A hot route is a tactical football play adjustment where a receiver changes their intended route based on the defense's alignment to gain a strategic advantage. This quick decision-making enhances your team's ability to exploit defensive weaknesses and create better scoring opportunities. Explore the rest of the article to master the intricacies of hot routes and improve your game strategy.
Table of Comparison
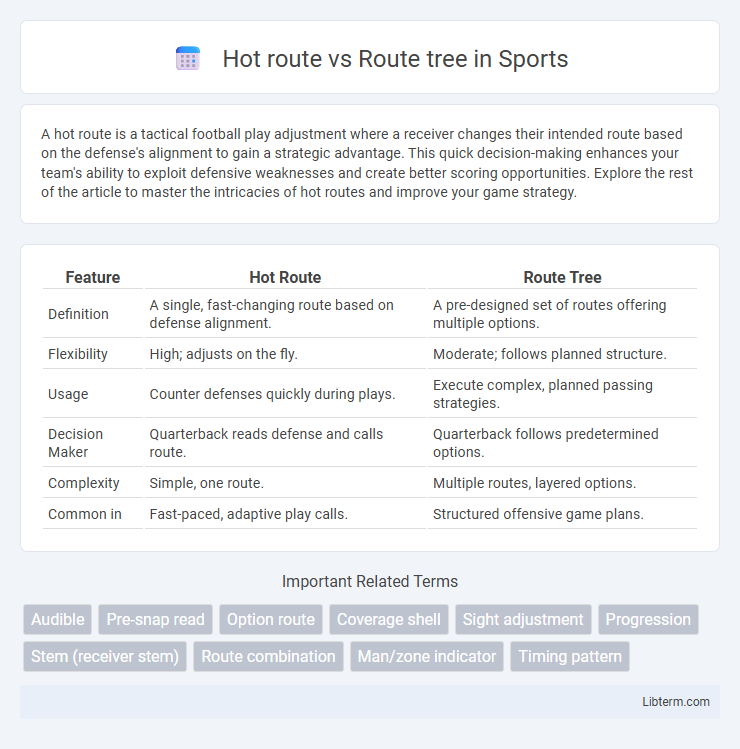
| Feature | Hot Route | Route Tree |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A single, fast-changing route based on defense alignment. | A pre-designed set of routes offering multiple options. |
| Flexibility | High; adjusts on the fly. | Moderate; follows planned structure. |
| Usage | Counter defenses quickly during plays. | Execute complex, planned passing strategies. |
| Decision Maker | Quarterback reads defense and calls route. | Quarterback follows predetermined options. |
| Complexity | Simple, one route. | Multiple routes, layered options. |
| Common in | Fast-paced, adaptive play calls. | Structured offensive game plans. |
Introduction to Hot Route vs Route Tree
Hot Route and Route Tree are two methodologies used in navigation and routing systems to optimize path selection and data processing. Hot Route focuses on frequently traveled paths by prioritizing high-traffic routes, improving efficiency through real-time updates and dynamic adjustments. Route Tree, on the other hand, organizes all possible routes into a hierarchical structure, enabling systematic exploration and route selection based on defined criteria and branching logic.
Definitions: What is a Hot Route?
A Hot Route is a focused path within a routing system designed to optimize performance by prioritizing frequently accessed routes for faster processing. It enables quicker data retrieval and reduced latency by directing traffic through these pre-defined segments. Unlike a Route Tree, which represents the entire hierarchical routing structure, a Hot Route isolates critical pathways to enhance efficiency.
Definitions: What is a Route Tree?
A Route Tree is a hierarchical structure used in network routing to organize and manage multiple routing paths efficiently. It allows for the aggregation of routes, reducing the routing table size and improving lookup speed by grouping routes with common prefixes. This structure contrasts with Hot Routes, which represent the most frequently used or optimal paths in the routing table, focusing primarily on performance rather than structural organization.
Key Differences Between Hot Routes and Route Tree
Hot routes prioritize high-traffic paths by directly optimizing them for faster performance, often used in delivery and logistics to reduce travel time. Route trees organize routes hierarchically from a central node, enabling scalable and systematic route planning but may not focus on immediate traffic conditions. Key differences include hot routes' emphasis on speed and traffic prioritization versus route trees' structural and hierarchical route organization.
Importance of Hot Routes in Offensive Schemes
Hot routes are critical in offensive schemes as they allow quarterbacks to quickly adjust passing options based on defensive pressure, enhancing the offense's adaptability against blitzes and tight coverage. These routes prioritize rapid decision-making by providing short, high-percentage targets, increasing the likelihood of successful completions during fast-developing plays. In contrast, route trees represent the full array of predetermined routes, but without the flexibility offered by hot routes to counteract aggressive defenses effectively.
How Route Trees Structure Receiver Assignments
Route trees structure receiver assignments by organizing routing rules into a hierarchical, branched format where each node represents a decision point based on criteria like sender address or message type. Hot routes prioritize immediate, direct routing by mapping specific sender-receiver pairs without hierarchical checks, enabling faster message processing but less flexibility. Route trees enhance scalability and maintainability by allowing multiple routes to share branches, efficiently managing complex receiver assignments across diverse conditions.
Situational Use: When to Call a Hot Route
A hot route is best used in high-priority, time-sensitive situations within call center management when immediate rerouting based on specific criteria like caller urgency or queue overflow is necessary. Route trees offer a broader, more complex decision-making framework where multiple conditions and branching logic determine call flow, suitable for general routing scenarios. Employ hot routes to override default paths instantly during emergencies or peak times, ensuring rapid response and minimizing wait times.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Hot Routes
Hot routes in visual scripting offer faster execution by converting node connections directly into code, improving runtime performance and reducing overhead compared to traditional route trees. However, hot routes sacrifice flexibility, as their static structure limits dynamic changes during gameplay and complicates debugging due to less visual clarity. The trade-off between increased speed and reduced adaptability must be considered when choosing hot routes over route trees for game development workflows.
Training Receivers: Mastering the Route Tree
Training receivers to master the route tree enhances their ability to read defenses and adjust routes on the fly, leading to more effective passing plays. Unlike hot routes that require immediate adaptation to blitzes or pressure, understanding the full route tree allows receivers to exploit zone coverage and find open spaces. Mastery of the route tree improves timing and communication between quarterback and receiver, optimizing overall offensive efficiency.
Impact on Defense: How Hot Routes and Route Trees Challenge Coverage
Hot routes and route trees significantly impact defensive coverage by introducing unpredictable adjustments and layered route combinations, forcing defenders to quickly adapt and communicate. Hot routes allow quarterbacks to modify receiver routes based on defensive alignment, creating mismatches and exploiting coverage weaknesses. Route trees expand pass options with multiple route depths and patterns, complicating zone and man coverage assignments and increasing the risk of blown coverages.
Hot route Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com