Plank is a fundamental core exercise that enhances stability and strengthens muscles in your abdomen, back, and shoulders. Performing planks regularly improves posture, reduces risk of injury, and boosts overall functional fitness. Discover the best techniques and variations to maximize your plank workouts as you read the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
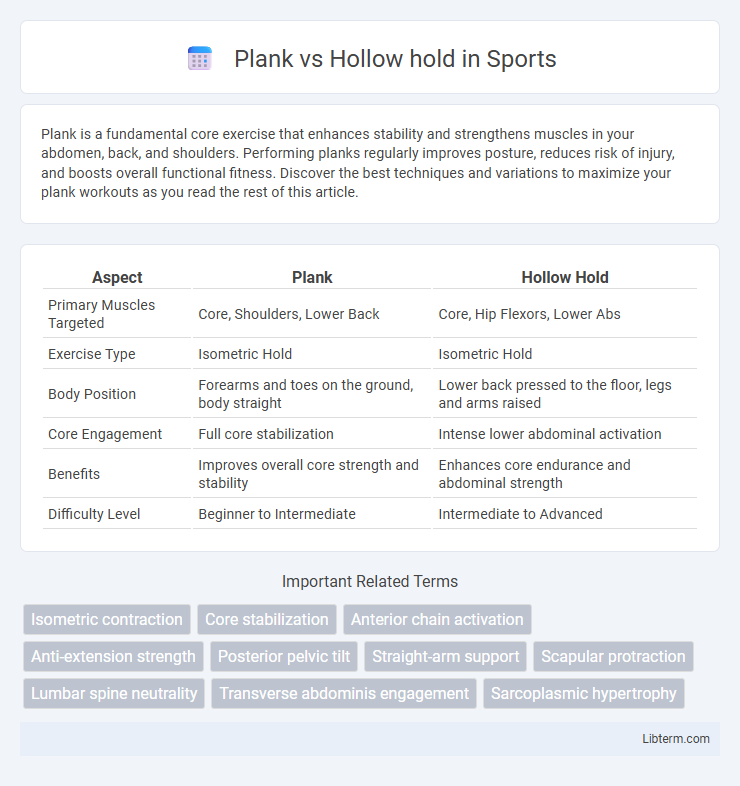
| Aspect | Plank | Hollow Hold |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Muscles Targeted | Core, Shoulders, Lower Back | Core, Hip Flexors, Lower Abs |
| Exercise Type | Isometric Hold | Isometric Hold |
| Body Position | Forearms and toes on the ground, body straight | Lower back pressed to the floor, legs and arms raised |
| Core Engagement | Full core stabilization | Intense lower abdominal activation |
| Benefits | Improves overall core strength and stability | Enhances core endurance and abdominal strength |
| Difficulty Level | Beginner to Intermediate | Intermediate to Advanced |
Introduction: Plank vs Hollow Hold
Plank and hollow hold are core strengthening exercises that target different muscle groups and movement patterns. Planks emphasize static isometric contraction primarily engaging the transverse abdominis, rectus abdominis, and obliques, improving overall core stability and spinal alignment. Hollow holds activate the deep core and hip flexors by maintaining a posterior pelvic tilt with extended limbs, enhancing body control and preventing lumbar hyperextension.
What Is a Plank?
A plank is a core-strengthening isometric exercise that engages multiple muscle groups, including the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, obliques, and lower back muscles. It involves maintaining a position similar to a push-up, with the body held in a straight line from head to heels, supported by forearms and toes. Planks improve stability, endurance, and overall core strength without requiring dynamic movement.
What Is a Hollow Hold?
A hollow hold is a core strengthening exercise that involves engaging the abdominal muscles while keeping the lower back pressed firmly against the ground, creating a concave shape with the body. Unlike a plank, which targets overall core stability by maintaining a straight line from head to heels in a prone position, a hollow hold specifically emphasizes abdominal muscle activation by lifting the shoulders and legs off the floor. This exercise builds endurance and strength in the rectus abdominis and transverse abdominis, making it essential for gymnasts and athletes focusing on core control.
Muscle Groups Targeted
The plank primarily targets the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques, while also engaging the shoulders, chest, and lower back muscles for stability. The hollow hold emphasizes the deep core muscles, especially the transverse abdominis and lower rectus abdominis, with significant activation in the hip flexors and lower back to maintain the hollow body position. Both exercises improve core strength but differ in muscle engagement intensity and dynamic tension.
Benefits of Plank Exercise
Plank exercise effectively engages core muscles, enhancing stability and strength critical for overall body balance and injury prevention. It activates multiple muscle groups including the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques, promoting improved posture and spinal alignment. Consistent plank practice boosts endurance and supports functional movement, making it a versatile component in fitness routines.
Benefits of Hollow Hold Exercise
The hollow hold exercise enhances core strength by targeting deep abdominal muscles, including the transverse abdominis and rectus abdominis, promoting improved stability and posture. It also engages the hip flexors and lower back muscles, aiding in body control and balance during dynamic movements. Unlike the plank, the hollow hold emphasizes maintaining a posterior pelvic tilt, which optimizes spinal alignment and reduces the risk of lower back strain.
Key Differences Between Plank and Hollow Hold
The plank primarily targets the anterior core, focusing on isometric endurance of the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and shoulders, while the hollow hold emphasizes creating full-body tension by engaging the entire midsection, including the lower abs and hip flexors. The plank maintains a neutral spine with weight supported on forearms and toes, contrasting with the hollow hold's flattened lower back pressed into the floor and elevated legs and shoulders to create a concave shape. Planks improve static stability and postural support, whereas hollow holds develop dynamic core strength and the ability to resist extension, essential for gymnastics and advanced body control.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Maintaining proper form in plank and hollow hold exercises is crucial to prevent common mistakes such as sagging hips, raised buttocks, and improper neck alignment. Engaging the core fully and keeping a neutral spine avoids lower back strain and ensures maximum muscle activation. Avoid holding your breath and ensure consistent breathing to maintain stability and endurance during the exercises.
Which Core Exercise Is Better for You?
The plank primarily targets the entire core with an emphasis on the rectus abdominis and transverse abdominis, enhancing overall stability and endurance. The hollow hold specifically engages the deep core muscles including the lower abs and lumbar region, promoting improved body control and spinal alignment. Choosing the better exercise depends on your fitness goals: planks are ideal for building full-core strength and endurance, while hollow holds excel in developing core tension and gymnastic control.
Plank and Hollow Hold: Sample Workouts
Plank and Hollow Hold sample workouts target core strength and stability through isometric holds, with variations improving endurance and muscle engagement. A plank workout might include forearm plank holds for 30-60 seconds, followed by side planks and plank shoulder taps to activate the transverse abdominis and obliques. Hollow hold routines typically consist of lying supine while lifting legs and shoulders off the ground, held for 20-40 seconds, combined with hollow body rocks to enhance rectus abdominis activation and improve overall core control.
Plank Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com