Isolation can significantly impact mental health by increasing feelings of loneliness and stress. Understanding the causes and effects of isolation helps in developing strategies to maintain social connections and emotional well-being. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective ways to combat isolation and improve your overall health.
Table of Comparison
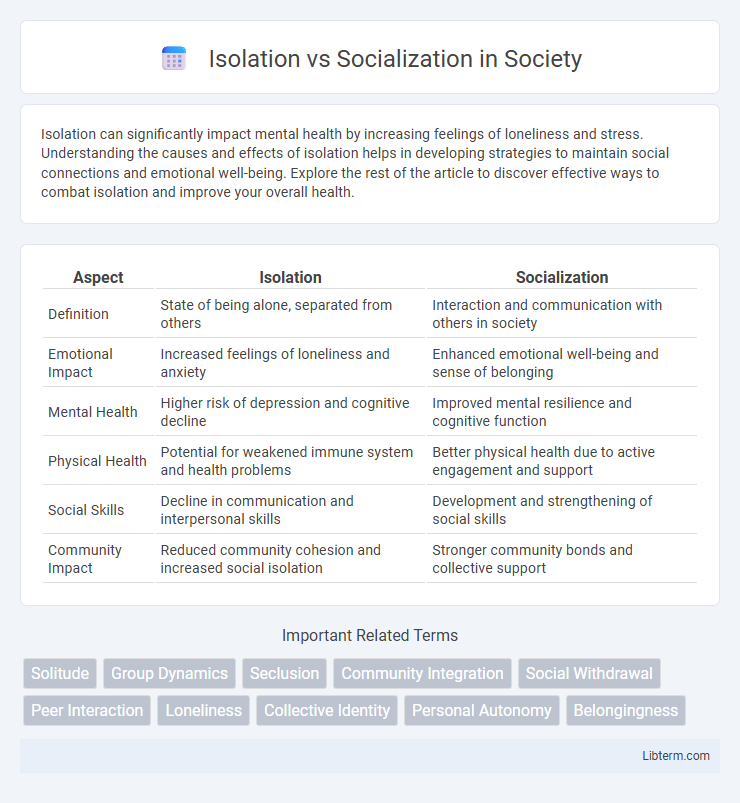
| Aspect | Isolation | Socialization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State of being alone, separated from others | Interaction and communication with others in society |
| Emotional Impact | Increased feelings of loneliness and anxiety | Enhanced emotional well-being and sense of belonging |
| Mental Health | Higher risk of depression and cognitive decline | Improved mental resilience and cognitive function |
| Physical Health | Potential for weakened immune system and health problems | Better physical health due to active engagement and support |
| Social Skills | Decline in communication and interpersonal skills | Development and strengthening of social skills |
| Community Impact | Reduced community cohesion and increased social isolation | Stronger community bonds and collective support |
Understanding Isolation and Socialization
Isolation refers to the state of being separated from others, leading to limited social interactions and potential feelings of loneliness, whereas socialization involves engaging with people to build relationships and develop social skills crucial for mental and emotional well-being. Understanding isolation includes recognizing its causes such as physical barriers, mental health issues, or social anxiety, while socialization emphasizes the importance of community, communication, and shared experiences for personal growth. Both concepts significantly impact human behavior, influencing emotional resilience and overall quality of life.
Psychological Impact of Isolation
Prolonged social isolation can lead to increased risks of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline, significantly impacting mental health. Lack of social interaction disrupts emotional regulation and exacerbates feelings of loneliness, which are linked to heightened stress hormone levels and impaired immune function. Studies reveal that individuals with limited social connections face higher morbidity and mortality rates compared to those with active social lives.
Benefits of Socialization on Mental Health
Socialization enhances mental health by reducing feelings of loneliness and depression through meaningful interpersonal connections. Engaging in social activities stimulates cognitive functions and promotes emotional resilience against stress. Support networks built through socialization provide essential encouragement and a sense of belonging that improves overall psychological well-being.
Factors Leading to Social Withdrawal
Factors leading to social withdrawal often include chronic stress, anxiety disorders, and traumatic experiences that disrupt social confidence. Biological elements such as neurochemical imbalances and genetic predispositions may also contribute to isolation behaviors. Environmental influences like prolonged loneliness, lack of supportive relationships, and negative social interactions further exacerbate withdrawal tendencies.
The Role of Technology in Social Interaction
Technology transforms social interaction by enabling remote communication through platforms like Zoom, social media, and messaging apps, reducing physical isolation. Virtual environments facilitate connections across geographic boundaries, supporting socialization for those with mobility limitations or social anxiety. However, excessive reliance on digital communication can sometimes diminish face-to-face interaction quality, impacting emotional connection and social skills development.
Socialization Strategies for Introverts
Socialization strategies for introverts emphasize quality over quantity, encouraging meaningful one-on-one interactions or small group settings that reduce social fatigue. Structured activities such as interest-based clubs or online communities provide controlled environments where introverts can engage comfortably while building connections. Setting clear personal boundaries and scheduling downtime afterward helps introverts recharge and maintain a healthy social balance.
Balancing Alone Time and Social Engagement
Balancing alone time and social engagement is essential for mental health and emotional well-being. Spending sufficient time in isolation allows for self-reflection, creativity, and stress reduction, while meaningful social interactions foster connection, support, and cognitive stimulation. Effective strategies include setting boundaries, scheduling regular social activities, and tuning into personal needs to maintain a healthy balance between solitude and socialization.
Long-term Effects of Chronic Isolation
Chronic isolation leads to significant long-term effects including cognitive decline, increased risk of mental health disorders like depression and anxiety, and impaired immune function. Studies show that prolonged social deprivation can accelerate neurodegeneration and elevate stress hormones, contributing to cardiovascular problems. Persistent isolation disrupts brain plasticity and reduces lifespan, highlighting the critical importance of social connections for physical and psychological well-being.
Building Healthy Social Connections
Building healthy social connections is essential for mental and emotional well-being, fostering a sense of belonging and support. Isolation, while sometimes necessary for self-reflection, can lead to loneliness and increased stress levels if prolonged. Engaging in meaningful face-to-face interactions and participating in community activities strengthen social bonds and improve overall life satisfaction.
Navigating Isolation in the Digital Age
Navigating isolation in the digital age requires understanding the impact of prolonged digital interactions on mental health and social skills. Virtual connections through social media and online platforms can mitigate feelings of loneliness but may also contribute to superficial relationships and increased anxiety. Developing healthy digital habits and balancing online engagement with offline experiences are essential for maintaining emotional well-being and authentic socialization.
Isolation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com