to shared traditions, languages, customs, and collective identities that predate formal governance structures, often emerging from kinship and communal ties in ancient civilizations. Political societies, by contrast, developed through the establishment of organized authority and legal institutions aimed at maintaining order, enacting laws, and exercising sovereignty, as observed in early city-states and empires like Mesopotamia and Ancient Greece. The historical evolution of these societies reveals how cultural cohesion provided the foundation for political systems, enabling structured governance and social control.
Key Characteristics: Culture vs Politics
Cultural society emphasizes shared beliefs, traditions, values, and social practices that create a collective identity and cohesion among members. Political society focuses on organized governance structures, power distribution, law enforcement, and decision-making processes to regulate behavior and maintain order. While culture shapes social norms and informal rules, politics defines formal institutions and authoritative control mechanisms.
The Role of Identity in Cultural Society
The role of identity in cultural society centers on shared traditions, customs, language, and values that bind individuals, fostering social cohesion and a collective sense of belonging. Cultural societies prioritize preserving heritage and collective memory, influencing social norms and group behavior more than political institutions do. Unlike political society, which relies on governance structures and laws, cultural society derives its authority and stability from the strength of identity and communal bonds.
Power Structures in Political Society
Power structures in political society are characterized by formalized institutions that regulate authority through laws, governance, and organized hierarchies, often concentrating power in state apparatuses such as governments, courts, and military forces. Unlike cultural societies that rely on shared norms, traditions, and communal values for social cohesion, political societies enforce compliance via codified rules and sanctioned authority figures. The legitimacy of power in political societies is maintained through legal-rational frameworks and often involves mechanisms of surveillance, coercion, and policy implementation to preserve order and control.
Interactions Between Cultural and Political Societies
Interactions between cultural and political societies shape societal norms and governance structures by influencing identity, values, and power dynamics. Cultural societies transmit traditions, beliefs, and social behaviors that political societies codify into policies and laws, creating a feedback loop that affects national unity and political legitimacy. Conflicts and cooperation arise as cultural diversity challenges political authority, while political decisions can reinforce or suppress cultural expressions.
Societal Change: Cultural Movements vs Political Movements
Cultural movements drive societal change by reshaping beliefs, values, and social norms through art, religion, and education, fostering a gradual transformation in collective identity. Political movements focus on altering governance structures, policies, and power relations, often resulting in legislative reforms and shifts in political authority. Both types of movements intersect but differ in mechanisms, with cultural movements influencing long-term social consciousness and political movements targeting immediate institutional change.
Case Studies: Global Perspectives on Society Types
Case studies from India and Nigeria illustrate the distinction between cultural and political societies, where cultural societies prioritize shared traditions and rituals fostering social cohesion, while political societies emphasize governance structures and authority enforcement. In Papua New Guinea, cultural societies often organize around kinship and clan systems, contrasting with political societies that centralize power through formal institutions. Examining these global perspectives reveals how societies balance cultural identity and political control to maintain social order and collective well-being.
Building Cohesion Between Culture and Politics
Cultural society emphasizes shared values, traditions, and collective identity that foster social cohesion through common symbols and practices, while political society centers on governance structures, laws, and civic engagement that regulate power and public order. Building cohesion between culture and politics requires integrating cultural narratives into political discourse, ensuring policies reflect community values, and promoting inclusive participation that respects diverse cultural identities. This synergy strengthens social bonds and legitimizes political authority by aligning governance with the cultural fabric of society.
Cultural society Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com