Powerball is a popular lottery game known for its massive jackpots and thrilling gameplay that captivates millions of participants worldwide. Players select numbers in hopes of matching the winning combination drawn, offering life-changing prizes that can transform your financial future overnight. Discover how Powerball works, tips for increasing your odds, and the latest jackpot updates in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
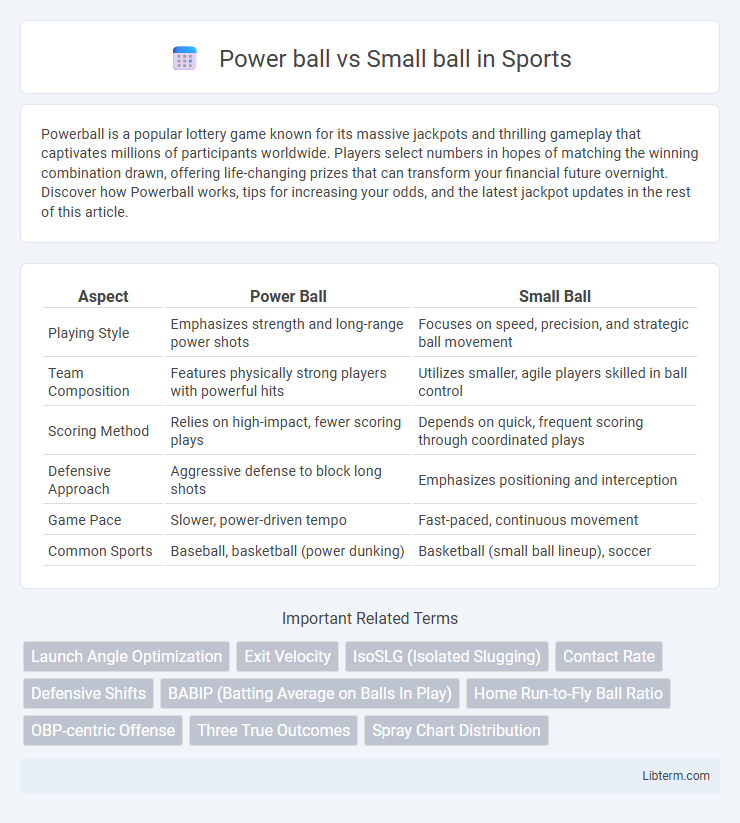
| Aspect | Power Ball | Small Ball |
|---|---|---|
| Playing Style | Emphasizes strength and long-range power shots | Focuses on speed, precision, and strategic ball movement |
| Team Composition | Features physically strong players with powerful hits | Utilizes smaller, agile players skilled in ball control |
| Scoring Method | Relies on high-impact, fewer scoring plays | Depends on quick, frequent scoring through coordinated plays |
| Defensive Approach | Aggressive defense to block long shots | Emphasizes positioning and interception |
| Game Pace | Slower, power-driven tempo | Fast-paced, continuous movement |
| Common Sports | Baseball, basketball (power dunking) | Basketball (small ball lineup), soccer |
Introduction to Power Ball and Small Ball Strategies
Power Ball strategy emphasizes high-value, low-frequency shots, often targeting three-pointers and post plays to maximize points per possession. Small Ball strategy focuses on speed, agility, and spacing, utilizing smaller lineups to increase tempo, create mismatches, and enhance ball movement. Both approaches fundamentally alter offensive dynamics, influencing team composition and playstyle in modern basketball.
Defining Power Ball: Key Characteristics
Power ball in basketball is characterized by emphasis on physicality, size, and strength, prioritizing dominant post players who excel in scoring near the basket and securing rebounds. This style relies on powerful inside plays, aggressive defense, and high-percentage shots from close range. Key metrics for power ball include points in the paint, offensive rebounds, and field goal percentage in the restricted area.
Understanding Small Ball: Core Principles
Small ball centers on maximizing efficiency through high-percentage shots, prioritizing three-pointers, layups, and free throws to increase scoring opportunities. This strategy emphasizes speed, spacing, and ball movement, often utilizing smaller, versatile players to exploit mismatches. By minimizing turnovers and focusing on quick, precise plays, small ball creates sustained offensive pressure and optimizes scoring potential.
Historical Evolution of Power Ball and Small Ball
Power ball strategies, originating in the 1980s NBA, emphasized dominant inside scoring, relying on tall centers and high-percentage post plays to control the game. Small ball emerged prominently in the 2010s, driven by increased three-point shooting and positionless basketball, prioritizing speed, spacing, and versatility to exploit defensive mismatches. The historical evolution reflects a shift from traditional, paint-dominated tactics to faster-paced, perimeter-oriented styles that capitalize on analytics and player mobility.
Advantages of Power Ball in Modern Sports
Power Ball training enhances grip strength, wrist stability, and forearm muscle endurance, making it ideal for athletes in sports like baseball, tennis, and rock climbing. The device's dynamic resistance improves rotational power and coordination, translating to faster swing speeds and increased throwing velocity. Its compact, portable design allows for efficient, versatile workouts that boost performance without the need for bulky gym equipment.
Strengths of Small Ball in Competitive Play
Small ball offers faster court spacing and increased ball movement, creating more scoring opportunities through drives and open perimeter shots. Its emphasis on speed and agility allows teams to exploit mismatches and maintain high offensive tempo. This approach also strengthens defensive versatility, enabling quick rotations and effective switching during competitive play.
Situational Effectiveness: When to Use Each Approach
Power ball strategy excels in late-game scenarios requiring high-impact plays and quick comebacks due to its emphasis on three-point shooting and spacing. Small ball is most effective in controlling pace and exploiting mismatches, particularly during fast breaks and when maintaining offensive versatility against bigger lineups. Teams often switch between both approaches depending on game tempo, player availability, and opponent defensive schemes to maximize situational effectiveness.
Notable Teams and Players: Power Ball vs. Small Ball
Notable teams like the Golden State Warriors exemplify small ball, utilizing speed and perimeter shooting with players such as Stephen Curry and Klay Thompson to stretch defenses. Power ball is embodied by teams like the Detroit Pistons in the early 2000s, led by players such as Ben Wallace and Rasheed Wallace, focusing on physical dominance and inside scoring. The contrast highlights the strategic differences where small ball emphasizes spacing and pace while power ball relies on size and strength in the paint.
Statistical Comparison and Performance Metrics
Power ball strategies emphasize high-value scoring through three-pointers and shots in the paint, resulting in higher average points per possession and effective field goal percentages, while small ball prioritizes speed and spacing, often leading to increased pace, more assists, and greater defensive switchability. Statistical comparisons reveal power ball teams typically record higher offensive ratings but may suffer in defensive efficiency due to slower lineups, whereas small ball lineups improve defensive metrics like opponent points per possession and increase rebounding rates due to versatile players. Performance metrics such as true shooting percentage (TS%) and net rating often favor power ball in half-court sets, while small ball excels in transition offense and forced turnovers, highlighting trade-offs tailored to team composition and game tempo.
Future Trends: The Ongoing Debate Between Power Ball and Small Ball
Future trends in basketball emphasize a dynamic interplay between Power Ball's emphasis on size, strength, and three-point shooting, and Small Ball's focus on speed, versatility, and floor spacing. Advanced analytics reveal teams leveraging Small Ball lineups often gain advantages in pace and offensive efficiency, while Power Ball strategies continue to dominate in rebounding and interior defense. Emerging player development programs increasingly blend these approaches, fostering versatile athletes capable of excelling in hybrid roles that reflect the evolving demands of modern basketball.
Power ball Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com