Chest save techniques are essential for stabilizing trauma patients by protecting vital organs and preventing further injury. Effective methods include applying pressure dressings, immobilizing the chest, and ensuring open airways to maintain adequate breathing. Discover comprehensive steps and expert tips to enhance your lifesaving skills in the full article.
Table of Comparison
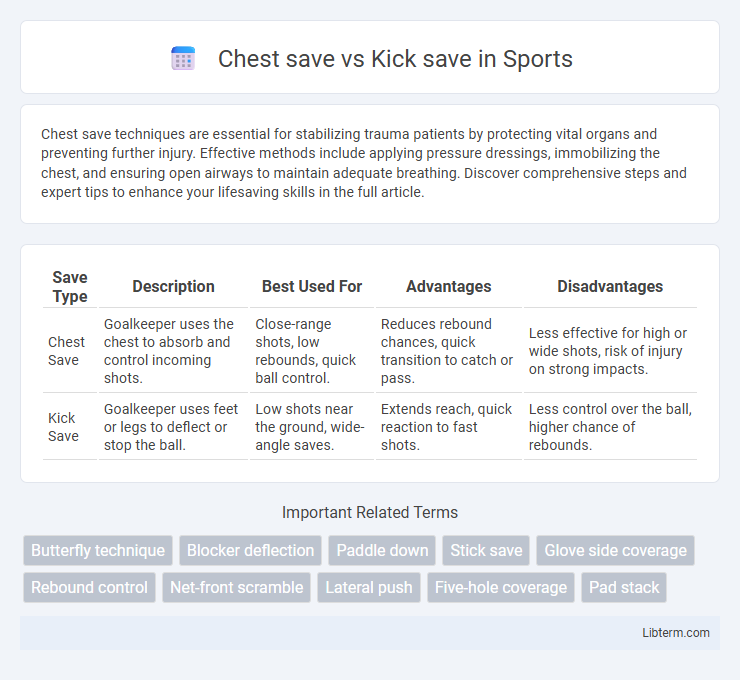
| Save Type | Description | Best Used For | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest Save | Goalkeeper uses the chest to absorb and control incoming shots. | Close-range shots, low rebounds, quick ball control. | Reduces rebound chances, quick transition to catch or pass. | Less effective for high or wide shots, risk of injury on strong impacts. |
| Kick Save | Goalkeeper uses feet or legs to deflect or stop the ball. | Low shots near the ground, wide-angle saves. | Extends reach, quick reaction to fast shots. | Less control over the ball, higher chance of rebounds. |
Understanding Chest Save and Kick Save Techniques
Chest save technique involves using the torso to absorb and secure the ball, providing a stable barrier and minimizing rebound chances in close-range shots. Kick save relies on quick leg movements to deflect low shots, combining reflexes with precise foot positioning to redirect the ball away from the goal. Mastery of both techniques enhances a goalkeeper's versatility and effectiveness in diverse game scenarios.
Key Differences Between Chest Saves and Kick Saves
Chest saves involve goalkeepers using their torso and arms to securely catch or deflect the ball close to the body, offering maximum control and reducing rebound chances. Kick saves rely on the goalkeeper's feet or legs to block or redirect shots, often used for low or fast-moving balls when the hands are not in an optimal position. The key differences lie in the body part utilized, the level of ball control after the save, and the typical scenarios in which each technique is employed during a match.
Situations Best Suited for Chest Saves
Chest saves are best suited for close-range shots and powerful strikes aimed at the center of the torso, allowing goalkeepers to use their body as a barrier to absorb impact. They are highly effective in one-on-one situations or during crowded penalty box scenarios where quick reflexes and secure ball control are essential. Compared to kick saves, chest saves provide better control over rebounds, reducing the chance of second-chance opportunities for opponents.
When to Use Kick Saves in Gameplay
Kick saves are essential during high-pressure moments when quick reflexes are needed to block fast, low shots aimed at the corners of the goal. Goalkeepers use kick saves to extend their range and keep the ball out of the net, especially when their hands cannot reach or when diving is not an option. Mastering kick saves improves defensive tactics, allowing goalkeepers to control rebounds and maintain possession more effectively during intense gameplay.
Advantages of Chest Saves in Goalkeeping
Chest saves in goalkeeping offer superior control and quick ball retention, allowing the goalkeeper to immediately distribute the ball or initiate counterattacks. They provide increased safety by cushioning shots and reducing rebound risks compared to kick saves. Furthermore, chest saves enable goalkeepers to effectively block close-range shots where maneuvering for a kick save is impractical.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Kick Saves
Kick saves offer faster reaction times and greater reach compared to chest saves, enabling goalkeepers to block shots aimed at the corners of the goal more effectively. However, kick saves can be less controlled and riskier, potentially leading to rebounds or lost possession if not executed correctly. This technique demands strong leg power and precision, posing challenges for less experienced goalkeepers but providing dynamic coverage in high-pressure situations.
Common Mistakes in Chest and Kick Saves
Common mistakes in chest saves include improper hand positioning, which reduces control and increases rebound risk, and leaning too far forward, causing loss of balance and slower recovery. In kick saves, errors often involve delayed leg movement or insufficient knee bend, leading to decreased save power and accuracy. Both techniques require precise timing and body alignment to enhance save effectiveness and prevent rebounds.
Training Drills for Chest and Kick Save Mastery
Training drills for Chest save mastery emphasize reflex enhancement and upper torso strength, utilizing rapid ball rebound exercises and wall-mounted rebounders to simulate close-range shots. Kick save drills focus on lower body agility and precision, incorporating lateral shuffles combined with targeted pad saves and resistance band workouts to improve explosive leg power. Consistent practice of these drills develops the essential coordination and muscle memory required for effective goaltending in competitive hockey scenarios.
Famous Chest and Kick Saves in Soccer History
Lev Yashin's iconic chest save against Pele in the 1962 World Cup exemplifies the power and precision required for effective chest saves in soccer history. Gordon Banks' legendary kick save from Pele's header during the 1970 World Cup remains one of the most celebrated moments, showcasing incredible reflexes and agility. These saves highlight the distinct techniques and critical roles chest and kick saves play in preserving goal security at the highest levels of the sport.
Expert Tips for Improving Save Selection Skills
Mastering save selection in soccer requires understanding the distinct advantages of chest saves and kick saves. Chest saves offer greater control and the ability to quickly distribute the ball, while kick saves provide powerful clearances in high-pressure situations. Experts recommend practicing situational awareness and reaction drills to improve decision-making speed and effectiveness between these two critical techniques.
Chest save Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com