Interpersonal trust forms the foundation of strong relationships by fostering open communication and mutual understanding. Building this trust requires consistent honesty, reliability, and empathy to create a safe environment where individuals feel valued and respected. Discover effective strategies to enhance your interpersonal trust in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
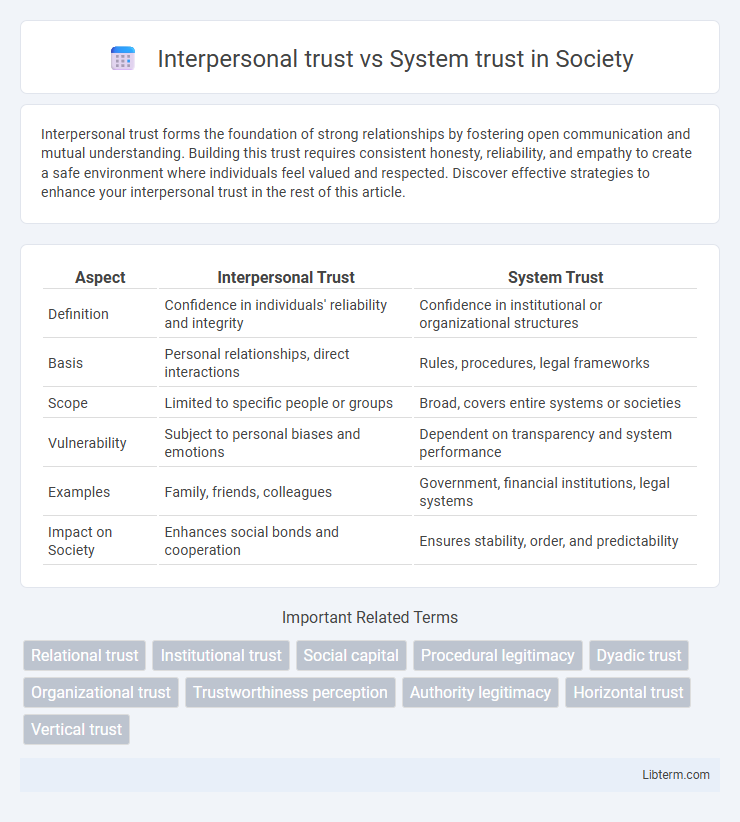
| Aspect | Interpersonal Trust | System Trust |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Confidence in individuals' reliability and integrity | Confidence in institutional or organizational structures |
| Basis | Personal relationships, direct interactions | Rules, procedures, legal frameworks |
| Scope | Limited to specific people or groups | Broad, covers entire systems or societies |
| Vulnerability | Subject to personal biases and emotions | Dependent on transparency and system performance |
| Examples | Family, friends, colleagues | Government, financial institutions, legal systems |
| Impact on Society | Enhances social bonds and cooperation | Ensures stability, order, and predictability |
Defining Interpersonal Trust
Interpersonal trust refers to the confidence one person places in another individual's reliability, honesty, and integrity within personal or professional relationships. It is built through consistent interactions, emotional connections, and demonstrated competence. Unlike system trust, which relies on institutional structures and processes, interpersonal trust hinges on direct human experience and social bonding.
What is System Trust?
System trust refers to the confidence individuals place in institutional structures, technologies, or formal procedures to function reliably and fairly without personal interaction. It is built on the perceived transparency, consistency, and accountability of systems such as legal frameworks, digital platforms, or organizational processes. Unlike interpersonal trust, which depends on personal relationships, system trust is sustained through established rules and verifiable performance metrics.
Key Differences Between Interpersonal and System Trust
Interpersonal trust involves confidence in the intentions and reliability of specific individuals based on personal interactions, while system trust relies on the belief in institutional structures, technology, or protocols to function correctly without direct human involvement. Key differences include the source of trust--personal relationships versus abstract systems--and the scope, where interpersonal trust is context-specific and system trust encompasses broader organizational or technological environments. Interpersonal trust often requires emotional connection and reciprocity, whereas system trust depends on transparency, consistency, and perceived competence of the system.
The Role of Personal Relationships in Trust-Building
Interpersonal trust hinges on direct, shared experiences and emotional connections between individuals, fostering reliability and openness through personal interactions. System trust, by contrast, depends on confidence in institutional structures, protocols, and technology designed to deliver consistent outcomes without personal involvement. Personal relationships play a critical role in trust-building by enhancing transparency, empathy, and accountability, which are often missing in system trust, thereby creating stronger, more resilient networks of collaboration.
Institutions and the Foundation of System Trust
Institutions play a critical role in building system trust by establishing reliable rules, transparency, and accountability that foster collective confidence beyond personal relationships. The foundation of system trust relies on the consistent performance and legitimacy of legal frameworks, governance structures, and public services that ensure predictable outcomes. Unlike interpersonal trust, which depends on direct interactions, system trust emerges from the perceived stability and fairness of institutional mechanisms supporting societal cooperation.
Factors That Influence Interpersonal Trust
Interpersonal trust is influenced by factors such as communication clarity, perceived integrity, and past shared experiences that build reliability between individuals. Emotional intelligence and empathy enhance mutual understanding, fostering deeper trust at a personal level. Consistency in behavior and transparency also play critical roles in strengthening interpersonal trust, distinguishing it from system trust which relies more on institutional structures and protocols.
Elements Shaping System Trust
Elements shaping system trust include perceived reliability, transparency, and security of the system's processes, fostering confidence in its consistent performance. Institutional mechanisms such as regulations, accountability, and fairness play critical roles in reinforcing system trust by ensuring equitable treatment and reducing uncertainty. User experience, including ease of use and responsiveness, further enhances trust by demonstrating the system's capability to meet expectations effectively.
The Impact of Technology on Trust Dynamics
Technology shapes interpersonal trust by enabling instant communication and enhanced transparency, accelerating relationship-building and fostering reliability among individuals. System trust is influenced by technological infrastructures such as blockchain and AI algorithms, which automate processes and ensure data integrity, increasing confidence in digital platforms. The integration of advanced cybersecurity measures further reinforces both interpersonal and system trust by protecting sensitive information and mitigating risks in virtual interactions.
Strengthening Interpersonal and System Trust
Strengthening interpersonal trust requires consistent communication, transparency, and demonstrating reliability in personal interactions. System trust is reinforced through robust policies, secure technologies, and accountability mechanisms that ensure fairness and integrity. Combining these approaches enhances overall confidence in both human relationships and institutional structures.
Interpersonal Trust vs System Trust: Real-World Examples
Interpersonal trust thrives in close relationships such as friendships or workplace teams where reliability and emotional support are critical, exemplified by colleagues relying on each other to meet deadlines. System trust operates in structured environments like banking or public transportation, where individuals depend on protocols and institutional safeguards, such as using ATMs or trusting airline safety regulations. Real-world examples highlight interpersonal trust through mentorship programs fostering collaboration, while system trust is evident in e-commerce platforms ensuring secure transactions.
Interpersonal trust Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com