A bowling lane is a long, narrow surface where the ball is rolled towards pins in the classic game of bowling. Its smooth, polished wooden or synthetic finish ensures consistent ball movement and accuracy. Discover how understanding the lane's design can improve your technique and elevate your game in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
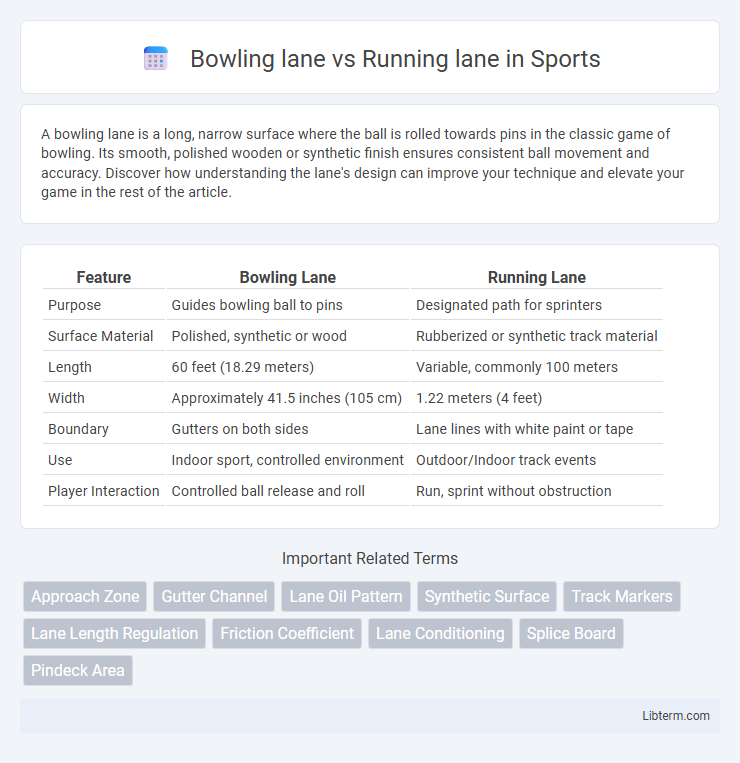
| Feature | Bowling Lane | Running Lane |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Guides bowling ball to pins | Designated path for sprinters |
| Surface Material | Polished, synthetic or wood | Rubberized or synthetic track material |
| Length | 60 feet (18.29 meters) | Variable, commonly 100 meters |
| Width | Approximately 41.5 inches (105 cm) | 1.22 meters (4 feet) |
| Boundary | Gutters on both sides | Lane lines with white paint or tape |
| Use | Indoor sport, controlled environment | Outdoor/Indoor track events |
| Player Interaction | Controlled ball release and roll | Run, sprint without obstruction |
Introduction to Bowling Lanes vs Running Lanes
Bowling lanes are smooth, narrow tracks made of polished wood or synthetic materials designed for rolling bowling balls toward pins, typically measuring 60 feet in length and 42 inches in width. Running lanes, found on outdoor or indoor tracks, are marked strips usually 1.22 meters wide, intended for athletes to sprint or race over distances ranging from 100 meters to 400 meters. The primary function of bowling lanes emphasizes precise ball control and pin targeting, while running lanes focus on speed, stride, and individual athlete performance in standardized track events.
Structure and Design Differences
Bowling lanes feature a smooth, polished wooden or synthetic surface measuring 60 feet from the foul line to the headpin, designed with side gutters and pin decks for precision ball roll and pin action. Running lanes, found on tracks, are made from textured synthetic materials like polyurethane to provide traction and shock absorption, typically marked with lane lines and starting blocks for athlete positioning. The structural difference lies in the flat, narrow, and contained design of bowling lanes versus the elongated, cushioned, and open design of running lanes optimized for speed and safety.
Surface Materials and Composition
Bowling lanes are typically made from hard rock maple or synthetic materials like phenolic resin that provide a smooth, durable surface designed to withstand constant ball impact and resist wear. Running lanes feature asphalt or rubberized surfaces engineered for shock absorption and traction, enhancing athlete performance and reducing injury risks. The composition differences are driven by the distinct impact and safety requirements of bowling, which demands a slick sliding surface, versus running, which requires cushioning and grip.
Key Functionality and Purposes
A bowling lane is designed specifically for the sport of bowling, featuring a smooth, polished surface that allows the bowling ball to glide toward the pins, with gutters on each side to catch stray balls. A running lane, typically found on athletic tracks, provides athletes with a marked, rubberized surface optimized for traction, speed, and safety during sprints or long-distance running. Key functionality of a bowling lane focuses on ball control and scoring accuracy, while a running lane emphasizes consistent footing and lane discipline to ensure fair competition.
Maintenance and Durability
Bowling lanes require specialized maintenance involving regular oiling, cleaning, and surface refinishing to preserve the lane's smoothness and protect against ball impact damage. Running lanes, typically made from synthetic or rubberized materials, demand routine inspection and resurfacing to maintain shock absorption and prevent wear from constant foot traffic. The durability of bowling lanes centers on resistance to ball abrasion, while running lanes focus on cushioning and traction longevity under repetitive dynamic loads.
Safety Protocols and Considerations
Bowling lanes require strict safety protocols such as maintaining clear areas around the lane to prevent slips and ensuring proper footwear to avoid injuries, while running lanes prioritize surface traction and lane width to reduce trip hazards and accommodate multiple athletes safely. Both types of lanes necessitate regular inspections for surface damage and debris to prevent accidents. Proper lighting and signage are essential in both environments to guide users and enhance overall safety compliance.
Influence on Athlete Performance
Bowling lanes and running lanes differ significantly in surface composition and design, directly influencing athlete performance. Bowling lanes have polished wood or synthetic surfaces that affect ball speed and trajectory, requiring precise control, whereas running lanes consist of textured rubberized tracks that optimize traction, shock absorption, and energy return to enhance sprinting efficiency. The specific surface properties of each lane type impact the athlete's biomechanics and overall performance outcomes in their respective sports.
Popularity and Cultural Impact
Bowling lanes, integral to a sport enjoyed worldwide, have grown in popularity as recreational venues attract diverse age groups seeking social entertainment, reflected in the proliferation of bowling alleys in urban centers. Running lanes, fundamental to athletics and fitness culture, maintain significant cultural impact by promoting health, competition, and community events, with track and field sports holding historical importance in Olympic Games. The popularity of bowling lanes aligns more with leisure and social bonding, whereas running lanes symbolize athletic discipline and global sporting traditions.
Accessibility and Cost Factors
Bowling lanes generally require specialized construction with durable synthetic or wooden surfaces and automated pinsetters, leading to higher installation and maintenance costs compared to running lanes, which are simpler tracks typically made of rubberized or synthetic materials. Accessibility for bowling lanes depends on facility design, including adequate space for wheelchairs and adaptive equipment, whereas running lanes often offer greater accessibility due to their open layout and adaptability for varying mobility devices. Cost factors for running lanes are lower because they do not need complex mechanical systems, making them more feasible for community and recreational spaces focused on inclusive physical activity.
Choosing the Right Lane for Your Needs
Choosing the right lane depends on your activity: a bowling lane is specifically designed with polished wood or synthetic surfaces to ensure smooth ball roll and pin interaction, while a running lane features rubberized or synthetic tracks optimized for traction and shock absorption during foot strikes. For bowlers, factors such as lane oil patterns and surface material influence ball behavior, whereas runners prioritize lane width, cushioning, and weather resistance. Understanding these distinctions helps select the appropriate lane for performance and safety in both sports.
Bowling lane Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com