A kick serve is a tennis serve that bounces high and with topspin, making it difficult for opponents to return effectively. Mastering this serve can add a powerful weapon to your game, especially on second serves where consistency and unpredictability are key. Discover how to perfect your kick serve and elevate your performance by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
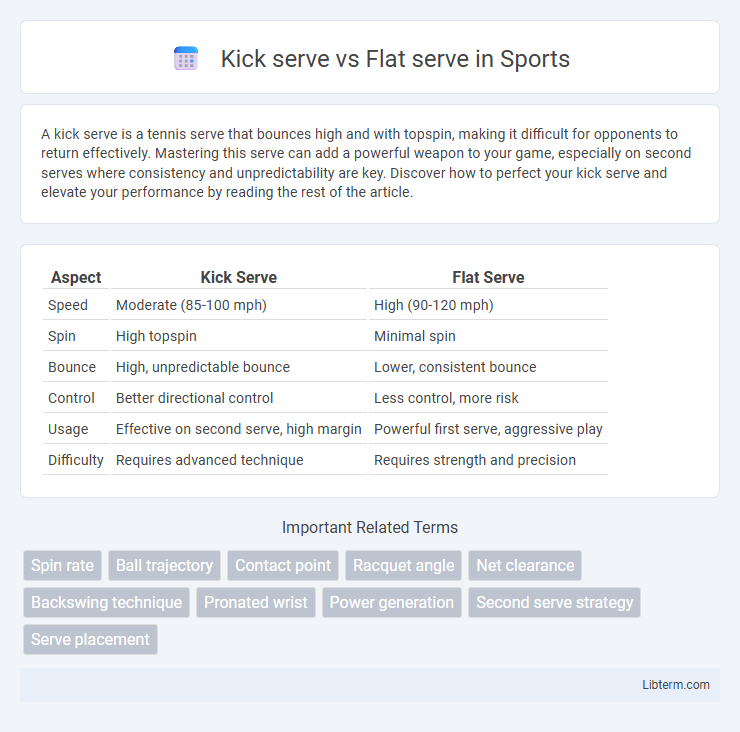
| Aspect | Kick Serve | Flat Serve |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Moderate (85-100 mph) | High (90-120 mph) |
| Spin | High topspin | Minimal spin |
| Bounce | High, unpredictable bounce | Lower, consistent bounce |
| Control | Better directional control | Less control, more risk |
| Usage | Effective on second serve, high margin | Powerful first serve, aggressive play |
| Difficulty | Requires advanced technique | Requires strength and precision |
Introduction to Kick Serve vs Flat Serve
Kick serves generate high topspin, causing the ball to bounce higher and making it effective for pushing opponents back in baseline rallies. Flat serves focus on maximum speed and minimal spin, resulting in fast, aggressive shots aimed at winning points outright or forcing weak returns. Understanding the differences between kick serves and flat serves allows players to diversify their service strategies for varied court conditions and opponent playing styles.
Key Differences Between Kick and Flat Serves
Kick serves generate high topspin, causing the ball to bounce higher and with greater margin over the net, ideal for consistency and control. Flat serves are delivered with minimal spin, maximizing speed and speed, resulting in a faster, more direct trajectory aimed at overpowering opponents. The choice between kick and flat serves depends on situational strategy, player skill, and desired match dynamics.
Mechanics of the Kick Serve
The kick serve relies on an upward brushing motion of the racket to impart high topspin, causing the ball to bounce higher and with unpredictable trajectory compared to the flat serve. Key mechanics include a higher ball toss slightly behind the head and a pronounced wrist snap to generate spin and lift, making it effective for disrupting opponents' rhythm. This serve demands precise timing and body rotation to maximize racket head speed and spin while maintaining control and consistency.
Mechanics of the Flat Serve
The flat serve generates maximum power and speed by striking the ball with a neutral racquet face, producing minimal spin and a direct trajectory. The mechanics involve a precise toss slightly in front of the body, an explosive extension of the arm and wrist snap to maximize racquet head speed, and a firm, concise contact point to drive the ball flat. This technique demands excellent timing and strength to maintain control while delivering a penetrating serve that challenges the receiver.
Spin and Ball Trajectory Comparison
Kick serve generates significant topspin, causing the ball to arc higher and drop sharply into the service box, making it more challenging for opponents to predict and return. Flat serve, with minimal spin, follows a straighter, faster trajectory that maximizes speed and penetration but offers less margin of error and control. The enhanced topspin of the kick serve results in a higher bounce and increased safety over the net, while the flat serve prioritizes power and speed over spin-induced ball movement.
Power and Speed: Flat vs Kick Serve
The flat serve generates maximum power and speed, often reaching velocities above 120 mph, making it ideal for quick, aggressive points. The kick serve, while generally slower at speeds between 60-80 mph, produces a high, spinning bounce that disrupts the opponent's timing and positioning. Tennis players prioritize the flat serve for outright pace and the kick serve for strategic placement and spin-induced difficulty.
Serve Placement and Accuracy
Kick serves produce a high bounce that challenges opponents with unpredictable placement, making them ideal for targeting the backhand side and wide service boxes. Flat serves generate maximum speed and minimal spin, resulting in a more direct trajectory that excels in precise targeting of the body or corners. Accuracy in kick serves relies on controlled spin and depth, while flat serves demand precise timing and placement to exploit openings effectively.
Advantages of Using a Kick Serve
A kick serve generates a high, heavy bounce, making it difficult for opponents to return effectively, especially on clay and hard courts. This serve creates greater margin for error by allowing more net clearance, reducing double faults while maintaining power and spin. Players benefit from the kick serve's reliability and strategic versatility, disrupting opponent rhythm and setting up offensive opportunities.
Advantages of Using a Flat Serve
A flat serve delivers maximum speed and power, making it highly effective for aces and forcing weak returns. Its minimal spin allows the ball to travel faster and skid off the court surface, reducing the opponent's reaction time. Players using a flat serve can dominate service games by applying pressure and controlling the pace from the outset.
Choosing the Right Serve for Your Game
Choosing the right serve between a kick serve and a flat serve depends on your playing style and match strategy. A kick serve offers higher margin for error with its heavy topspin and bounce, making it ideal for consistency and defensive play. A flat serve delivers maximum speed and power, suited for aggressive players looking to dominate points with quick, forceful serves.
Kick serve Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com