Properly shutting down your device is crucial to prevent data loss and maintain system health. Follow specific steps for your operating system to ensure all applications close safely and updates are installed correctly. Discover detailed shutdown procedures and tips to extend your device's lifespan in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
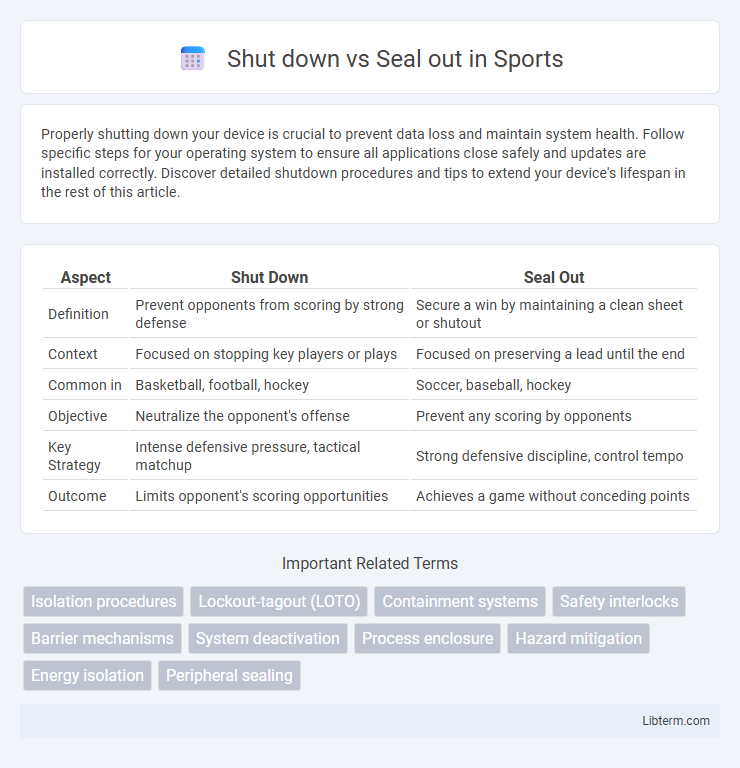
| Aspect | Shut Down | Seal Out |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Prevent opponents from scoring by strong defense | Secure a win by maintaining a clean sheet or shutout |
| Context | Focused on stopping key players or plays | Focused on preserving a lead until the end |
| Common in | Basketball, football, hockey | Soccer, baseball, hockey |
| Objective | Neutralize the opponent's offense | Prevent any scoring by opponents |
| Key Strategy | Intense defensive pressure, tactical matchup | Strong defensive discipline, control tempo |
| Outcome | Limits opponent's scoring opportunities | Achieves a game without conceding points |
Understanding Shut Down and Seal Out: Key Differences
Shut down involves completely stopping operations, often requiring de-energization and physical isolation to ensure safety during maintenance or emergencies. Seal out refers to isolating specific sections or equipment using barriers or seals to prevent contamination or unauthorized access while other operations continue. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective safety protocols and operational efficiency in industrial settings.
When to Shut Down vs When to Seal Out
Shut down is appropriate during prolonged inactivity or maintenance periods to completely stop equipment and conserve energy or prevent damage. Seal out is used when only isolating a section or process temporarily, maintaining pressure and preventing contamination while allowing partial operation elsewhere. Choosing between shut down and seal out depends on the duration, operational requirements, and safety considerations of the process involved.
Industrial Safety: The Role of Shut Down and Seal Out
Shut down and seal out procedures play crucial roles in industrial safety by preventing the release of hazardous substances and protecting workers during maintenance operations. Shut down involves stopping equipment or processes, while seal out ensures physical isolation, creating a secure environment by locking and tagging energy sources to prevent accidental restart. Proper implementation of both methods reduces risks of accidents and enhances compliance with safety regulations such as OSHA's Lockout/Tagout standards.
Environmental Impact: Choosing Shut Down or Seal Out
Shutting down industrial equipment temporarily reduces emissions by stopping operations, but incomplete sealing can allow pollutants to escape, impacting air quality. Seal out methods provide environmental protection by preventing hazardous substances from leaking, minimizing soil and water contamination during inactive periods. Selecting seal out over shutdown enhances containment, leading to improved environmental safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
Energy Efficiency: Shut Down vs Seal Out Strategies
Shut down strategies minimize energy consumption by completely powering off equipment during inactivity, eliminating standby power losses. Seal out methods enhance energy efficiency by preventing air leakage and thermal exchange, maintaining optimal indoor temperatures without the need for constant equipment operation. Combining shut down with effective seal out techniques yields significant reductions in energy waste and operational costs.
Cost Considerations for Shut Down and Seal Out
Shut down procedures generally incur higher costs due to complete system halts, including labor, downtime, and restart expenses, whereas seal out methods focus on isolating sections to minimize operational disruptions and associated expenses. Seal out techniques often reduce maintenance costs by allowing partial operation and targeted isolation, reducing overall downtime and improving resource allocation. Cost considerations for shut down emphasize total production loss and extensive labor, while seal out strategies prioritize efficiency and minimizing financial impact on continuous processes.
Equipment Longevity: Shut Down vs Seal Out
Shut down procedures involve completely powering off equipment, which can reduce wear from operational stress but may increase risks of corrosion or internal degradation if not properly maintained. Seal out methods isolate specific components or sections without full shutdown, enabling continued operation while minimizing exposure to contaminants, which helps preserve seal integrity and extends equipment life. Choosing between shut down and seal out depends on maintenance goals, environmental conditions, and the need to balance operational uptime with equipment longevity.
Regulatory Compliance: Shut Down and Seal Out Protocols
Shut down and Seal out protocols are critical for ensuring regulatory compliance in industrial operations, particularly in hazardous environments. Shut down procedures involve stopping equipment safely to prevent unintended energy release, while Seal out includes physically isolating energy sources to eliminate the risk of accidental re-energization. Adherence to OSHA and EPA standards for lockout/tagout and confined space entry underscores the importance of these protocols in maintaining workplace safety and meeting legal requirements.
Best Practices for Implementing Shut Down and Seal Out
Best practices for implementing shut down and seal out emphasize precise isolation of equipment to ensure safety and prevent contamination. Effective shut down procedures involve de-energizing all hazardous energy sources and verifying zero energy state with proper lockout/tagout devices. Seal out requires airtight sealing of valves or pipelines to prevent leakage, using certified gaskets or sealing compounds compliant with industry standards such as OSHA and ANSI for maximum containment integrity.
Case Studies: Successful Shut Down and Seal Out Applications
Case studies reveal that successful shut down applications often involve comprehensive isolation of equipment to ensure safe maintenance and prevent leakage, as demonstrated in refinery turnarounds where entire units are depressurized and drained. Seal out strategies excel in scenarios requiring containment of hazardous materials without full system interruption, illustrated by chemical plants using containment seals around rotating equipment to minimize emissions. Both methods, validated by industry experience, enhance operational safety and environmental compliance through precise application of isolation or containment techniques.
Shut down Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com