Push block puzzles challenge your spatial reasoning and problem-solving skills by requiring you to move blocks strategically to clear a path or reach a goal. Mastering these puzzles enhances your logical thinking and patience, making them a favorite in both casual gaming and educational environments. Discover effective strategies and tips to improve your gameplay in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
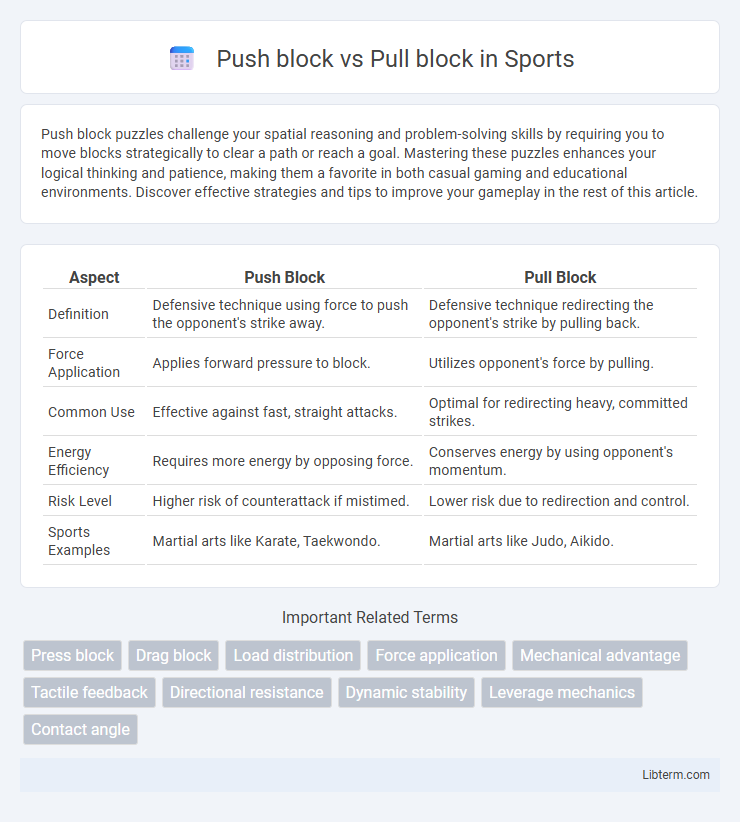
| Aspect | Push Block | Pull Block |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Defensive technique using force to push the opponent's strike away. | Defensive technique redirecting the opponent's strike by pulling back. |
| Force Application | Applies forward pressure to block. | Utilizes opponent's force by pulling. |
| Common Use | Effective against fast, straight attacks. | Optimal for redirecting heavy, committed strikes. |
| Energy Efficiency | Requires more energy by opposing force. | Conserves energy by using opponent's momentum. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk of counterattack if mistimed. | Lower risk due to redirection and control. |
| Sports Examples | Martial arts like Karate, Taekwondo. | Martial arts like Judo, Aikido. |
Introduction to Push Block and Pull Block
Push block and pull block techniques are essential tools in precision fabric cutting and garment making. Push block involves applying forward pressure to efficiently guide fabric through cutting machines, enhancing stability and control. Pull block, by contrast, uses backward pulling motion to carefully maneuver fabric, improving accuracy in detailed or curved cuts.
Understanding the Push Block Technique
The push block technique in woodworking involves applying forward pressure on the workpiece using the palm and fingers while the thumb guides it over the blade, ensuring maximum control and safety. This method reduces the risk of kickback by keeping hands away from the cutting edge and stabilizes the material during precise cuts, enhancing accuracy on table saws or jointers. Understanding this technique is crucial for woodworkers aiming to maintain consistent feed rate and avoid injuries during complex or repetitive cutting tasks.
Overview of Pull Block Method
The Pull Block method in software development emphasizes extracting necessary data or functionalities only when required, minimizing resource usage and improving application responsiveness. Unlike the Push Block approach, which sends data proactively, Pull Block relies on client requests to initiate data transfer, enhancing control over information flow and reducing unnecessary processing. This method is especially effective in scenarios with variable demand, ensuring efficient synchronization and optimized network performance.
Key Differences Between Push Block and Pull Block
Push block systems apply force by pushing material or components forward, typically used in conveyor or manufacturing processes where items are moved in a continuous flow. Pull block systems, conversely, exert force by pulling materials or components, often employed to maintain tension or control positioning in assembly lines. Key differences include direction of applied force, applications in different mechanical operations, and the type of stress exerted on materials, with push blocks focusing on compressive forces and pull blocks emphasizing tensile forces.
Advantages of Using Push Block
Push blocks enhance user interaction by allowing users to input data directly into the system, enabling real-time feedback and immediate processing. This facilitates smoother integration in applications requiring continuous data flow, improving responsiveness and reducing latency. Utilizing push blocks also minimizes resource consumption by transmitting only relevant data changes instead of requesting information repetitively.
Benefits of the Pull Block Approach
The Pull Block approach enhances system efficiency by allowing components to request data only when needed, reducing unnecessary processing and network load. It improves scalability by enabling dynamic data retrieval, which adapts to varying demand without overwhelming the system. This method fosters better resource utilization and responsiveness in distributed architectures or data-driven applications.
Common Applications for Each Method
Push block systems are commonly used in manufacturing assembly lines, where precise, automated movement of materials ensures consistent production flow and reduces manual labor. Pull block methods are favored in inventory management and lean manufacturing, enabling just-in-time resource allocation and minimizing overproduction by responding directly to demand signals. Both methods optimize workflow efficiency, with push blocks driving planned sequences and pull blocks enhancing responsiveness to real-time requirements.
Safety Considerations: Push Block vs Pull Block
Push blocks offer enhanced safety by keeping hands away from cutting blades and reducing the risk of kickback during woodworking operations. Pull blocks, while effective for guiding stock, may expose fingers to closer proximity with cutting surfaces, increasing potential hazards if not used carefully. Proper use of push blocks significantly minimizes injury risks by providing stable control and maintaining a safe distance from machinery.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Choosing between push block and pull block techniques depends on project scale, resource availability, and desired workflow efficiency. Push block methods excel in environments prioritizing rapid task completion by pushing materials or data forward, ideal for assembly lines or streamlined production. Pull block strategies emphasize demand-driven processes, reducing waste and aligning inventory with actual consumption, making them optimal for projects requiring flexibility and just-in-time resource management.
Conclusion: Push Block or Pull Block?
Push block systems offer greater control over data flow and reduced latency by actively sending information to receivers, making them ideal for real-time applications. Pull block mechanisms provide flexibility and efficient resource use by allowing receivers to request data as needed, suitable for on-demand processing scenarios. Choosing between push and pull blocks depends on the specific use case requirements for data timeliness and system responsiveness.
Push block Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com