Mastering the half-court offense is essential for controlling the pace and maximizing scoring opportunities during basketball games. This offensive strategy focuses on precise ball movement, player spacing, and coordinated plays to break down tight defenses effectively. Explore the rest of the article to unlock key tactics that can elevate Your team's performance in half-court situations.
Table of Comparison
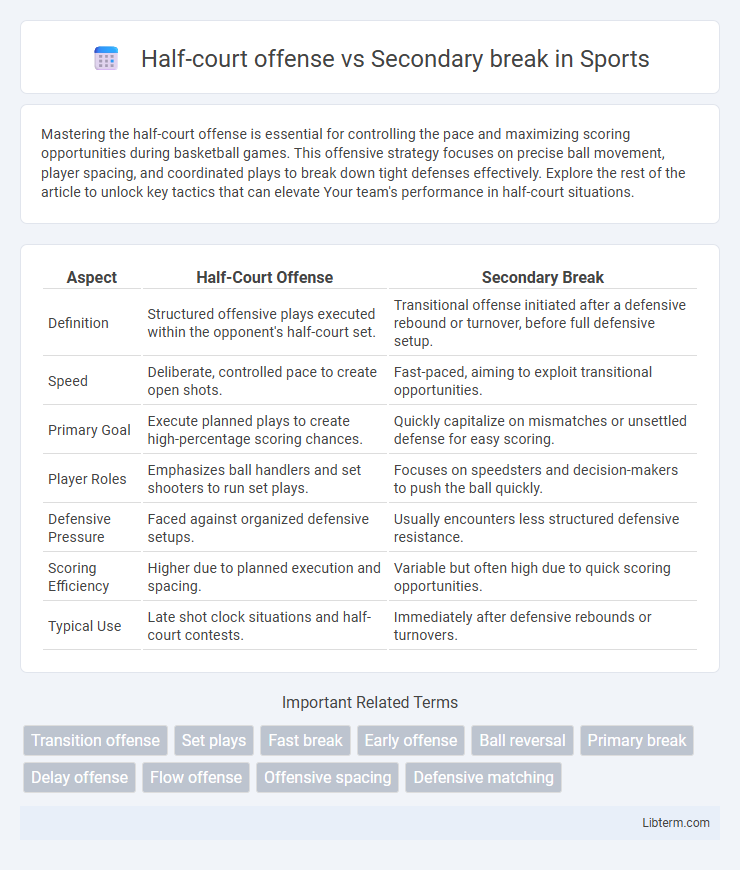
| Aspect | Half-Court Offense | Secondary Break |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured offensive plays executed within the opponent's half-court set. | Transitional offense initiated after a defensive rebound or turnover, before full defensive setup. |
| Speed | Deliberate, controlled pace to create open shots. | Fast-paced, aiming to exploit transitional opportunities. |
| Primary Goal | Execute planned plays to create high-percentage scoring chances. | Quickly capitalize on mismatches or unsettled defense for easy scoring. |
| Player Roles | Emphasizes ball handlers and set shooters to run set plays. | Focuses on speedsters and decision-makers to push the ball quickly. |
| Defensive Pressure | Faced against organized defensive setups. | Usually encounters less structured defensive resistance. |
| Scoring Efficiency | Higher due to planned execution and spacing. | Variable but often high due to quick scoring opportunities. |
| Typical Use | Late shot clock situations and half-court contests. | Immediately after defensive rebounds or turnovers. |
Introduction to Half-Court Offense and Secondary Break
Half-court offense centers on structured plays and precise spacing to create high-percentage scoring opportunities within the offensive team's half of the court, relying heavily on player movement and set plays. The secondary break occurs immediately after an initial fast break opportunity is slowed or stopped, requiring quick decision-making to exploit transition gaps before the defense fully sets up. Understanding these concepts enhances a team's ability to efficiently transition from fast-paced scoring attempts to controlled offensive execution.
Key Principles of Half-Court Offense
Half-court offense emphasizes structured ball movement, precise spacing, and coordinated player movement to create high-percentage scoring opportunities against set defenses. Key principles include maintaining proper spacing to avoid defensive congestion, utilizing screens and cuts to generate open shots or driving lanes, and effective communication to ensure synchronization among teammates. Mastery of these concepts enhances offensive efficiency by exploiting defensive weaknesses in a controlled, paced environment.
Fundamentals of the Secondary Break
The fundamentals of the secondary break emphasize quick decision-making and efficient spacing after a defensive rebound to capitalize on transition opportunities before the defense is set. Players must execute precise outlet passes and maintain high floor balance to create open lanes or mismatches, differing from the methodical setup of a half-court offense. Mastery of timing, communication, and conditioning enhances the secondary break's effectiveness, allowing teams to exploit defensive disorganization and maximize scoring chances.
Situational Use: When to Choose Half-Court Offense
Half-court offense is ideal during structured moments when the defense is set and the team seeks high-percentage shots through well-executed plays and ball movement. Teams select half-court offense in late-game scenarios or when aiming to control tempo and minimize turnovers, especially against aggressive pressing defenses in secondary breaks. Employing this strategy maximizes scoring efficiency by exploiting tactical spacing and precise execution within the three-point arc.
Advantages of Running a Secondary Break
Running a secondary break in basketball maximizes scoring opportunities by exploiting defensive mismatches before the defense sets up, increasing the pace and flow of the game. It allows teams to maintain offensive rhythm through quick ball movement and player cuts, reducing the risk of turnovers common in half-court offenses. Effective secondary breaks enhance transition scoring efficiency, often leading to higher-percentage shots and boosting overall team offensive output.
Common Challenges in Half-Court Offense
Half-court offense often struggles with shot clock pressure and tight defensive schemes that limit open scoring opportunities. Players face challenges in effective ball movement and creating high-percentage shots against well-organized defenses. Coordinating screens and exploiting mismatches become critical to breaking down compact defensive formations.
Integrating Secondary Break with Transition Plays
Integrating secondary break with transition plays enhances half-court offense by maintaining offensive pressure and exploiting defensive vulnerabilities before set defenses establish. Secondary break opportunities arise when the initial fast break misses or is controlled by the defense, allowing teams to attack mismatches and create high-percentage scoring chances in transition. Efficient secondary break execution requires quick decision-making, precise spacing, and seamless communication to capitalize on early offensive advantages and increase overall scoring efficiency.
Player Roles and Responsibilities
In half-court offense, players focus on precise spacing, setting screens, and executing set plays to create high-percentage shots, with guards typically handling ball distribution and wings cutting or posting up for scoring opportunities. In a secondary break, roles shift towards quick decision-making and positioning for offensive rebounds or fast break continuation, where forwards and bigs aggressively pursue rebounds while guards push the pace for fast scoring chances. Defensive players must also transition efficiently to maintain pressure, with guards pressing ball handlers and bigs protecting the paint to disrupt secondary break chances.
Tactical Adjustments Against Different Defenses
Adjusting tactics for half-court offense requires precise ball movement and player spacing to counteract man-to-man and zone defenses, emphasizing pick-and-rolls and isolations to exploit mismatches. In contrast, secondary break strategies prioritize quick transitions and spacing to capitalize on defensive disorganization, focusing on quick passes and attack angles before the defense sets up. Effective tactical adjustments involve recognizing defensive setups early and shifting offensive tempo and formation to maintain efficiency and scoring opportunities.
Comparing Effectiveness: Stats and Real-Game Examples
Half-court offenses generate higher shooting percentages, typically around 45-50%, emphasizing structured plays and ball movement to create open shots, as seen in the Golden State Warriors' late-game sets. Secondary breaks exploit turnovers and defensive resets, leading to faster scoring opportunities with efficiency rates near 55%, exemplified by the Phoenix Suns' fast-paced transition scoring off rebounds. Statistical analysis reveals teams with strong secondary break execution often outscore opponents by 7-10 points per game in transition opportunities, highlighting its impact over controlled half-court sets during high-tempo contests.
Half-court offense Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com