The one-point stance is a fundamental position in football, providing stability and power before the snap. Mastering this stance enhances your balance, allowing for quicker reactions and stronger blocking or tackling. Discover how to perfect the one-point stance to improve your game in the following article.
Table of Comparison
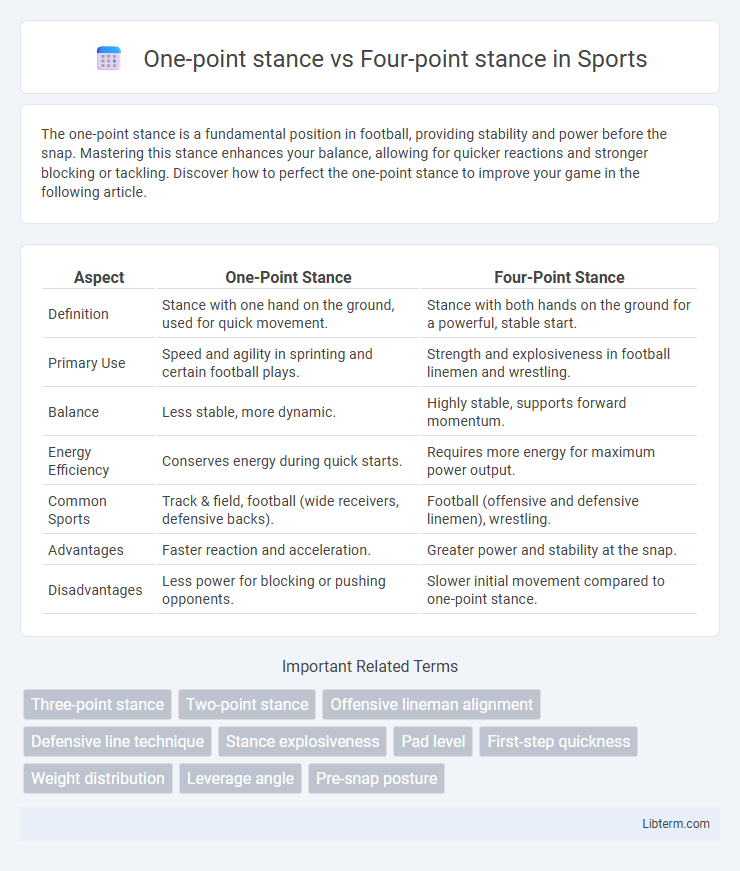
| Aspect | One-Point Stance | Four-Point Stance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stance with one hand on the ground, used for quick movement. | Stance with both hands on the ground for a powerful, stable start. |
| Primary Use | Speed and agility in sprinting and certain football plays. | Strength and explosiveness in football linemen and wrestling. |
| Balance | Less stable, more dynamic. | Highly stable, supports forward momentum. |
| Energy Efficiency | Conserves energy during quick starts. | Requires more energy for maximum power output. |
| Common Sports | Track & field, football (wide receivers, defensive backs). | Football (offensive and defensive linemen), wrestling. |
| Advantages | Faster reaction and acceleration. | Greater power and stability at the snap. |
| Disadvantages | Less power for blocking or pushing opponents. | Slower initial movement compared to one-point stance. |
Introduction to Stance Techniques in Sports
One-point stance and four-point stance are fundamental positioning techniques in sports like football, each offering distinct advantages. The one-point stance positions an athlete on one hand with three legs supporting, enhancing quick forward movement and agility. The four-point stance, with both hands and feet grounded, provides maximum stability and power, ideal for explosive starts and defensive strength.
Defining the One-Point Stance
The one-point stance is defined by placing only one hand on the ground, typically with the feet shoulder-width apart, creating a balanced and agile position essential for quick bursts of speed in football. This stance emphasizes forward lean and leverage, allowing players to explode off the line effectively. In contrast, the four-point stance involves both hands and feet on the ground, offering a more stable but less dynamic starting position.
Understanding the Four-Point Stance
The four-point stance provides greater stability by placing both hands and both feet on the ground, creating a solid base essential in situations requiring maximum balance and control. This stance is commonly used in sports like football for blocking or sprint starts, where explosive power and quick reactions are needed. Understanding the biomechanics of the four-point stance highlights its advantage in distributing weight evenly and enhancing forward propulsion compared to the one-point stance.
Key Advantages of the One-Point Stance
The one-point stance offers enhanced stability and balance by concentrating weight on a single foot, enabling quicker directional changes and improved power transfer in movements. This stance optimizes force generation through better alignment of the body's center of gravity, crucial for explosive actions in sports like football and martial arts. Compared to the four-point stance, it allows greater mobility and quicker reaction times, making it ideal for athletes requiring agility and speed.
Major Benefits of the Four-Point Stance
The four-point stance offers superior stability and balance by distributing weight evenly across four points of contact, reducing the risk of tipping or slipping during activity. This stance enhances power generation and control, allowing athletes to execute movements with greater force and precision. Compared to the one-point stance, the four-point stance promotes improved posture and injury prevention by providing a more solid and adaptable base.
Situational Uses: When to Use Each Stance
The one-point stance is ideal for situations requiring quick mobility and rapid direction changes, commonly used by quarterbacks and defensive backs in football due to its balance and readiness to sprint. The four-point stance suits linemen in football who need maximum stability and power at the snap, providing greater leverage for blocking or pushing opponents in short-yardage or goal-line scenarios. Choosing between stances depends on the player's role and situational demands, prioritizing either speed and agility or strength and stability.
Impact on Acceleration and Speed
One-point stance enhances acceleration by positioning the body to generate immediate forward momentum, making it ideal for explosive starts in sprinting. Four-point stance offers greater stability and balance, but it can slightly reduce initial acceleration due to the need for coordinated movement from multiple contact points. Athletes prioritizing quick bursts of speed often prefer the one-point stance to maximize their acceleration and overall sprint performance.
Common Mistakes in Stance Selection
Common mistakes in stance selection between one-point and four-point stances include improper weight distribution, leading to instability and decreased control. Many athletes mistakenly place too much weight on the lead foot in a one-point stance, causing imbalance and slower reaction times. In four-point stances, incorrect hand placement often results in reduced power generation and increased vulnerability to opponents.
Athlete Profiles: Who Prefers Which Stance
Power athletes such as linemen and wrestlers often favor the four-point stance due to its stability and strong base for explosive starts. In contrast, speed-focused athletes like sprinters and skill position football players prefer the one-point stance for greater mobility and quicker transitions. Coaches typically recommend stance selection based on the athlete's role, size, and specific movement demands to optimize performance outcomes.
Expert Recommendations and Best Practices
Experts recommend the one-point stance for greater agility and speed, commonly favored in cricket bowling for its balance and dynamic movement. The four-point stance is advised for increased stability and power, often used in football linemen positions to maintain a strong, grounded posture. Best practices suggest selecting the stance based on the sport's biomechanical demands, optimizing performance by matching stance to specific athletic roles.
One-point stance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com