Option trading offers flexible strategies to hedge risks and enhance portfolio returns by allowing you to buy or sell assets at predetermined prices. Mastering the fundamentals of option premiums, expiration dates, and strike prices is essential for effective decision-making. Explore the rest of this article to unlock the full potential of options and elevate your investment approach.
Table of Comparison
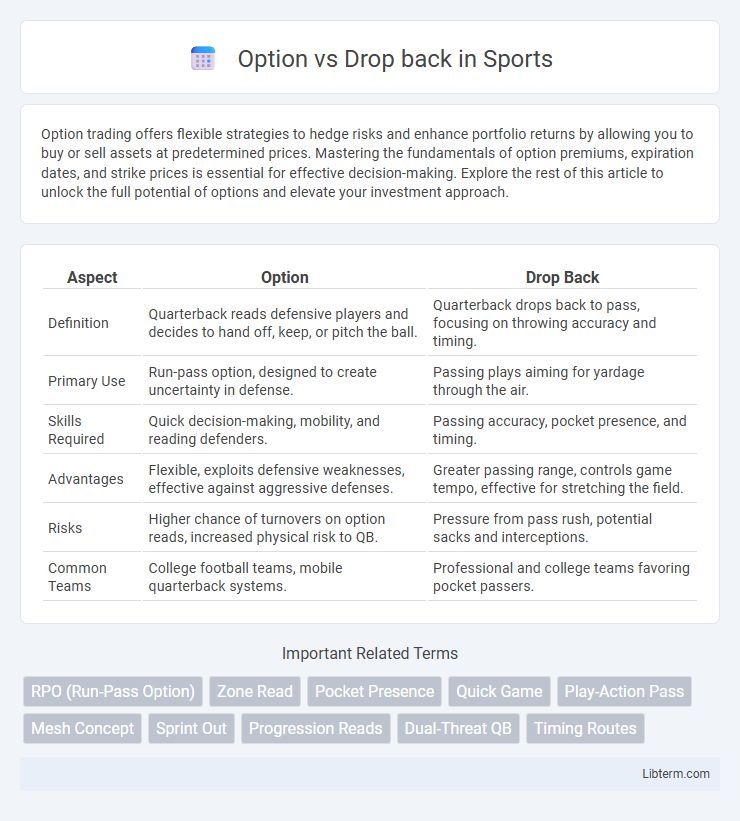
| Aspect | Option | Drop Back |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Quarterback reads defensive players and decides to hand off, keep, or pitch the ball. | Quarterback drops back to pass, focusing on throwing accuracy and timing. |
| Primary Use | Run-pass option, designed to create uncertainty in defense. | Passing plays aiming for yardage through the air. |
| Skills Required | Quick decision-making, mobility, and reading defenders. | Passing accuracy, pocket presence, and timing. |
| Advantages | Flexible, exploits defensive weaknesses, effective against aggressive defenses. | Greater passing range, controls game tempo, effective for stretching the field. |
| Risks | Higher chance of turnovers on option reads, increased physical risk to QB. | Pressure from pass rush, potential sacks and interceptions. |
| Common Teams | College football teams, mobile quarterback systems. | Professional and college teams favoring pocket passers. |
Introduction to Option and Drop Back Plays
Option plays involve a quarterback making real-time decisions by reading defensive players and choosing to hand off, keep, or pitch the ball, maximizing offensive versatility and exploiting defensive weaknesses. Drop back plays feature the quarterback retreating several steps after the snap to survey the field and execute a passing play, emphasizing pocket presence and precise route timing. Both strategies focus on exploiting different defensive schemes to create successful offensive opportunities.
Key Differences Between Option and Drop Back Offenses
Option offenses emphasize a quarterback's ability to read defensive players and decide whether to hand off, keep, or pitch the ball, relying heavily on real-time decision-making and versatility. Drop back offenses focus on the quarterback primarily taking a three- or five-step drop to set up passing plays, prioritizing pocket presence, timing, and downfield throws. The key difference lies in the option's dynamic, read-based rushing decisions compared to the drop back's structured, rhythm-based passing approach.
Historical Evolution of Option vs Drop Back Strategies
Option and drop back passing strategies evolved distinctly through football history, with option plays gaining prominence in the early 20th century as a versatile run-pass threat. Drop back passing became more refined with the forward pass legalization and quarterback-centric offenses emerging post-1930s, emphasizing timing and pocket presence. The interplay between these strategies reflects the tactical shift from run-heavy offenses to balanced and pass-oriented executions in modern football.
Tactical Advantages of the Option Play
The Option play in football offers tactical advantages by forcing the defense to commit to multiple threats simultaneously, creating uncertainty and hesitation. Unlike traditional drop back passing, the Option allows the quarterback to read defensive players in real-time, choosing to hand off, keep, or pitch the ball based on defensive alignment and pressure. This dynamic approach maximizes yardage potential and exploits defensive over-commitment, making it a powerful tool for controlling the tempo and exploiting mismatches on the field.
Strengths of the Drop Back Passing Game
The drop back passing game excels in creating structured, precise reads for quarterbacks, allowing for calibrated throws over varied distances with consistent pocket protection. This method maximizes offensive timing and route discipline, enabling receivers to exploit mismatches and defensive coverages effectively. Its strength lies in promoting a balanced attack that sustains drives through accuracy, timing, and strategic downfield progression.
Personnel and Skill Sets Required
Option offenses demand versatile quarterbacks skilled in quick reads, ball-handling, and decision-making under pressure, paired with athletic fullbacks and running backs capable of executing pitches and inside dives. Drop back passing relies on quarterbacks with strong pocket presence, arm strength, and accuracy, supported by wide receivers proficient in route running and timing to create separation downfield. Offensive linemen in option schemes excel in agility for blocking on the move, whereas drop back offenses prioritize size, strength, and pass protection technique.
Situational Effectiveness: When to Use Each Approach
Option plays excel in quick decision-making against aggressive pass rushes, ideal for read-based schemes and stretch plays in open field scenarios. Drop back thrives in structured passing attacks, maximizing time for route development and precision, especially effective in long-yardage or third-and-long situations. Selecting the approach depends on defensive alignment, pressure intensity, and desired timing to exploit coverage weaknesses efficiently.
Defending Against Option and Drop Back Plays
Defending against option plays requires disciplined assignment football, with defenders maintaining containment responsibilities to prevent quarterbacks from successfully pitching or running the ball. Effective drop-back defense emphasizes disrupting the pocket through pressure and maintaining strong coverage to limit passing windows. Teams that excel at recognizing option reads and applying timely pressure on drop-back quarterbacks reduce offensive effectiveness and force turnovers.
Impact on Team Dynamics and Play Calling
Option plays extend quarterback decision-making, enhancing offensive unpredictability and forcing defenses to adapt dynamically, which cultivates a more versatile team approach. Drop back passing emphasizes structured timing and precision, often reinforcing a hierarchical quarterback-centric leadership that can streamline play calling but reduce spontaneous adjustments. Teams utilizing option schemes typically foster collaborative on-field communication, while drop back offenses rely heavily on pre-snap reads and coach-driven play design.
Future Trends in Offensive Play Selection
Option plays and drop-back passes represent distinct offensive strategies that emphasize either quarterback mobility or pocket passing, respectively. Future trends in offensive play selection increasingly leverage hybrid concepts combining option principles with sophisticated drop-back reads, facilitated by real-time data analytics and player tracking technologies. This integration aims to enhance decision-making speed and adaptability, optimizing offensive efficiency against evolving defensive schemes.
Option Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com