Inside zone running is a fundamental technique in football, focusing on powerful, precise footwork to exploit gaps between the offensive linemen. Mastering this play enhances your team's rushing attack by creating reliable lane options and forcing defenses to commit to blocks. Explore the article to uncover the key strategies and drills that can elevate your inside zone game.
Table of Comparison
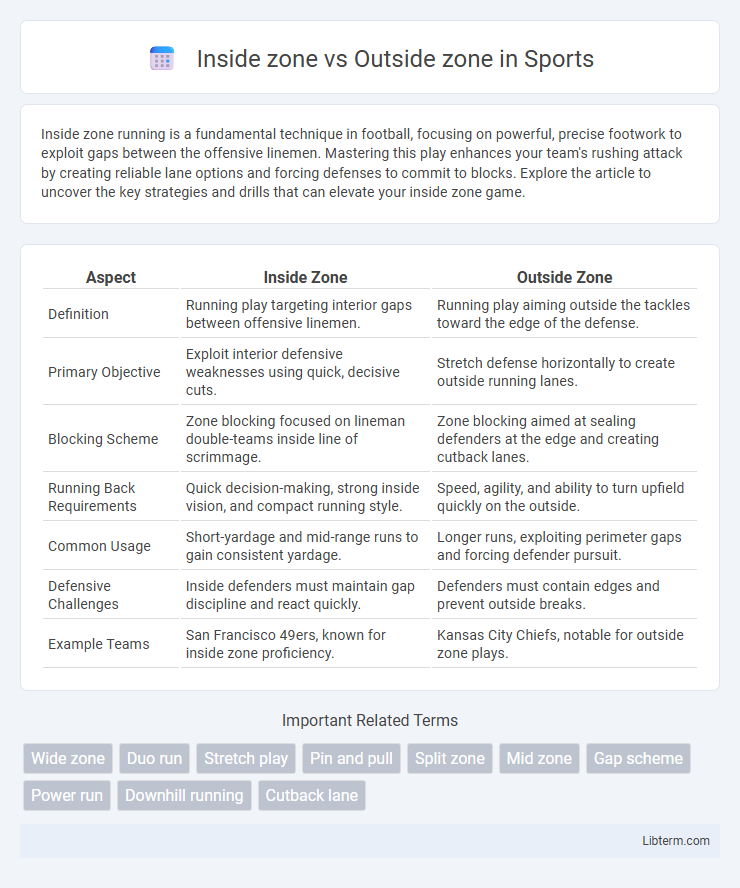
| Aspect | Inside Zone | Outside Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Running play targeting interior gaps between offensive linemen. | Running play aiming outside the tackles toward the edge of the defense. |
| Primary Objective | Exploit interior defensive weaknesses using quick, decisive cuts. | Stretch defense horizontally to create outside running lanes. |
| Blocking Scheme | Zone blocking focused on lineman double-teams inside line of scrimmage. | Zone blocking aimed at sealing defenders at the edge and creating cutback lanes. |
| Running Back Requirements | Quick decision-making, strong inside vision, and compact running style. | Speed, agility, and ability to turn upfield quickly on the outside. |
| Common Usage | Short-yardage and mid-range runs to gain consistent yardage. | Longer runs, exploiting perimeter gaps and forcing defender pursuit. |
| Defensive Challenges | Inside defenders must maintain gap discipline and react quickly. | Defenders must contain edges and prevent outside breaks. |
| Example Teams | San Francisco 49ers, known for inside zone proficiency. | Kansas City Chiefs, notable for outside zone plays. |
Understanding Zone Running Schemes
Understanding zone running schemes involves differentiating between inside zone and outside zone plays, both essential concepts in football offenses. Inside zone runs target gaps between the offensive guards and tackles, emphasizing linemen creating cutback lanes and running backs reading defensive reactions for optimal paths. Outside zone plays stretch the defense horizontally, with linemen moving laterally to seal defenders and running backs aiming to reach the edge before deciding to cut upfield or bounce outside.
What is Inside Zone?
Inside zone is a running play in football where the offensive line blocks defenders primarily toward the play's interior, creating lanes between the center and guards. The running back targets these inside gaps, reading blocks and deciding to cut upfield through the most promising hole. This scheme emphasizes quick, zone-based blocking techniques designed to exploit defensive alignment and leverage inside pressure.
Key Characteristics of Inside Zone
Inside zone runs emphasize quick, decisive handoffs to the running back, targeting gaps between the offensive guard and center. This play focuses on zone blocking techniques where linemen move laterally to create cutback lanes, relying on agility and coordination. Success depends on the back's vision and ability to find creases within tight defensive fronts.
What is Outside Zone?
Outside zone blocking is an offensive line technique in football where linemen block laterally toward the sideline, aiming to create running lanes outside the tackles. This approach contrasts with the inside zone, which targets gaps between the guards and tackles. Outside zone emphasizes speed and agility, allowing the running back to read blocks and choose the optimal path along the edge of the defense.
Key Characteristics of Outside Zone
The outside zone run in football emphasizes reaching the edge of the offensive line to create cutback lanes by stretching the defense horizontally. This play relies on the offensive linemen executing zone blocking schemes with emphasis on reaching defenders on the perimeter or sealing them inside, allowing the running back to read and choose the best gap outside the tackles. Speed and agility are critical for backs in the outside zone, as they must quickly navigate to the edge and exploit space created by the blockers' lateral movement.
Blocking Techniques: Inside vs Outside Zone
Inside zone blocking techniques emphasize maintaining leverage by blocking defenders directly inside the offensive line, using a combination of reach blocks and drive blocks to create running lanes between the guard and tackle. Outside zone blocking focuses on horizontal movement, requiring linemen to block defenders laterally toward the sideline, often employing zone steps and controlling defenders at the second level to stretch the defense horizontally. Both techniques rely on precise footwork and coordination, but inside zone prioritizes vertical push, while outside zone prioritizes lateral space creation.
Offensive Line Responsibilities
Inside zone and outside zone blocking schemes demand distinct offensive line responsibilities to maximize rushing success. In the inside zone, linemen prioritize quick, lateral movement to create vertical running lanes by targeting defenders in the B-gap area, maintaining zone integrity through combo blocks and second-level engagements. Conversely, outside zone blocking emphasizes reaching edge defenders and sealing them out, requiring linemen to execute stretch blocks with agile footwork to open horizontal cutback lanes for the running back.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Scheme
Inside zone schemes offer offensive linemen clear inside leverage, enhancing run blocking efficiency and creating downhill rushing lanes typically benefiting power runners; however, defenders can anticipate cuts inside, presenting challenges in defensive penetration scenarios. Outside zone schemes extend play direction horizontally, enabling running backs to stretch defenses sideline-to-sideline and exploit cutback lanes, although this requires highly agile linemen and backs to maintain effective pursuit angles and timing. Both schemes demand precise coordination but provide strategic versatility by diversifying rushing attack options and adapting to defensive alignments.
When to Use Inside vs Outside Zone
Inside zone running works best in short-yardage or goal-line situations where offensive linemen can create tight gaps for quick-hitting runs. Outside zone running excels in open-field scenarios, allowing backs to stretch the defense laterally and exploit edge pursuit angles. Choosing between inside and outside zone depends on defensive alignment, down-and-distance, and the running back's agility and vision.
Impact on Running Back Play
Inside zone runs emphasize zone blocking with linemen targeting defenders closer to the formation's interior, creating cutback lanes that rely on the running back's vision and patience. Outside zone runs stress lateral movement of blocking schemes toward the edge, requiring the running back to accelerate outside and make quick decisions on whether to bounce the run or cut upfield. The impact on running back play differs as inside zone prioritizes decisive cuts and power, while outside zone demands speed, agility, and spatial awareness.
Inside zone Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com