Batting average is a key statistic in baseball that measures a player's hitting performance by dividing the number of hits by official at-bats. This metric helps evaluate a batter's consistency and ability to reach base, providing insights into their offensive value. Discover how understanding your batting average can enhance your appreciation of the game in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
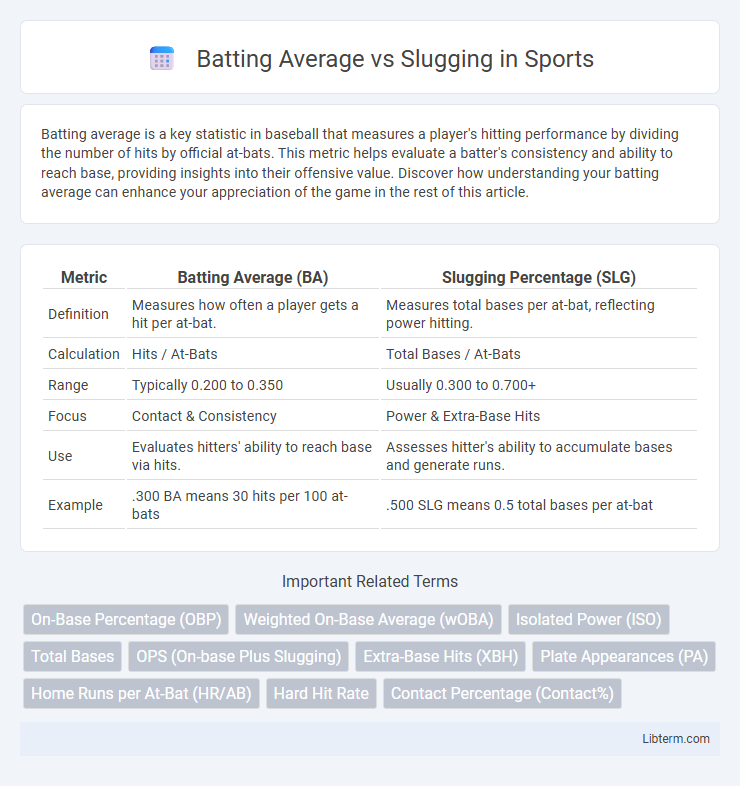
| Metric | Batting Average (BA) | Slugging Percentage (SLG) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures how often a player gets a hit per at-bat. | Measures total bases per at-bat, reflecting power hitting. |
| Calculation | Hits / At-Bats | Total Bases / At-Bats |
| Range | Typically 0.200 to 0.350 | Usually 0.300 to 0.700+ |
| Focus | Contact & Consistency | Power & Extra-Base Hits |
| Use | Evaluates hitters' ability to reach base via hits. | Assesses hitter's ability to accumulate bases and generate runs. |
| Example | .300 BA means 30 hits per 100 at-bats | .500 SLG means 0.5 total bases per at-bat |
Introduction to Batting Average and Slugging
Batting average measures a hitter's success rate by dividing hits by official at-bats, reflecting consistency at the plate. Slugging percentage evaluates a player's power by calculating total bases per at-bat, emphasizing extra-base hits like doubles, triples, and home runs. Together, batting average and slugging percentage provide a comprehensive view of a batter's effectiveness and power-hitting capabilities.
Defining Batting Average
Batting average measures a player's hitting success by dividing hits by at-bats, reflecting how often a batter reaches base via a hit. In contrast, slugging percentage evaluates the quality of hits by assigning weights based on bases earned, emphasizing power hitting. Understanding batting average provides insight into a hitter's consistency, while slugging percentage highlights their ability to generate extra-base hits.
What Is Slugging Percentage?
Slugging percentage measures a baseball player's power-hitting ability by calculating total bases achieved per at-bat, offering a deeper insight into offensive performance than batting average. Unlike batting average, which counts hits regardless of type, slugging percentage weights hits by their extra-base value--singles, doubles, triples, and home runs--to reflect a hitter's impact on scoring potential. This metric is crucial for evaluating players' power and productivity, helping teams identify consistent run producers beyond just the number of hits.
Calculating Batting Average vs Slugging
Calculating batting average involves dividing the number of hits by the total at-bats, measuring a player's ability to get on base. Slugging percentage is calculated by total bases achieved on hits divided by at-bats, reflecting a batter's power-hitting performance. Understanding both stats provides insight into a player's overall offensive contribution, with batting average emphasizing contact and slugging highlighting extra-base hits.
Key Differences Between Batting Average and Slugging
Batting average measures a player's hitting success by calculating hits per at-bat, while slugging percentage evaluates the power of a hitter by assigning weighted values to different hit types, such as singles, doubles, triples, and home runs. Key differences include batting average treating all hits equally regardless of type, whereas slugging percentage emphasizes extra-base hits to reflect a player's ability to generate runs. Slugging percentage often provides deeper insight into offensive impact by capturing both contact skill and power hitting.
Historical Significance in Baseball Analytics
Batting average, a key historical metric in baseball analytics, measures a hitter's ability to reach base via hits, reflecting early 20th-century emphasis on contact hitting and consistency. Slugging percentage evolved as a complementary statistic, capturing power hitting by accounting for total bases per at-bat, which gained prominence during the mid-20th century as home runs and extra-base hits became more valued. The historical significance of these metrics underscores baseball's analytical transition from simplistic contact evaluation towards a more nuanced understanding of offensive production and overall player value.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Metric
Batting average measures a player's ability to get hits, providing a clear snapshot of contact skill but ignores the quality of those hits and power contribution. Slugging percentage accounts for total bases per at-bat, highlighting a hitter's power and extra-base hits but can overvalue power hitters who have lower contact rates. While batting average offers simplicity and straightforward consistency, slugging percentage delivers deeper insight into offensive productivity by emphasizing impact hits.
Impact on Player Evaluation and Team Strategy
Batting average measures a player's ability to get hits, reflecting consistency in reaching base, while slugging percentage quantifies power-hitting by accounting for extra-base hits, impacting a player's overall offensive contribution. Teams prioritize slugging to enhance run production, influencing lineup construction and strategic resource allocation toward power hitters. Combining batting average and slugging percentages offers a comprehensive evaluation of a player's offensive value, shaping scouting decisions and in-game strategies.
Modern Trends in Hitting Statistics
Modern trends in hitting statistics highlight a shift toward valuing slugging percentage over traditional batting average, as power hitting increasingly influences game outcomes. Advanced analytics emphasize on-base plus slugging (OPS) and weighted metrics like wOBA to better capture a player's overall offensive contribution. This evolution reflects a broader understanding that slugging percentage more accurately predicts run production and team success in contemporary baseball.
Conclusion: Which Metric Matters Most?
Slugging percentage offers a more comprehensive evaluation of a player's offensive impact by accounting for total bases and power-hitting ability, unlike batting average which only measures hit frequency. While batting average remains a useful indicator for consistent contact, slugging percentage better predicts run production and overall offensive value. For teams aiming to maximize scoring opportunities, slugging percentage typically matters more in player assessment and strategic decisions.
Batting Average Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com