Supination refers to the outward roll of the foot during normal motion, playing a crucial role in shock absorption and balance. It affects how your weight is distributed when walking or running, potentially influencing foot and leg health. Explore the rest of the article to understand how supination impacts your movement and ways to address it.
Table of Comparison
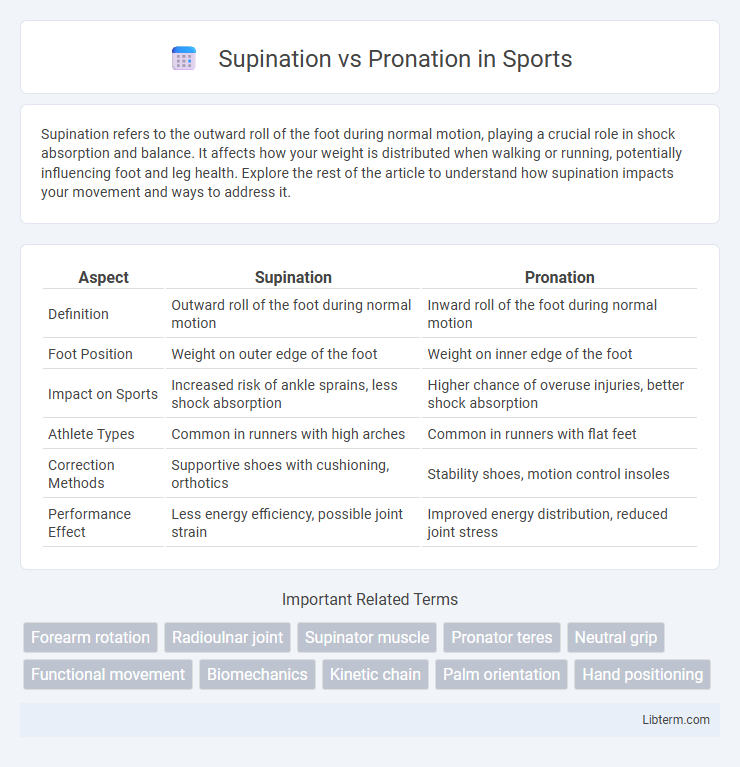
| Aspect | Supination | Pronation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outward roll of the foot during normal motion | Inward roll of the foot during normal motion |
| Foot Position | Weight on outer edge of the foot | Weight on inner edge of the foot |
| Impact on Sports | Increased risk of ankle sprains, less shock absorption | Higher chance of overuse injuries, better shock absorption |
| Athlete Types | Common in runners with high arches | Common in runners with flat feet |
| Correction Methods | Supportive shoes with cushioning, orthotics | Stability shoes, motion control insoles |
| Performance Effect | Less energy efficiency, possible joint strain | Improved energy distribution, reduced joint stress |
Understanding Supination and Pronation
Supination and pronation describe the rotational movements of the forearm or foot that impact biomechanics and posture. Supination involves rotating the forearm or foot outward, turning the palm or sole upward or outward, while pronation is the inward rotation that turns the palm or sole downward or inward. Understanding these movements is essential for diagnosing gait abnormalities, preventing injuries, and optimizing athletic performance.
The Biomechanics of Foot Movement
Supination and pronation describe the rotational movements of the foot during gait, where supination involves outward rolling and pronation involves inward rolling of the foot. Biomechanically, pronation allows for shock absorption by flattening the arch, while supination provides stability and a rigid lever for propulsion. These movements are critical in distributing forces across the foot, influencing overall lower limb alignment and risk of injury.
Key Differences Between Supination and Pronation
Supination involves the outward roll of the foot or hand, where the sole faces upward or outward, while pronation refers to the inward roll, with the sole facing downward or inward. Key differences include the alignment of the ankle and wrist joints, affecting gait and hand positioning during activities such as walking or weightlifting. Understanding these movements is crucial for diagnosing foot disorders, improving athletic performance, and selecting appropriate footwear or ergonomic tools.
Causes of Supination and Pronation
Supination occurs when the foot rolls outward during walking or running, often caused by high arches, weak ankle muscles, or improper footwear that lacks adequate cushioning. Pronation involves the inward roll of the foot and is typically caused by flat feet, muscle imbalances, or overuse on hard surfaces, leading to excessive stress on the inner foot. Both conditions can result from biomechanical abnormalities, repetitive strain, or structural issues in the legs and feet.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Signs and symptoms to watch for in supination include excessive outward rolling of the foot, resulting in ankle instability, heel pain, and increased risk of stress fractures. Pronation typically presents with inward rolling of the foot, causing arch pain, shin splints, and knee discomfort due to improper weight distribution. Both conditions may lead to joint strain and require timely assessment to prevent chronic biomechanical issues.
Effects on Gait and Posture
Supination and pronation significantly influence gait mechanics and posture by altering foot strike patterns and weight distribution. Excessive supination leads to increased pressure on the outer foot edge, potentially causing instability and reduced shock absorption, while overpronation results in inward rolling of the foot, promoting excessive strain on the knees and hips. Proper alignment and balance of supination and pronation are critical to maintaining efficient locomotion and preventing musculoskeletal injuries.
Common Injuries Linked to Each
Supination often leads to injuries such as ankle sprains, plantar fasciitis, and iliotibial band syndrome due to excessive outward rolling of the foot. Pronation is commonly associated with shin splints, bunions, and patellar tendinitis, resulting from the foot rolling inward excessively. Both biomechanical patterns can contribute to knee, hip, and lower back pain if left unaddressed during physical activities.
Diagnosis: How Experts Identify Your Gait
Gait analysis is essential for diagnosing supination and pronation by evaluating foot alignment, pressure distribution, and movement patterns during walking or running. Experts use tools like pressure mats, video motion analysis, and wearable sensors to measure deviations in foot strike and arch behavior. Accurate diagnosis helps tailor interventions such as custom orthotics or targeted exercises to correct gait abnormalities and prevent injury.
Treatment Options and Preventative Measures
Treatment options for supination and pronation primarily include custom orthotic insoles to correct foot alignment and physical therapy exercises aimed at strengthening the ankle and improving balance. Preventative measures emphasize wearing supportive footwear with proper arch support, maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the feet, and incorporating regular stretching and strengthening routines to enhance foot mobility. Early intervention with these strategies can minimize pain, prevent injuries, and improve overall foot biomechanics in individuals experiencing supination or pronation.
Choosing the Right Footwear for Your Gait
Selecting the right footwear for supination or pronation involves understanding your gait to prevent injuries and enhance comfort. Supinators require shoes with ample cushioning and flexibility to absorb shock and support the outer foot, while pronators benefit from motion control or stability shoes that provide extra arch support and correct inward rolling. Using gait analysis tools or consulting a podiatrist ensures optimal footwear that aligns with your specific foot biomechanics, promoting balance and reducing strain.
Supination Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com