A post route is a designated path used to deliver mail and packages efficiently within a specific area. Understanding how post routes are organized can help optimize your mailing process and ensure timely delivery. Explore the rest of the article to learn how post routes impact postal services and your correspondence.
Table of Comparison
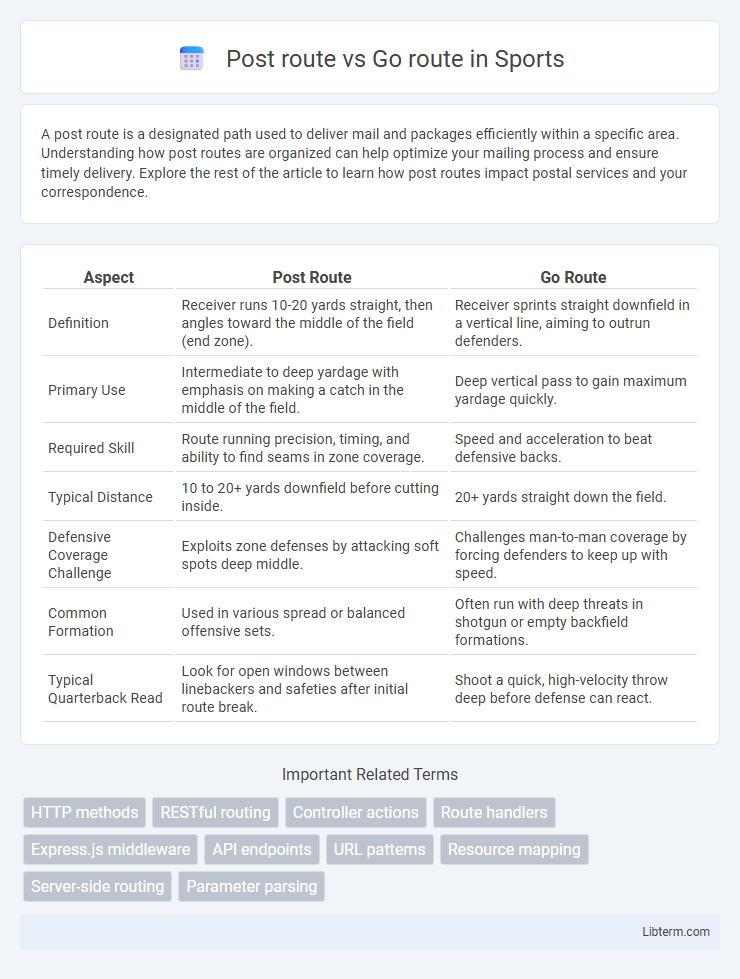
| Aspect | Post Route | Go Route |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Receiver runs 10-20 yards straight, then angles toward the middle of the field (end zone). | Receiver sprints straight downfield in a vertical line, aiming to outrun defenders. |
| Primary Use | Intermediate to deep yardage with emphasis on making a catch in the middle of the field. | Deep vertical pass to gain maximum yardage quickly. |
| Required Skill | Route running precision, timing, and ability to find seams in zone coverage. | Speed and acceleration to beat defensive backs. |
| Typical Distance | 10 to 20+ yards downfield before cutting inside. | 20+ yards straight down the field. |
| Defensive Coverage Challenge | Exploits zone defenses by attacking soft spots deep middle. | Challenges man-to-man coverage by forcing defenders to keep up with speed. |
| Common Formation | Used in various spread or balanced offensive sets. | Often run with deep threats in shotgun or empty backfield formations. |
| Typical Quarterback Read | Look for open windows between linebackers and safeties after initial route break. | Shoot a quick, high-velocity throw deep before defense can react. |
Introduction to POST Route and GO Route
POST route handles HTTP POST requests, primarily used to submit data to a server for processing, such as form submissions or file uploads, enabling secure data transmission. GO route, commonly referred to as GET route, manages HTTP GET requests aimed at retrieving data without causing side effects on the server, essential for fetching resources like web pages or API data. Understanding the distinction between POST and GET routes is crucial for designing RESTful APIs and web applications that balance data security and efficient data retrieval.
Core Differences Between POST and GO Routes
POST routes handle data submission to the server, typically used for creating or updating resources, and often require a request body containing the data. GO routes are less common terminology but may refer to routes implemented using the Go programming language or RESTful GET routes, which retrieve data without modifying server state. Core differences include POST routes being state-changing with payloads, whereas GO/GET routes are idempotent and primarily data-fetching operations.
How POST Route Works: Key Features
POST routes handle data submission by sending information in the request body, enabling secure and efficient transmission of large or sensitive data. They do not expose data in the URL, enhancing privacy compared to GET requests. POST routes typically trigger server-side processing, such as creating or updating resources, making them essential for form submissions and API interactions.
Understanding GO Route: Main Characteristics
Go route is a URL mapping method in web development designed for efficient navigation handling within applications, emphasizing fast, incremental page loading and seamless user experience. It typically supports dynamic routing with minimal server interaction, allowing smooth transitions by pre-fetching data and rendering views client-side. This approach contrasts with POST routes that handle form submissions or data changes, as GO routes primarily manage content retrieval and page state.
Use Cases: When to Choose POST Route
POST routes are ideal for submitting sensitive or large amounts of data, such as user registration forms, file uploads, or payment processing, where data should not appear in the URL. They are used in scenarios requiring server-side data modification, including creating, updating, or deleting resources in databases. Choosing a POST route ensures secure transmission of information and prevents exposure of parameters in browser history or server logs.
Use Cases: When to Choose GO Route
Go routes are ideal for internal navigation where fast, seamless page transitions enhance user experience without reloading the entire webpage. They are commonly used for client-side routing in single-page applications (SPAs) to dynamically update content based on user interactions. Choose Go routes when prioritizing quick navigation, state preservation, and minimal latency within the app environment.
Performance Comparison: POST vs GO Route
POST routes typically involve handling more data payloads, resulting in longer processing times compared to Go routes, which are designed for efficient, lightweight request handling. Go routes leverage Go's concurrency model and compiled nature to deliver faster response times and lower latency under high load conditions. Performance benchmarks often show Go routes outperforming POST routes by minimizing resource consumption and optimizing execution speed in web server environments.
Security Considerations for POST and GO Routes
POST routes enhance security by transmitting data within the HTTP request body, preventing sensitive information from appearing in URLs, which mitigates risks like exposure in browser history or server logs. GO routes, typically associated with GET methods, expose parameters in the URL, making them vulnerable to interception, bookmarking, or caching by intermediate servers. Implementing POST routes for sensitive operations, combined with HTTPS encryption and validation checks, helps safeguard data integrity and confidentiality against common web threats.
Best Practices for Implementing POST and GO Routes
POST routes should be used for submitting data to the server, as they support secure data transmission and enable payload inclusion in the request body. GET routes are ideal for retrieving data without side effects, with parameters passed via URL query strings to maintain idempotency and cacheability. Best practices include validating and sanitizing input on POST routes, limiting GET routes to safe data retrieval, and avoiding sensitive data exposure in URL parameters.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Routing Method
Selecting the right routing method depends on the intended application and data handling needs; POST routes are optimal for submitting sensitive or large amounts of data securely, as they do not expose information in the URL. GET routes are ideal for retrieving data, enabling efficient caching and bookmarking due to their idempotent and safe nature. Understanding these distinctions ensures appropriate use of HTTP methods, enhancing both performance and security in web applications.
Post route Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com