Understanding the best route for your journey can save time and reduce travel stress, whether you're driving, cycling, or walking. Factors such as traffic conditions, distance, and road quality play a crucial role in determining the optimal path. Explore the rest of the article to discover strategies for choosing the most efficient route tailored to your needs.
Table of Comparison
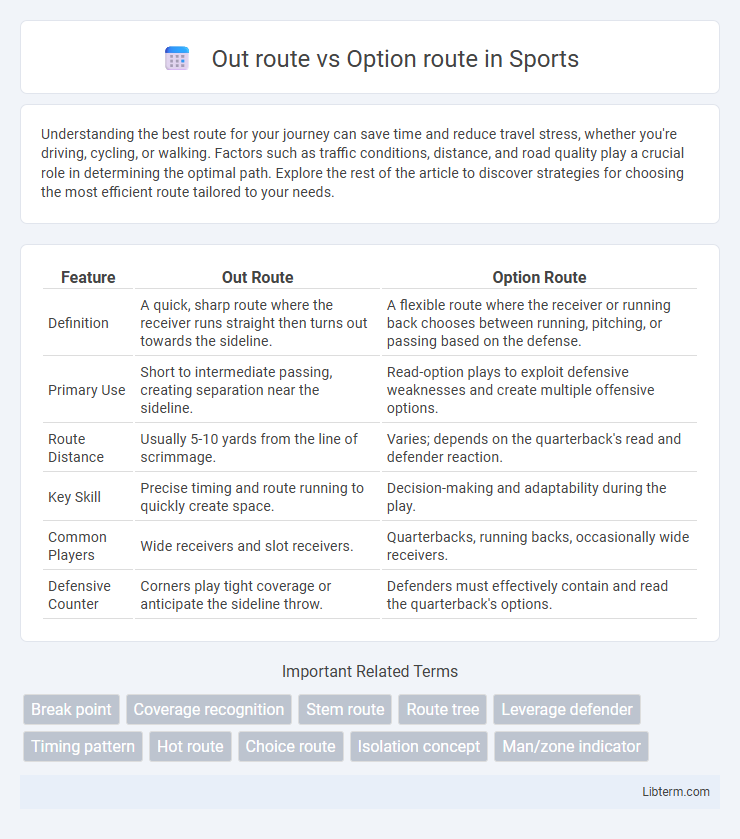
| Feature | Out Route | Option Route |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A quick, sharp route where the receiver runs straight then turns out towards the sideline. | A flexible route where the receiver or running back chooses between running, pitching, or passing based on the defense. |
| Primary Use | Short to intermediate passing, creating separation near the sideline. | Read-option plays to exploit defensive weaknesses and create multiple offensive options. |
| Route Distance | Usually 5-10 yards from the line of scrimmage. | Varies; depends on the quarterback's read and defender reaction. |
| Key Skill | Precise timing and route running to quickly create space. | Decision-making and adaptability during the play. |
| Common Players | Wide receivers and slot receivers. | Quarterbacks, running backs, occasionally wide receivers. |
| Defensive Counter | Corners play tight coverage or anticipate the sideline throw. | Defenders must effectively contain and read the quarterback's options. |
Understanding the Basics: Out Route vs Option Route
Out route and option route are key concepts in fantasy football lineup decisions. Out route prioritizes projecting players' optimal performance scenarios, focusing on maximizing estimated points by selecting specific plays, while option route emphasizes flexibility, allowing players to adapt routes based on defensive coverage and in-game conditions. Understanding these concepts enhances strategic lineup adjustments by balancing high-upside targeted plays with versatile responses to defensive schemes.
Key Differences Between Out Route and Option Route
Out routes direct calls to external numbers or destinations outside the telecommunications system, enabling external connectivity and cloud call management. Option routes offer flexible call handling by routing within a system based on user-selected options or IVR inputs, optimizing internal call distribution and user experience. Key differences include out routes managing external call flow, while option routes focus on internal call navigation and response options.
Route Definitions: Out Route Explained
Out route defines the specific path that outgoing calls follow in a telephony system, directing calls to appropriate trunks or gateways based on predefined criteria such as dial patterns and permissions. It ensures efficient call routing by matching destination numbers with route patterns, optimizing call flow and cost management. Comparing this to option routes, which offer flexible routing choices based on dynamic conditions, out routes remain static and rule-based, providing predictable and consistent call handling.
Route Definitions: Option Route Explained
Option routes provide a flexible routing method within network configurations, allowing multiple potential paths to the same destination based on criteria such as cost, policy, or availability. Unlike out routes, which are typically fixed and predefined paths for outbound traffic, option routes enable dynamic decision-making by selecting the best route at runtime. This method optimizes network performance and redundancy by leveraging routing protocols and metrics to adjust paths on demand.
Situational Usage: When to Call an Out Route
An out route is best utilized when a receiver needs to create immediate separation near the sideline, often during third-down or two-minute drill scenarios to gain quick yardage or stop the clock. Option routes provide flexibility based on defensive coverage, allowing the receiver to adjust their breaking point in real-time, but calling an out route is advantageous when a precise, sharp sideline cut is required to exploit zone or man coverage weaknesses. Understanding defensive alignment and down-distance situations helps quarterbacks decide when the out route's quick, decisive pattern can maximize yardage and maintain game tempo.
Situational Usage: When to Call an Option Route
Option Route is preferred over Out Route during unpredictable traffic conditions or unexpected road closures, offering drivers flexible, real-time alternatives to avoid delays. Out Route guides drivers along predetermined paths with fixed directions, suited for routine trips with minimal variability. When navigation demands adaptability due to dynamic environments or last-minute changes, calling an Option Route enhances route efficiency and time savings.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Out Route
The Out route offers advantages such as increased flexibility in navigation and better control over traffic flow in network routing protocols like OSPF, allowing for efficient path selection to avoid congestion. However, its disadvantages include potential complexity in configuration and the risk of suboptimal routing if not properly managed, leading to increased latency or packet loss. Network administrators must weigh these factors against their specific infrastructure needs to maximize performance and reliability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Option Route
Option routes in networking offer flexibility by allowing dynamic path selection based on specific conditions or policies, which enhances traffic management and fault tolerance. However, they can introduce complexity in configuration and may require more processing power for real-time decision-making, potentially increasing latency. Compared to out routes, option routes provide tailored routing options but demand careful management to avoid misrouting and ensure network efficiency.
Defensive Strategies Against Out and Option Routes
Defensive strategies against out routes emphasize pressing the receiver at the line of scrimmage and maintaining outside leverage to force the receiver back toward the defender's help or sideline. When defending option routes, defenders must read the route runner's cues and adjust coverage dynamically, effectively balancing between covering the primary route and staying alert to sudden cuts or route adjustments. Employing disciplined zone drops and communication among linebackers and defensive backs enhances the defense's ability to prevent big gains from both out and option routes.
Impact on Offensive Play Design: Out vs Option Route
Out routes provide precise timing and clear separation, allowing quarterbacks to quickly read defenses and execute short to intermediate passes with high accuracy. Option routes offer dynamic flexibility, enabling receivers to adjust their break points based on defensive coverage, creating challenges for defenders and enhancing yards-after-catch opportunities. Combining out routes with option routes diversifies offensive play design by balancing structured timing patterns with adaptable route adjustments, increasing offensive unpredictability.
Out route Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com