Dead ball situations occur when play temporarily stops due to fouls, out-of-bounds, or other interruptions in sports like football and basketball. These pauses allow players to reset strategies, officials to make decisions, and fans to anticipate the next phase of the game. Explore the article to understand how dead ball moments impact your favorite sports and influence game outcomes.
Table of Comparison
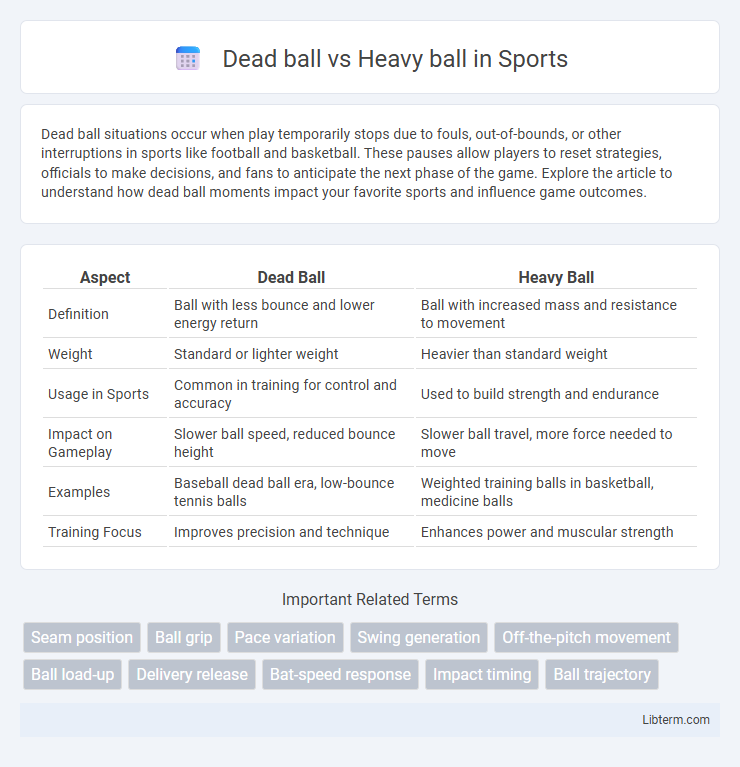
| Aspect | Dead Ball | Heavy Ball |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ball with less bounce and lower energy return | Ball with increased mass and resistance to movement |
| Weight | Standard or lighter weight | Heavier than standard weight |
| Usage in Sports | Common in training for control and accuracy | Used to build strength and endurance |
| Impact on Gameplay | Slower ball speed, reduced bounce height | Slower ball travel, more force needed to move |
| Examples | Baseball dead ball era, low-bounce tennis balls | Weighted training balls in basketball, medicine balls |
| Training Focus | Improves precision and technique | Enhances power and muscular strength |
Understanding the Concepts: Dead Ball vs Heavy Ball
Dead ball refers to a ball that has lost its energy and momentum, resulting in a slow or no movement after impact, commonly seen in sports like baseball or cricket when the ball comes to rest. Heavy ball describes a ball with greater mass or density, which affects its speed, trajectory, and the force required to move or stop it, influencing the dynamics of gameplay in sports such as medicine ball training or shot put. Understanding the difference between dead ball and heavy ball is crucial for athletes and coaches to optimize performance strategies and equipment selection based on the ball's physical properties.
Key Differences Between Dead Ball and Heavy Ball
Dead ball refers to a sports ball that lacks bounce or liveliness, often resulting in slower gameplay and reduced ball control, while a heavy ball is physically denser and harder, requiring more force to manipulate and affecting player endurance and strategy. The dead ball typically impacts rebound characteristics and is common in sports like cricket and baseball during pauses, whereas the heavy ball influences strength training and skill development in sports such as shot put or weighted baseball drills. Understanding the weight, bounce, and gameplay effects of both dead and heavy balls is crucial for optimizing performance and selecting appropriate equipment for training or competition.
The Physics Behind Dead Ball and Heavy Ball
Dead ball and heavy ball differ primarily in their kinetic energy and momentum during impact; a heavy ball has greater mass, increasing its momentum (mass x velocity) and resulting in more forceful collisions based on Newton's second law of motion. The dead ball's reduced elasticity causes lower coefficient of restitution, thereby absorbing more energy and producing slower rebound speeds. Air resistance and drag coefficients further influence the trajectory and energy dissipation, with the heavy ball maintaining velocity better due to higher inertia.
Impact on Gameplay: Dead Ball Effects
Dead balls significantly slow down the pace of gameplay by reducing ball bounce and speed, making quick offensive maneuvers more difficult. Players experience increased fatigue and strategic adjustments due to the need for stronger shots and precise control. This effect often leads to longer rallies and a more physically demanding match, impacting overall player performance and match duration.
How Heavy Ball Influences Results
Heavy ball training enhances muscle strength and power output by increasing resistance during dynamic movements, promoting greater neuromuscular activation. This increased load leads to improved acceleration and force generation, resulting in enhanced performance metrics such as jump height and sprint speed. Studies show athletes using heavy ball exercises experience significant gains in explosive strength compared to those training with dead balls or standard weights.
Recognizing Dead Ball Conditions in Matches
Recognizing dead ball conditions in matches is crucial for maintaining game flow and enforcing rules accurately. Dead ball occurs when play is temporarily stopped, such as after a foul, out-of-bounds, or a stoppage called by the referee, ensuring player safety and fair play. Understanding specific situations like a ball crossing the goal line or a whistle signaling an infraction helps players and officials respond appropriately to resume active gameplay.
Identifying Heavy Ball in Play
A heavy ball in play is characterized by its increased mass or density compared to a dead ball, which is typically lighter and less impactful. Identifying a heavy ball involves observing its slower velocity, deeper trajectory, and greater resistance upon contact, often resulting in a more powerful and forceful play. This distinction is crucial in sports like baseball and cricket, where ball weight affects flight dynamics, player handling, and game strategy.
Strategies for Countering Dead Ball
Countering a dead ball requires focusing on maintaining momentum through quick footwork and explosive power to overcome the lack of ball responsiveness. Strategic emphasis on enhancing grip strength and utilizing wrist snap techniques can generate improved ball control and spin. Adapting shot selection by targeting pins and optimizing ball speed minimizes the dead ball's tendency to deflect without impact, improving strike potential.
Techniques to Handle Heavy Ball Deliveries
Handling heavy ball deliveries requires a solid stance, with a lower center of gravity to maintain balance under increased impact force. Employing softer hands and flexible wrists helps absorb the ball's energy, reducing rebound and controlling deflections. Batters must also time their shots precisely, utilizing a compact swing to stabilize contact and maximize shot accuracy against heavier balls.
Choosing the Right Approach: Dead Ball vs Heavy Ball
Choosing the right approach between dead ball and heavy ball techniques depends on the specific sport and desired outcome. Dead ball shots, characterized by minimal spin and low velocity, offer precision and control, ideal for scenarios requiring accuracy over power. Heavy ball techniques generate increased momentum and spin, maximizing force and impact to overwhelm opponents or achieve deeper penetration in games like table tennis or baseball.
Dead ball Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com