Trap defense is a strategic technique used in various games and combat sports to counter an opponent's aggressive moves by luring them into a vulnerable position. Mastering this tactic enhances your ability to anticipate and neutralize attacks effectively, ensuring a stronger defensive stance. Dive into the rest of the article to explore essential tips and techniques for perfecting your trap defense.
Table of Comparison
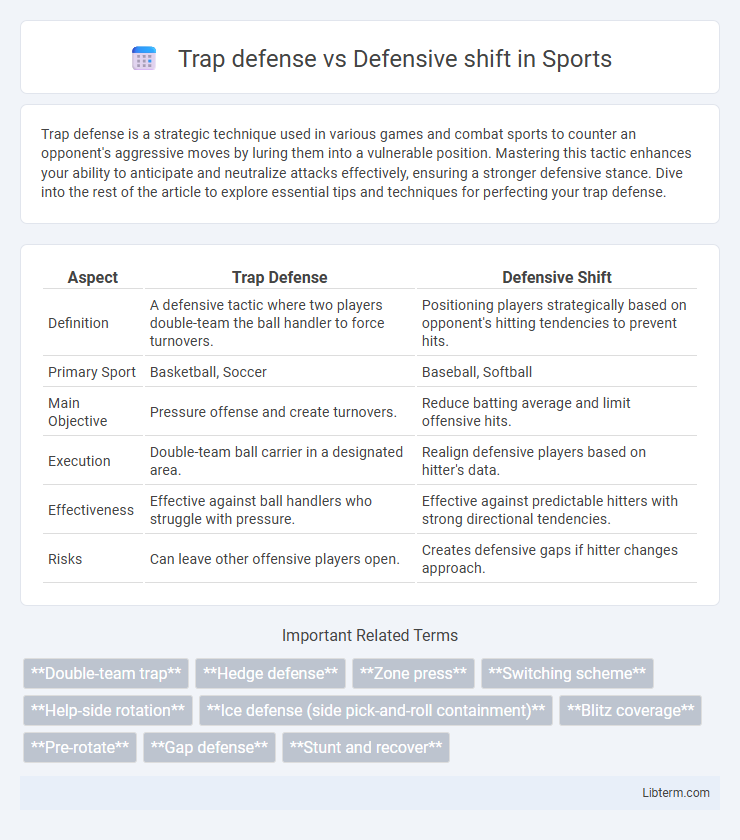
| Aspect | Trap Defense | Defensive Shift |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A defensive tactic where two players double-team the ball handler to force turnovers. | Positioning players strategically based on opponent's hitting tendencies to prevent hits. |
| Primary Sport | Basketball, Soccer | Baseball, Softball |
| Main Objective | Pressure offense and create turnovers. | Reduce batting average and limit offensive hits. |
| Execution | Double-team ball carrier in a designated area. | Realign defensive players based on hitter's data. |
| Effectiveness | Effective against ball handlers who struggle with pressure. | Effective against predictable hitters with strong directional tendencies. |
| Risks | Can leave other offensive players open. | Creates defensive gaps if hitter changes approach. |
Introduction to Trap Defense and Defensive Shift
Trap defense involves positioning defenders to create pressure traps that force turnovers or disrupt offensive plays, especially effective in basketball and football. Defensive shift refers to the strategic realignment of defenders to counter specific offensive formations or strengths, enhancing coverage and adaptability. Both techniques are crucial in sports tactics, with trap defense emphasizing aggressive containment and defensive shift focusing on flexible positioning.
Key Differences Between Trap Defense and Defensive Shift
Trap defense involves positioning defenders to double-team the ball handler and force turnovers by trapping them in specific court areas, emphasizing aggressive ball pressure. Defensive shift adjusts the overall defensive alignment based on opponent tendencies, often repositioning defenders to cover shooters or exploit offensive weaknesses without necessarily applying immediate pressure. The key difference lies in trap defense's focus on active engagement and trapping the ball carrier, whereas defensive shift is a strategic realignment of player positions to counter offensive threats.
Historical Evolution of Both Defensive Strategies
The trap defense originated in the 1980s as a tactical scheme designed to force turnovers by aggressively pressuring ball handlers and cutting off passing lanes, becoming popularized in basketball and hockey. Defensive shift evolved later, gaining prominence in baseball during the early 21st century as teams strategically positioned infielders based on batters' hitting tendencies to prevent hits to specific areas. Over time, both strategies have become essential in their respective sports, with trap defense emphasizing immediate ball control disruption and defensive shift focusing on predictive positioning to maximize defensive efficiency.
Core Principles of Trap Defense
Trap defense centers on cutting off passing lanes and applying intense pressure on the ball handler, forcing turnovers through coordinated double-teams. This strategy emphasizes spatial control by positioning defenders strategically to funnel opponents into crowded areas, disrupting offensive rhythm. Unlike broader defensive shifts, trap defense relies on anticipation, timing, and team communication to execute precise traps at key points on the court.
Core Principles of Defensive Shift
Core principles of the defensive shift emphasize repositioning infielders to optimize coverage based on batter tendencies and spray charts, enhancing likelihood of converting batted balls into outs. The shift relies heavily on data analytics to anticipate hitter behavior, maximizing defensive efficiency by aligning players where balls are most frequently hit. This strategy contrasts with trap defense, which focuses on containing hits within a specific zone, by adapting dynamically to situational and batter-specific data.
Situational Effectiveness: When to Use Each Strategy
Trap defense is most effective in fast-break situations and against teams that rely heavily on perimeter shooters, as it forces turnovers and disrupts ball movement early. Defensive shifts excel in late-game scenarios or critical possessions where opponents have predictable offensive sets, allowing for targeted pressure on key players and exploiting offensive weaknesses. Coaches should analyze the opponent's tendencies and game context to decide between the aggressive, high-risk trap defense and the more strategic, adaptable defensive shift.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Trap Defense
Trap defense offers significant advantages by aggressively pressuring ball handlers, forcing turnovers, and disrupting offensive rhythm, which can lead to fast-break opportunities. However, its disadvantages include vulnerabilities to quick passes and skilled perimeter shooters, potentially creating open scoring chances for the offensive team. Teams utilizing trap defense must maintain high communication and rotational speed to effectively cover defensive gaps and minimize risks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Defensive Shift
Defensive shift optimizes fielder positioning based on hitter tendencies, increasing the likelihood of converting ground balls into outs and reducing opponent batting averages in targeted zones. However, it can create large gaps in the outfield or infield, making teams vulnerable to hits in the unguarded areas and potentially increasing extra-base hits. Reliance on data-driven shifts may also reduce defensive flexibility against unexpected hitting patterns or adjustments by the opposing batter.
Player Roles and Responsibilities in Each System
Trap defense requires perimeter defenders to aggressively double-team ball handlers, forcing traps near corners while wings rotate quickly to cover passing lanes and secure rebounds. In contrast, the Defensive shift emphasizes positional flexibility, with players adjusting roles dynamically to counter offensive formations, prioritizing switches and help defense based on opponent tendencies. Point guards in trap defense often initiate pressure, while in a Defensive shift, they manage communication and coordinate team reactions to shifting offensive threats.
Impact on Game Outcomes and Statistical Analysis
Trap defense limits offensive movement by forcing turnovers and reducing scoring opportunities, significantly lowering opponent shooting percentages. Defensive shift reallocates players based on hitter tendencies, increasing defensive efficiency metrics such as range factor and run prevention rates. Statistical analysis reveals teams employing these tactics see measurable improvements in win probability and reduced opponent slugging percentage.
Trap defense Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com