Activity plays a crucial role in maintaining physical health, boosting mental well-being, and enhancing overall energy levels. Engaging in regular exercise can help prevent chronic diseases and improve your mood by releasing endorphins. Explore this article to discover effective ways to incorporate more activity into your daily routine.
Table of Comparison
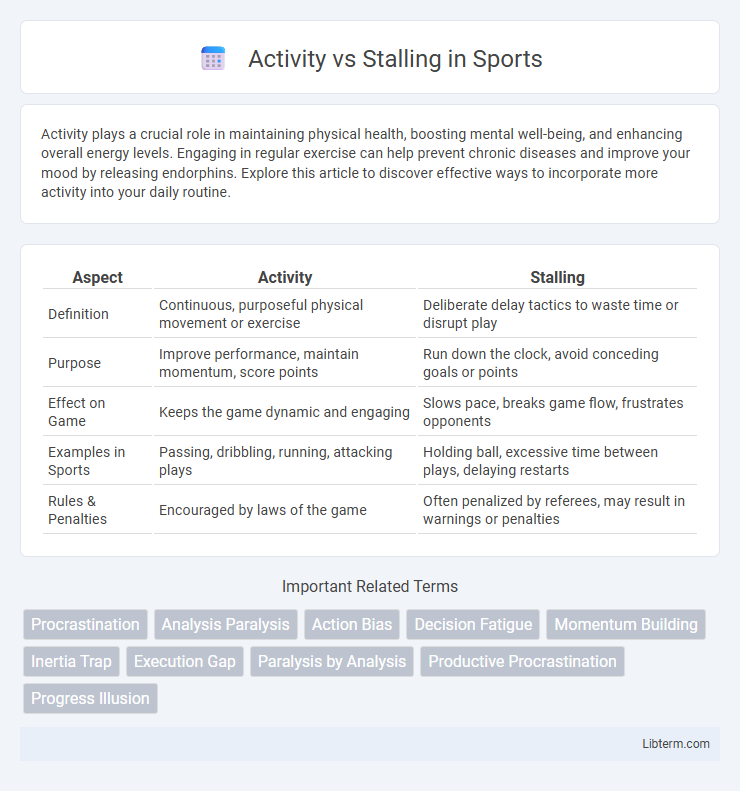
| Aspect | Activity | Stalling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous, purposeful physical movement or exercise | Deliberate delay tactics to waste time or disrupt play |
| Purpose | Improve performance, maintain momentum, score points | Run down the clock, avoid conceding goals or points |
| Effect on Game | Keeps the game dynamic and engaging | Slows pace, breaks game flow, frustrates opponents |
| Examples in Sports | Passing, dribbling, running, attacking plays | Holding ball, excessive time between plays, delaying restarts |
| Rules & Penalties | Encouraged by laws of the game | Often penalized by referees, may result in warnings or penalties |
Understanding Activity vs Stalling
Understanding activity versus stalling is crucial in optimizing task performance and decision-making processes. Activity refers to proactive engagement and progress toward goals, while stalling signifies hesitation or delay without productive output. Recognizing the signs of stalling enables effective intervention to maintain momentum and achieve desired outcomes.
Signs You’re Just Staying Busy
Constantly juggling tasks without clear goals often indicates stalling rather than genuine progress. Signs you're just staying busy include repeatedly checking emails, attending non-essential meetings, and multitasking ineffectively. True activity drives measurable results and moves projects forward, unlike busyness that masks procrastination.
The Psychology Behind Stalling
Stalling behavior often stems from underlying psychological factors such as fear of failure, perfectionism, and anxiety, which inhibit productive activity by triggering avoidance mechanisms. Cognitive dissonance plays a key role, where individuals delay tasks to reconcile conflicting emotions or self-perceptions regarding competence and outcome expectations. Understanding the neural correlates linked to procrastination, including alterations in the prefrontal cortex and limbic system, provides insights into why stalling persists despite awareness of negative consequences.
Why Activity Doesn’t Always Mean Progress
Activity doesn't always equate to progress because being busy with tasks can lack strategic direction and measurable outcomes. Many individuals confuse motion with advancement, resulting in effort-intensive routines that fail to address core objectives. Focusing on goal-oriented actions with clear metrics ensures that activity translates into genuine progress and meaningful achievements.
Common Reasons People Stall
People often stall due to fear of failure, perfectionism, or lack of clear goals, which disrupts productive activity. Procrastination fueled by overwhelm or uncertainty leads to extended delays in task completion. Addressing these psychological and organizational barriers promotes consistent forward momentum and avoids stagnation.
Impact of Stalling on Goals
Stalling hampers progress by creating delays that disrupt workflow and reduce overall productivity, directly impacting the timely achievement of goals. Prolonged inactivity can cause missed deadlines and increased stress, leading to decreased motivation and engagement among team members. Effective time management strategies are essential to minimize stalling and maintain consistent forward momentum toward objectives.
Strategies to Move from Stalling to Action
Effective strategies to transition from stalling to action include setting clear, achievable goals and breaking tasks into manageable steps to reduce overwhelm. Employing time management techniques like the Pomodoro method can enhance focus and maintain momentum during work sessions. Leveraging accountability partners or using progress tracking tools fosters commitment and reinforces consistent activity toward task completion.
How to Measure Meaningful Progress
Measuring meaningful progress involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) that directly impact project goals rather than simply logging hours spent. Activity is valuable when it leads to tangible outcomes, such as completed milestones or deliverables, while stalling can be identified by stagnant metrics like unchanged feature counts or unresolved issues. Employing objective data from project management tools and regular status assessments ensures efforts align with strategic priorities and drive measurable advancement.
Tools to Prioritize Productive Tasks
Effective tools like Eisenhower Matrix and Kanban boards help distinguish between activity and stalling by prioritizing productive tasks based on urgency and impact. Time-tracking apps such as RescueTime reveal unproductive habits, enabling users to focus on goal-oriented activities. Task management software like Trello and Asana streamline workflows, ensuring clear deadlines and accountability to maintain consistent productivity.
Building Habits for Consistent Action
Building habits for consistent action requires understanding the difference between activity and stalling, where activity involves purposeful steps toward goals while stalling often manifests as distraction or procrastination disguised as busyness. Effective habit formation emphasizes small, repetitive actions that build momentum, reinforcing neural pathways associated with productive behaviors. Leveraging tools like habit trackers and setting clear intentions can combat stalling by maintaining focus and accountability during the habit-building process.
Activity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com