Slot receivers excel at running precise routes from the middle of the field, exploiting mismatches against linebackers and safeties due to their speed and agility. Their versatility in both receiving and blocking makes them essential in modern offensive schemes, creating opportunities for big plays. Discover how understanding the role of a slot receiver can transform your view of football strategy by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
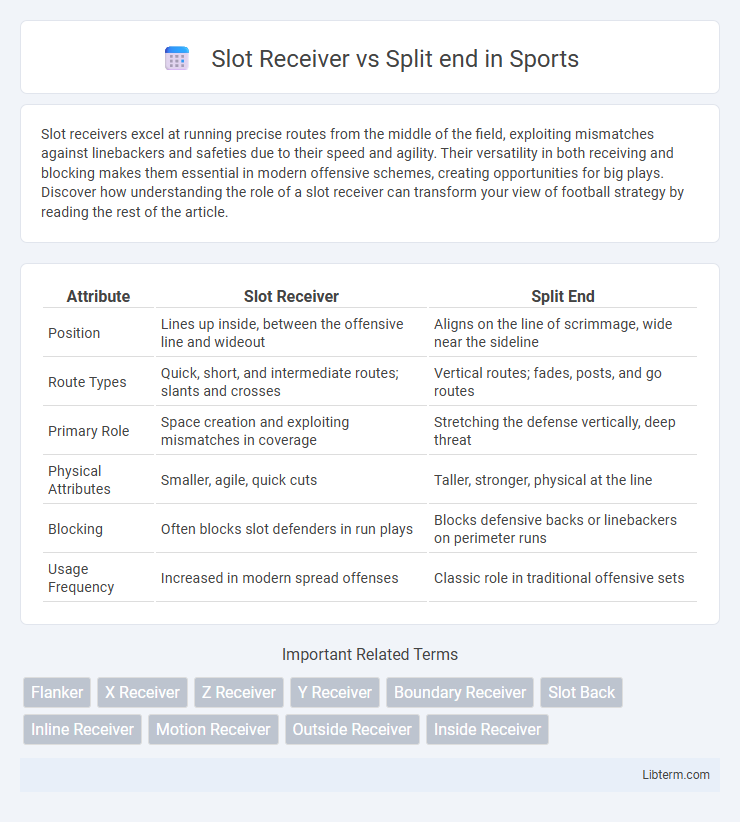
| Attribute | Slot Receiver | Split End |
|---|---|---|
| Position | Lines up inside, between the offensive line and wideout | Aligns on the line of scrimmage, wide near the sideline |
| Route Types | Quick, short, and intermediate routes; slants and crosses | Vertical routes; fades, posts, and go routes |
| Primary Role | Space creation and exploiting mismatches in coverage | Stretching the defense vertically, deep threat |
| Physical Attributes | Smaller, agile, quick cuts | Taller, stronger, physical at the line |
| Blocking | Often blocks slot defenders in run plays | Blocks defensive backs or linebackers on perimeter runs |
| Usage Frequency | Increased in modern spread offenses | Classic role in traditional offensive sets |
Understanding the Slot Receiver and Split End
The Slot Receiver lines up between the offensive line and the wide receiver, offering versatility in both running and passing plays due to their quickness and route-running skills. The Split End, positioned on the line of scrimmage wide from the offensive line, primarily serves as a deep threat or possession receiver, capitalizing on speed and catching ability. Understanding the distinction between these roles highlights their strategic use in offensive schemes to stretch defenses and create mismatches.
Key Differences in Positioning
Slot receivers line up between the offensive line and the wide receiver, positioning themselves inside the formation to exploit shorter, quicker routes and create mismatches against linebackers or nickel corners. Split ends align on the outside edge of the offensive line, often facing press coverage from cornerbacks and focusing more on vertical routes and outside runs. Their distinct alignments directly influence their route trees, blocking responsibilities, and the defensive matchups they face on the field.
Primary Roles on the Field
Slot receivers primarily operate in the middle of the field, using quick routes and agility to exploit defensive zones and create mismatches against linebackers and safeties. Split ends line up on the outside, stretching the defense vertically with deep routes and serving as primary targets for outside passing attacks. Both positions require precise route running and strong hands but differ in alignment and strategic responsibilities within offensive schemes.
Route Assignments and Patterns
Slot receivers primarily run routes that exploit the middle of the field such as slants, option routes, and crossing patterns, leveraging their quickness and agility to find soft spots in zone coverage. Split ends, positioned on the line of scrimmage, tend to run more vertical patterns like fades, posts, and outs designed to stretch the defense and create deep threats. Route assignments for slot receivers emphasize short-to-intermediate timing routes, while split ends focus on stretching the field vertically to open up underneath opportunities for other receivers.
Physical Traits and Athlete Profiles
Slot receivers typically possess quicker agility, smaller stature, and exceptional route-running skills, enabling sharp cuts in confined spaces, while split ends are often taller and more physical, excelling at contested catches on the outside. Slot receivers exhibit exceptional acceleration and change-of-direction speed, reflecting profiles similar to shifty running backs or scat backs. Split ends resemble traditional wide receivers with larger frames and longer wingspans, designed to dominate jump-ball situations and create separation downfield.
Impact on Offensive Schemes
Slot receivers create flexible offensive schemes by exploiting intermediate routes and mismatches against linebackers and nickel corners, enhancing passing diversity and timing-based plays. Split ends primarily stretch the field horizontally with downfield routes, forcing defenses to cover deep and opening space for run plays and play-action passes. The interplay between slot receivers and split ends enables offenses to balance vertical threats with quick, deceptive attacks, complicating defensive coverage assignments and generating dynamic play-calling options.
Blocking Responsibilities
Slot receivers primarily excel in blocking for inside runs, picking up blitzes, and supporting running backs on misdirection plays due to their alignment closer to the offensive line. Split ends, positioned on the line of scrimmage, have more limited blocking duties, generally focusing on sealing outside defenders to create running lanes on sweeps or outside runs. Effective blocking by both positions is crucial for successful running plays, with slot receivers often bearing a heavier responsibility in pass protection schemes against linebackers and defensive backs.
Coverage Matchups Faced
Slot receivers face more complex coverage matchups than split ends due to their alignment inside the formation, forcing defenders like nickel cornerbacks or linebackers into coverage. They often encounter zone coverages and press man-to-man, requiring quick route adjustments and separation skills. Split ends typically see outside cornerbacks in press coverage, emphasizing speed and outside leverage to create separation downfield.
Notable NFL Examples
Notable NFL examples of slot receivers include Wes Welker, Julian Edelman, and Cooper Kupp, who excel in quick, precise routes and creating mismatches against linebackers and safeties. In contrast, prominent split ends like Jerry Rice, Larry Fitzgerald, and Mike Evans primarily use their size and speed to stretch the field and dominate outside coverage. The distinct roles highlight how slot receivers thrive in the middle of the field with agility and route-running, while split ends capitalize on outside speed and separation.
Choosing the Right Position for Team Strategy
Selecting between a Slot Receiver and a Split End depends heavily on the team's offensive strategy and play style. The Slot Receiver excels in quick routes and space utilization, creating mismatches in the middle of the field, while the Split End typically serves as a primary deep threat on the outside, stretching defenses vertically. Balancing these roles based on opponent tendencies and quarterback strengths enhances overall offensive efficiency.
Slot Receiver Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com