Choosing the Go route accelerates development with its simple syntax and powerful concurrency features, making it ideal for scalable applications. Its statically typed nature ensures high performance and reliability without sacrificing readability. Explore the rest of the article to discover why Go could be the perfect choice for your next project.
Table of Comparison
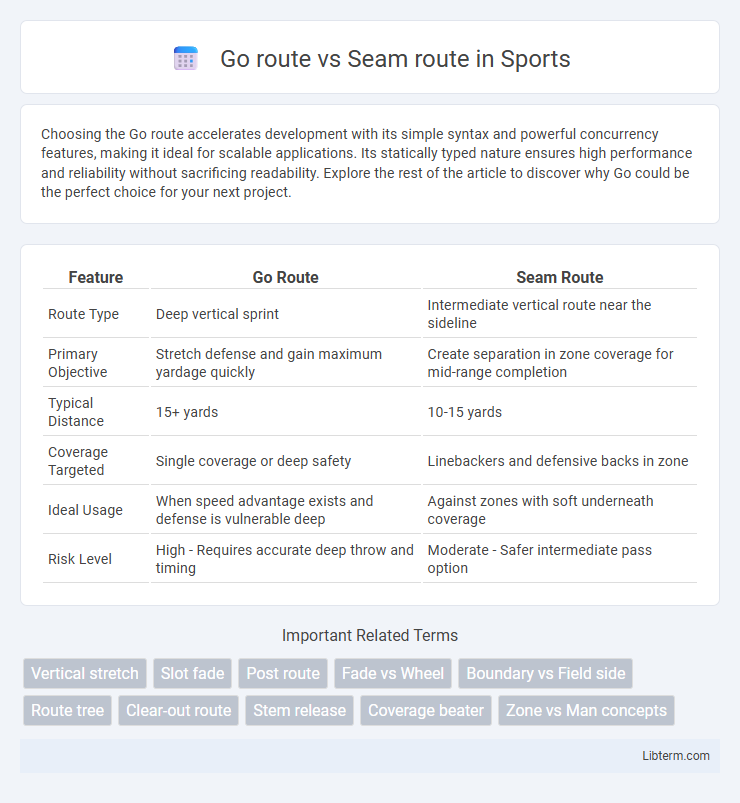
| Feature | Go Route | Seam Route |
|---|---|---|
| Route Type | Deep vertical sprint | Intermediate vertical route near the sideline |
| Primary Objective | Stretch defense and gain maximum yardage quickly | Create separation in zone coverage for mid-range completion |
| Typical Distance | 15+ yards | 10-15 yards |
| Coverage Targeted | Single coverage or deep safety | Linebackers and defensive backs in zone |
| Ideal Usage | When speed advantage exists and defense is vulnerable deep | Against zones with soft underneath coverage |
| Risk Level | High - Requires accurate deep throw and timing | Moderate - Safer intermediate pass option |
Introduction to Go Route and Seam Route
Go Route is a concurrency pattern in Go programming language that uses goroutines to manage multiple tasks simultaneously with lightweight threads, enhancing execution efficiency. Seam Route, contrastingly, is a routing mechanism in web frameworks that emphasizes seamless integration and flexible request handling for optimized web application performance. Both enable efficient task management but are applied in different programming contexts--Go Route for concurrent execution and Seam Route for routing web traffic.
Understanding the Basics of Routing
Go route and Seam route are fundamental concepts in web development frameworks that manage URL patterns and navigation. Go route typically refers to routing in Go language frameworks like Gin or Echo, where routes define handlers for HTTP requests based on specific URI patterns. Seam route, often associated with Seam framework in Java, integrates routing with business logic, emphasizing stateful navigation and context propagation across different UI components.
Key Features of Go Route
Go Route offers lightweight goroutines that enable efficient concurrent programming with minimal memory overhead and fast context switching. It provides built-in synchronization primitives and a simple, idiomatic API that integrates seamlessly with Go's runtime scheduler for optimal performance. Unlike Seam Route, Go Route emphasizes scalability and low-latency execution, making it ideal for high-throughput, distributed applications.
Key Features of Seam Route
Seam Route in web development offers seamless integration with Java EE components, providing built-in support for contextual lifecycle management and state management, which enhances scalability in enterprise applications. Its key features include advanced bijection for automatic injection, event-driven programming models, and enhanced component composition capabilities that outperform traditional Go routes. Seam Route's ability to manage conversational state across multiple HTTP requests makes it ideal for complex user interactions requiring persistent session data.
Performance Comparison: Go Route vs Seam Route
Go routes provide lightweight concurrency with minimal memory overhead, enabling thousands of goroutines to run efficiently on a single OS thread. Seam routes, typically implemented in frameworks focusing on stateful session management, often incur higher context-switching costs and memory usage due to maintaining runtime state. Benchmark tests consistently show Go routes outperform Seam routes in raw throughput and latency under high concurrency scenarios, making them ideal for scalable, performance-critical applications.
Ease of Integration and Usability
GoRoute offers seamless integration with Flutter's Navigator 2.0, providing simple APIs that streamline route management and improve developer productivity. SeamRoute emphasizes minimal setup and straightforward route declarations, making it highly accessible for developers seeking quick implementation. Both frameworks deliver strong usability, with GoRoute catering to complex navigation needs and SeamRoute excelling in rapid, lightweight integration.
Compatibility with Flutter Navigation Principles
GoRouter aligns seamlessly with Flutter's declarative navigation by enabling intuitive route definitions and dynamic deep linking, enhancing state management within Flutter apps. SeamRoute, while offering route abstraction, may introduce imperative patterns that can conflict with Flutter's navigation stack approach, potentially complicating route synchronization. Developers seeking tight integration with Flutter's Navigator 2.0 API often prefer GoRouter for its compatibility and streamlined navigation experience.
Scalability and Maintenance
Go routines offer lightweight concurrency with minimal memory overhead, enabling efficient scalability for large-scale applications due to their multiplexing on OS threads. Seam routes, typically used in JSF frameworks, integrate tightly with stateful components, which can complicate scalability as session management demands increase. Maintenance of Go routines benefits from Go's simple syntax and strong standard library support, while Seam routes require careful handling of session states and context propagation, increasing complexity in long-term upkeep.
Community Support and Ecosystem
Seam route boasts a robust community with a large number of active contributors, extensive documentation, and a well-established ecosystem encompassing plugins and integrations that streamline development workflows. Go route benefits from a growing, enthusiastic community focused on performance and scalability, supported by modern tooling and an expanding set of libraries tailored for microservices and cloud-native environments. Both frameworks emphasize community-driven enhancements, but Seam route's mature ecosystem provides more third-party resources and enterprise-grade solutions compared to the newer but rapidly evolving Go route ecosystem.
Choosing the Right Route Management Solution
Choosing the right route management solution depends on the specific needs of your Go application; Go route offers lightweight, high-performance routing ideal for microservices and RESTful APIs, whereas Seam route provides advanced features suited for complex enterprise workflows. Go route excels in simplicity and speed with minimal overhead, making it preferred for scalable, high-concurrency environments. Seam route supports rich middleware integration and dynamic route management, enhancing flexibility for applications requiring intricate route handling and security policies.
Go route Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com