The push-up hold is an effective exercise that strengthens your chest, shoulders, and core by engaging multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Maintaining a steady plank-like position challenges stability and endurance, enhancing overall muscular control. Discover how incorporating push-up holds into your routine can elevate your fitness journey by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
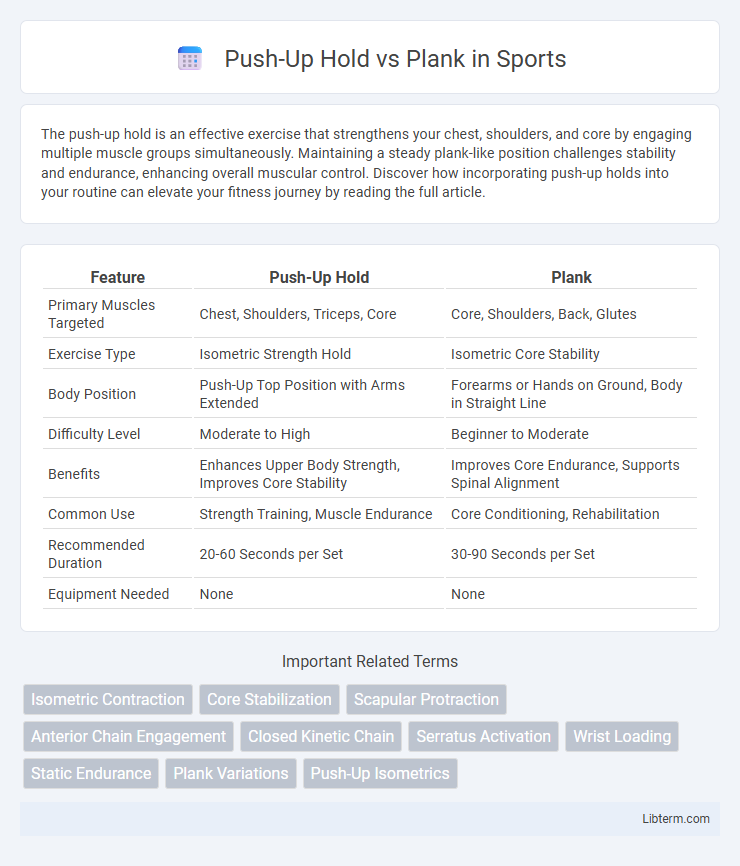
| Feature | Push-Up Hold | Plank |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Muscles Targeted | Chest, Shoulders, Triceps, Core | Core, Shoulders, Back, Glutes |
| Exercise Type | Isometric Strength Hold | Isometric Core Stability |
| Body Position | Push-Up Top Position with Arms Extended | Forearms or Hands on Ground, Body in Straight Line |
| Difficulty Level | Moderate to High | Beginner to Moderate |
| Benefits | Enhances Upper Body Strength, Improves Core Stability | Improves Core Endurance, Supports Spinal Alignment |
| Common Use | Strength Training, Muscle Endurance | Core Conditioning, Rehabilitation |
| Recommended Duration | 20-60 Seconds per Set | 30-90 Seconds per Set |
| Equipment Needed | None | None |
Introduction to Push-Up Hold and Plank
Push-Up Hold engages the chest, shoulders, and triceps by maintaining a lowered push-up position, enhancing isometric strength and core stability. Plank targets the entire core, including the abdominals, lower back, and glutes, by holding a straight-arm or forearm position, emphasizing endurance and spinal alignment. Both exercises improve muscular endurance and core activation but differ in muscle emphasis and joint positioning.
What Is a Push-Up Hold?
A push-up hold is an isometric exercise where you lower your body midway down in a push-up position and maintain that static stance, engaging the chest, shoulders, triceps, and core muscles. Unlike a plank, which primarily targets core stability by holding a straight-arm or forearm position on the floor, a push-up hold requires additional upper body strength due to the lowered arm angle. This exercise increases muscular endurance and strength by emphasizing tension in the upper body and core simultaneously.
What Is a Plank?
A plank is an isometric core exercise that involves maintaining a position similar to a push-up for an extended period, primarily targeting the transverse abdominis, rectus abdominis, and obliques. Unlike the push-up hold, which engages the chest, shoulders, and triceps more intensely due to slight elbow flexion, the plank emphasizes core stability with arms fully extended and hips aligned with the shoulders and ankles. This makes the plank an essential exercise for enhancing static core endurance and postural control.
Key Differences Between Push-Up Hold and Plank
Push-Up Hold primarily targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps by maintaining a bent-arm position just above the ground, emphasizing upper body strength and stability. In contrast, the Plank engages the core muscles intensively, including the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques, focusing on overall core endurance and spinal alignment. The Push-Up Hold demands greater joint flexion and dynamic muscle tension, while the Plank maintains a neutral arm extension, promoting isometric core stabilization.
Muscles Worked: Push-Up Hold vs Plank
Push-up holds primarily engage the chest muscles (pectoralis major), triceps, and shoulders (deltoids), while also activating the core for stabilization. Planks emphasize core strength by targeting the rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, and obliques, with secondary activation of the glutes and lower back muscles. Both exercises improve upper body endurance but differ in muscle emphasis due to variations in body positioning and load distribution.
Benefits of the Push-Up Hold
The push-up hold strengthens the chest, shoulders, and triceps while enhancing core stability more dynamically than a plank. It engages multiple upper body muscles simultaneously, promoting improved muscular endurance and joint stability. This exercise also activates the scapular stabilizers, reducing injury risk and boosting overall upper body strength.
Benefits of the Plank
The plank enhances core stability by engaging the transverse abdominis, rectus abdominis, and obliques, improving overall posture and reducing lower back pain. It activates multiple muscle groups including the shoulders, chest, and glutes, promoting full-body strength and endurance. Maintaining a plank position boosts balance and coordination, supporting functional fitness and injury prevention.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common mistakes in Push-Up Hold include sagging hips and flared elbows, which strain the lower back and shoulders; maintain a straight line from head to heels and keep elbows close to the body to prevent injury. In Plank, common errors are collapsing the torso and lifting the hips too high, reducing core engagement; engage the core fully and align the body horizontally to maximize effectiveness. Avoid these errors by focusing on proper form, engaging target muscles, and using mirrors or video feedback for self-correction.
Which Exercise Is Best for Your Fitness Goals?
Push-Up Holds primarily target upper body strength by engaging the chest, shoulders, and triceps while also activating the core, making them ideal for building muscle endurance and improving upper body stability. Planks focus extensively on core stability by activating the abdominal muscles, lower back, and glutes, which enhances overall balance and posture. Choosing between Push-Up Holds and Planks depends on your fitness goals: prioritize Push-Up Holds for upper body strength and endurance, and Planks for core conditioning and spinal support.
How to Incorporate Both Into Your Routine
Incorporate push-up holds and planks into your workout routine by alternating between the two exercises to target different muscle groups and enhance core stability. Perform push-up holds to engage the chest, shoulders, and triceps, then follow with planks to strengthen the abdominal muscles, lower back, and improve overall endurance. Combining these isometrically focused exercises maximizes upper body strength and core conditioning for balanced functional fitness.
Push-Up Hold Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com