Bureaucratic administration relies on established rules and hierarchical structures to ensure efficiency and consistency in organizational operations. This approach prioritizes clear roles, formal procedures, and standardized processes to reduce ambiguity and enhance accountability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how bureaucratic administration impacts your organization's success and decision-making.
Table of Comparison
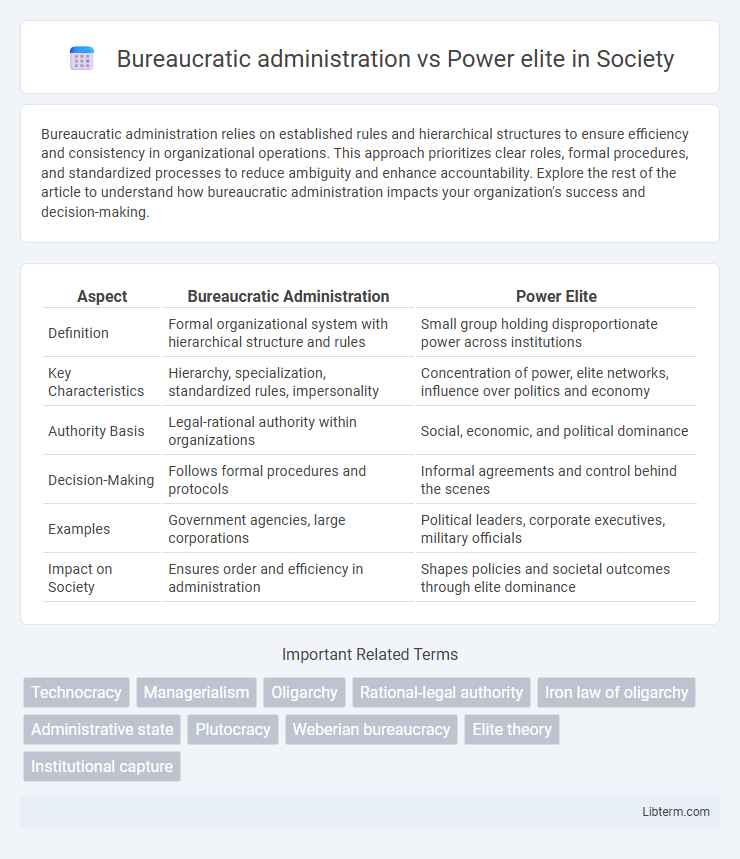
| Aspect | Bureaucratic Administration | Power Elite |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal organizational system with hierarchical structure and rules | Small group holding disproportionate power across institutions |
| Key Characteristics | Hierarchy, specialization, standardized rules, impersonality | Concentration of power, elite networks, influence over politics and economy |
| Authority Basis | Legal-rational authority within organizations | Social, economic, and political dominance |
| Decision-Making | Follows formal procedures and protocols | Informal agreements and control behind the scenes |
| Examples | Government agencies, large corporations | Political leaders, corporate executives, military officials |
| Impact on Society | Ensures order and efficiency in administration | Shapes policies and societal outcomes through elite dominance |
Understanding Bureaucratic Administration: Definition and Features
Bureaucratic administration is characterized by a structured hierarchy, formal rules, and specialized roles designed to achieve efficiency and consistency in organizational operations. Max Weber's theory highlights features such as a clear division of labor, impersonality, and merit-based promotion to ensure rational decision-making. This approach contrasts with the power elite model, which emphasizes centralized control by a small group rather than formal institutional processes.
The Power Elite: Who They Are and How They Operate
The Power Elite, as analyzed by C. Wright Mills, consists of a small group of military, corporate, and political leaders who dominate decision-making processes in modern society. Unlike bureaucratic administration, which relies on hierarchical rules and procedures, the Power Elite operates through informal networks and personal connections to shape policies and maintain their influence. This concentration of power challenges democratic norms by centralizing control in an interconnected elite rather than dispersed bureaucratic institutions.
Historical Evolution: Bureaucracy and Elite Rule
The historical evolution of bureaucratic administration traces back to the rise of complex states in ancient Mesopotamia and China, where structured hierarchies and codified rules enabled efficient governance across vast territories. In contrast, the power elite theory, articulated by sociologists like C. Wright Mills in the mid-20th century, highlights concentrated control by a small group of military, corporate, and political leaders dominating decision-making in modern societies. Over time, bureaucratic administration institutionalized authority through formal procedures, while power elite dynamics emphasize informal networks and elite cohesion shaping societal power structures.
Key Differences between Bureaucratic Administration and Power Elite
Bureaucratic administration is characterized by hierarchical structures, formal rules, and specialized roles designed to ensure efficiency and predictability in organizational operations. In contrast, the power elite refers to a small group of individuals who hold disproportionate influence over major political, economic, and social institutions, often operating beyond formal institutional boundaries. Key differences lie in bureaucratic administration's emphasis on procedural authority and impersonality, while the power elite relies on personal networks, concentration of power, and informal decision-making processes.
Decision-Making Processes in Bureaucracies vs. Elite Circles
Decision-making processes in bureaucratic administration prioritize formalized rules, hierarchical structures, and standardized procedures to ensure consistency and predictability across organizations. In contrast, power elite circles rely on informal networks, personal influence, and centralized authority to rapidly shape policies and decisions based on strategic interests. Bureaucracies emphasize collective input and accountability, while elite decision-making centers on exclusivity and concentrated control.
Influence on Policy: Administrative Procedures vs. Elite Interests
Bureaucratic administration influences policy through formalized administrative procedures, emphasizing rule-based decision-making, regulatory compliance, and systematic implementation. Power elite shape policy primarily by leveraging their socio-economic status, networks, and concentrated control over key institutions, aligning outcomes with elite interests. The contrast lies in bureaucracy's procedural legitimacy versus the elite's strategic manipulation of power to bypass or redirect administrative processes.
Public Accountability: Bureaucratic Transparency vs. Elite Secrecy
Bureaucratic administration emphasizes public accountability through structured transparency mechanisms such as open records, formal procedures, and oversight committees that ensure government actions are accessible to citizens. In contrast, the power elite often operate with elite secrecy, where decision-making occurs behind closed doors, limiting public scrutiny and concentrating influence within a closed network of political, corporate, and military leaders. This fundamental difference affects the degree of democratic control, with bureaucratic transparency fostering citizen participation and elite secrecy undermining public trust and accountability.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Bureaucratic and Elite Power
The case of the U.S. federal bureaucracy during the New Deal illustrates bureaucratic administration's role in implementing complex social programs through hierarchical structures and formal rules. By contrast, C. Wright Mills' analysis of the 1950s American power elite highlights how military leaders, corporate executives, and political officials concentrate power beyond bureaucratic constraints. In modern contexts, the Pentagon Papers reveal conflicts between bureaucratic agencies and elite decision-makers, demonstrating the tension between administrative procedures and elite influence over national policy.
Criticisms and Controversies: Challenges Facing Both Systems
Bureaucratic administration faces criticisms for inefficiency, rigidity, and excessive red tape that hinder innovation and responsiveness, while power elite theory draws controversy for its concentration of political, economic, and military power in the hands of a few, potentially undermining democratic processes. Both systems are challenged by issues of accountability, transparency, and the risk of perpetuating inequality through hierarchical structures and elite dominance. These controversies emphasize the need for reforms that balance organizational effectiveness with equitable power distribution and citizen participation.
Future Trends: Toward Inclusive Governance or Elite Consolidation?
Future trends in bureaucratic administration indicate a gradual shift toward digitization and transparency, fostering more inclusive governance by enhancing public participation and accountability. However, the power elite's entrenched influence continues to shape policy decisions, potentially consolidating authority within a narrow elite group. The balance between technology-driven inclusivity and elite dominance will determine the evolution of governance frameworks globally.
Bureaucratic administration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com