Multiculturalism fosters a society where diverse cultural identities coexist, enriching social experiences and promoting mutual respect. Embracing multicultural values enhances Your communication skills and broadens perspectives in personal and professional settings. Explore the article to discover how multiculturalism shapes inclusive communities and benefits everyone.
Table of Comparison
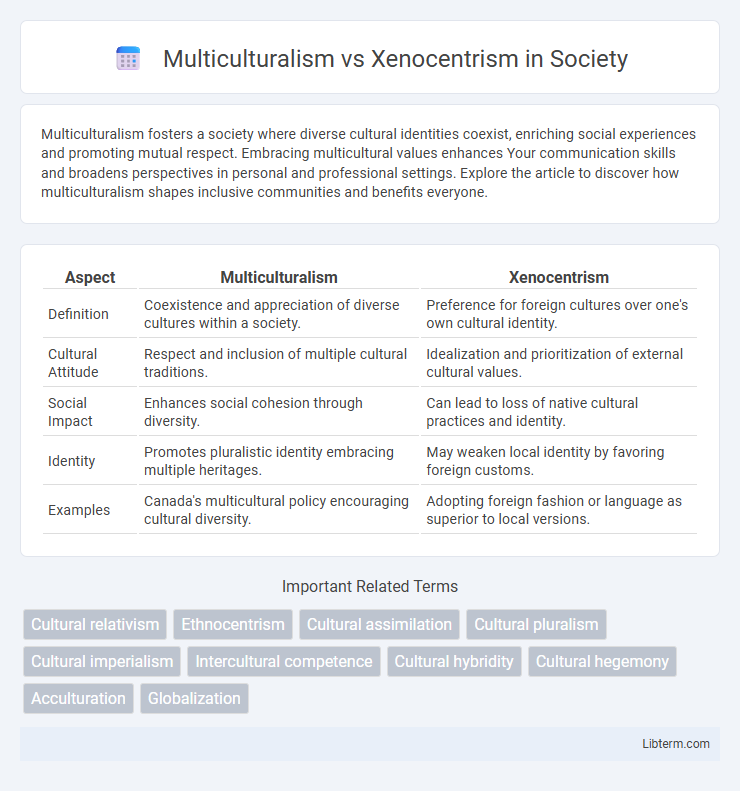
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Xenocentrism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence and appreciation of diverse cultures within a society. | Preference for foreign cultures over one's own cultural identity. |
| Cultural Attitude | Respect and inclusion of multiple cultural traditions. | Idealization and prioritization of external cultural values. |
| Social Impact | Enhances social cohesion through diversity. | Can lead to loss of native cultural practices and identity. |
| Identity | Promotes pluralistic identity embracing multiple heritages. | May weaken local identity by favoring foreign customs. |
| Examples | Canada's multicultural policy encouraging cultural diversity. | Adopting foreign fashion or language as superior to local versions. |
Understanding Multiculturalism: Embracing Diversity
Understanding multiculturalism involves recognizing and valuing the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, promoting inclusivity and mutual respect. Embracing diversity enhances social cohesion by encouraging intercultural dialogue and reducing prejudices. This approach contrasts with xenocentrism, which idealizes foreign cultures over one's own, potentially undermining local cultural appreciation and social harmony.
Defining Xenocentrism: Favoring the Foreign
Xenocentrism refers to a cultural bias where individuals or groups perceive foreign cultures as superior to their own, often leading to preferential attitudes toward foreign products, customs, or lifestyles. This phenomenon contrasts with multiculturalism, which embraces and values diverse cultures within a society without necessarily idealizing foreign influences. Understanding xenocentrism is crucial in analyzing consumer behavior, cultural identity, and social dynamics in globalized contexts.
Historical Context of Multiculturalism
Multiculturalism emerged as a political and social response during the late 20th century, particularly in Western democracies grappling with post-colonial migration and civil rights movements. This policy framework promotes the recognition and celebration of diverse cultural identities within a unified society, contrasting with xenocentrism, which idealizes foreign cultures often at the expense of one's own. Historical milestones such as the Canadian Multiculturalism Act of 1988 and the UK's Race Relations Act of 1976 highlight institutional commitments to fostering inclusive, culturally pluralistic societies.
Roots and Drivers of Xenocentrism
Xenocentrism arises from a perceived inferiority of one's own culture, often fueled by globalization, media influence, and historical experiences of colonization or economic dependency. Social and psychological drivers include the desire for prestige, status seeking, and the belief that foreign cultures possess superior qualities or lifestyles. This contrasts with multiculturalism's emphasis on valuing diversity and fostering mutual respect among cultural identities within a society.
Social Impacts of Multiculturalism in Modern Societies
Multiculturalism in modern societies fosters social cohesion by promoting cultural diversity, enhancing mutual respect, and encouraging inclusive policies that support minority rights. It contributes to economic innovation through diverse perspectives and increased global connectivity, while reducing social tensions by challenging xenophobic attitudes. This contrasts with xenocentrism, which often leads to idealizing foreign cultures at the expense of local traditions, potentially causing identity conflicts and social fragmentation.
The Consequences of Xenocentric Attitudes
Xenocentric attitudes often lead to diminished national pride and cultural identity, fostering a preference for foreign customs and products over domestic ones. This mindset can undermine social cohesion by creating divisions between those who favor external influences and those who value local traditions. Economic consequences may include reduced support for local industries and cultural erosion as global trends overshadow indigenous heritage.
Multiculturalism and National Identity
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a nation, strengthening national identity by fostering inclusivity and social cohesion. It encourages recognition and respect for different ethnic, linguistic, and religious groups, which enhances collective patriotism while valuing pluralism. National identity under multiculturalism evolves through shared democratic values and mutual cultural exchange, rather than a singular ethnic or cultural norm.
Xenocentrism vs. Ethnocentrism: Key Differences
Xenocentrism values foreign cultures over one's own, while ethnocentrism prioritizes and often glorifies a person's native culture. The key difference lies in perspective: xenocentrism idealizes external cultural traits, driving preference for foreign products, customs, or values, whereas ethnocentrism judges other cultures relative to one's own cultural standards, frequently leading to cultural superiority beliefs. These opposing mindsets influence social behavior, consumer choices, and intercultural relations significantly.
Challenges and Criticisms of Multicultural Policies
Multicultural policies often face criticism for fostering social fragmentation and weakening national identity, as critics argue they encourage group isolation rather than integration. These policies can struggle with balancing cultural preservation and promoting shared values, leading to tensions between majority and minority communities. Challenges also include potential economic inequalities and political disputes arising from perceived favoritism or neglect of certain cultural groups.
Promoting Balance: Towards Inclusive Global Perspectives
Multiculturalism fosters inclusive global perspectives by valuing diverse cultural identities and encouraging mutual respect and understanding across societies. Xenocentrism, characterized by a preference for foreign cultures over one's own, can undermine cultural self-esteem and social cohesion when unchecked. Promoting balance involves integrating multicultural awareness with critical appreciation of all cultures, enabling individuals and communities to embrace diversity without diminishing their cultural roots.
Multiculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com