Knockout is a powerful JavaScript library designed for creating rich, responsive web applications using the MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) pattern. It simplifies dynamic UI updates through declarative bindings between your data and HTML elements, making your web interfaces faster and easier to maintain. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Knockout can transform Your web development experience.
Table of Comparison
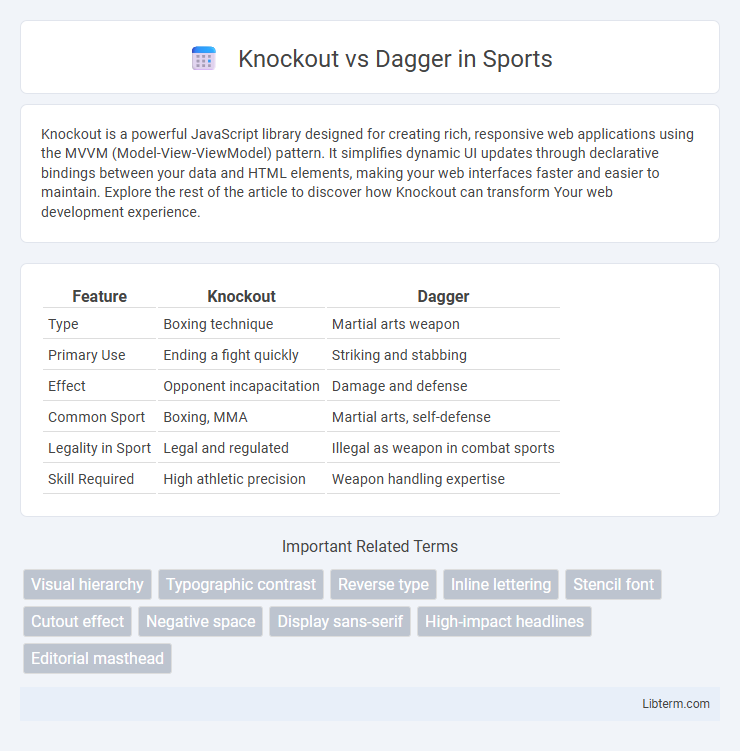
| Feature | Knockout | Dagger |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Boxing technique | Martial arts weapon |
| Primary Use | Ending a fight quickly | Striking and stabbing |
| Effect | Opponent incapacitation | Damage and defense |
| Common Sport | Boxing, MMA | Martial arts, self-defense |
| Legality in Sport | Legal and regulated | Illegal as weapon in combat sports |
| Skill Required | High athletic precision | Weapon handling expertise |
Introduction to Knockout and Dagger
Knockout is a JavaScript library that simplifies creating rich, responsive user interfaces using the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) pattern, enabling automatic UI updates through declarative bindings and observables. Dagger is a fully static, compile-time dependency injection framework for Java and Android, designed to generate code that efficiently provides dependencies and ensures type safety without runtime reflection. Both tools streamline development by addressing different challenges: Knockout enhances UI responsiveness, while Dagger manages complex dependency graphs.
Overview of Knockout
Knockout is a JavaScript library that simplifies dynamic UI development by implementing the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) pattern using declarative bindings and automatic UI updates. It enables developers to create rich, responsive web applications with minimal boilerplate code by syncing the UI with underlying data models in real time. Knockout's compact size, ease of integration, and compatibility with existing frameworks make it a popular choice for managing complex user interfaces efficiently.
Overview of Dagger
Dagger is a fully static, compile-time dependency injection framework for Java and Android, designed to generate code that is efficient and easy to debug. Unlike Knockout, which is primarily a JavaScript library for UI data binding, Dagger focuses on providing type-safe, performant injection without the runtime overhead. Its annotation-driven approach integrates seamlessly with popular development tools, enhancing modularity and testability in complex applications.
Core Features Comparison
Knockout specializes in declarative bindings and automatic UI updates through its observable pattern, making it ideal for simple data-driven interfaces. Dagger offers a robust compile-time dependency injection framework that ensures type safety and efficient object graph management in large-scale Java and Android applications. Both tools enhance code maintainability, but Knockout focuses on UI binding while Dagger emphasizes dependency injection and modular architecture.
Data Binding: Knockout vs Dagger
Knockout excels in data binding by providing a declarative syntax that automatically updates the UI when the underlying data model changes, leveraging observables for real-time synchronization. Dagger, primarily a dependency injection framework, does not offer native data binding capabilities but integrates well with third-party libraries like Android Data Binding or Jetpack Compose to manage UI updates. For projects emphasizing seamless, automatic two-way data binding, Knockout presents a more direct solution, whereas Dagger focuses on code modularity and scalability without inherent data binding features.
Dependency Injection: Dagger’s Advantage
Dagger offers compile-time dependency injection with generated code, resulting in faster runtime performance and minimal reflection usage compared to Knockout's manual or runtime-based approaches. Its static analysis detects errors during compilation, enhancing code safety and maintainability. The strong typing and scaffolding in Dagger reduce boilerplate and improve scalability in complex Android or Java projects.
Performance and Scalability
Knockout offers a lightweight, client-side JavaScript framework ideal for managing dynamic UI bindings with minimal overhead, enhancing performance for single-page applications. Dagger, as a compile-time dependency injection framework for Java and Android, significantly improves scalability by generating optimized code that reduces runtime reflection and startup latency. In large-scale projects, Dagger's compile-time validation and efficient object graph management enable better maintainability and faster load times compared to Knockout's primarily UI-focused features.
Use Cases and Suitability
Knockout excels in data-binding and UI development for dynamic web applications, making it ideal for projects requiring seamless synchronization between the model and the view. Dagger is suited for dependency injection in Android and Java applications, enhancing modularity, testability, and maintainability by automating object creation and dependency management. Choosing Knockout is best for front-end data-driven scenarios, while Dagger fits complex backend or Android architectures demanding robust dependency handling.
Community Support and Documentation
KnockoutJS benefits from a mature and active open-source community, offering extensive documentation, tutorials, and forums that facilitate quick troubleshooting and knowledge sharing. Dagger also has strong community backing, particularly in the Android development ecosystem, with comprehensive official documentation and a growing number of third-party resources, including blogs and GitHub repositories. While both frameworks provide solid support, Knockout's longer presence results in a broader range of community-driven content, whereas Dagger's documentation excels in integration specifics and advanced dependency injection patterns.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Knockout and Dagger
Choosing between Knockout and Dagger depends on the specific application requirements and developer preferences. Knockout excels in data-binding and UI responsiveness using the MVVM pattern, making it ideal for front-end web development. Dagger offers a robust, compile-time dependency injection framework suited for large-scale Java applications, significantly improving code scalability and maintainability.
Knockout Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com