A flat tennis serve is a powerful and fast shot that travels with minimal spin, making it difficult for opponents to react. This serve is ideal for players looking to deliver a direct and aggressive serve to gain points quickly. Discover how perfecting your flat serve can enhance your game by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
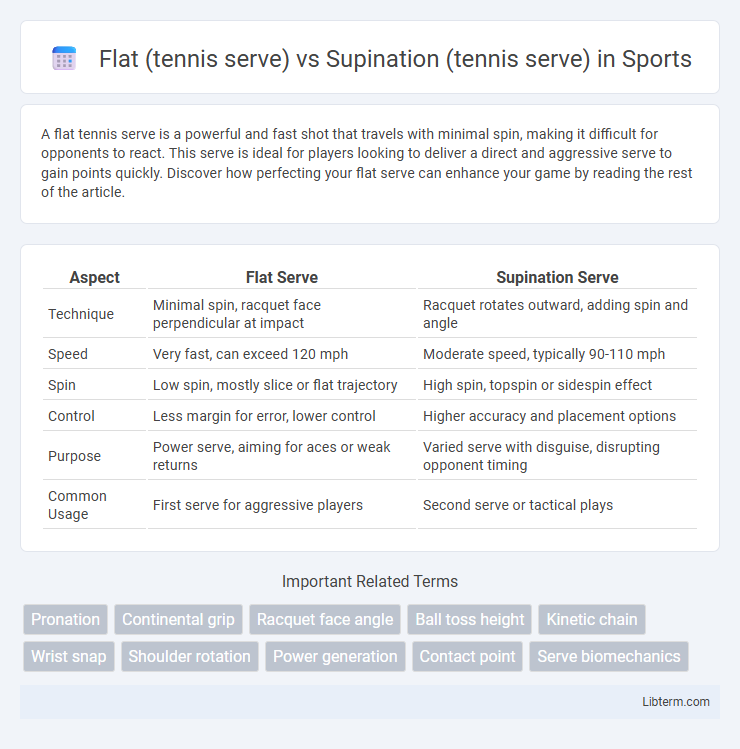
| Aspect | Flat Serve | Supination Serve |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Minimal spin, racquet face perpendicular at impact | Racquet rotates outward, adding spin and angle |
| Speed | Very fast, can exceed 120 mph | Moderate speed, typically 90-110 mph |
| Spin | Low spin, mostly slice or flat trajectory | High spin, topspin or sidespin effect |
| Control | Less margin for error, lower control | Higher accuracy and placement options |
| Purpose | Power serve, aiming for aces or weak returns | Varied serve with disguise, disrupting opponent timing |
| Common Usage | First serve for aggressive players | Second serve or tactical plays |
Introduction to Tennis Serve Techniques
Flat tennis serves generate maximum speed and power by hitting the ball with a neutral wrist position, creating a direct and fast trajectory. Supination in tennis serves involves rotating the forearm to impart side-spin, enhancing control and causing the ball to curve away from the opponent. Understanding the biomechanical differences improves serve effectiveness by balancing velocity with spin-based precision.
What is a Flat Serve?
A flat serve in tennis is characterized by minimal spin and maximum speed, achieved by hitting the ball with a fully extended arm and a firm wrist, resulting in a straight trajectory that reduces the opponent's reaction time. Supination in a tennis serve refers to the outward rotation of the forearm and wrist during the racket swing, which can add topspin or slice, contrasting with the flat serve's lack of spin. The flat serve is favored for its power and directness, often used to secure quick points on fast surfaces.
What is a Supination Serve?
A Supination serve in tennis involves outward rotation of the forearm, causing the palm to face upward and the racquet to brush the ball with a slicing motion, generating spin and control. Unlike a Flat serve that relies on power and speed with minimal spin, the Supination serve imparts pronounced topspin or sidespin, enhancing ball trajectory and placement accuracy. This technique often results in a more controlled serve that can challenge opponents with varying bounce and angles on the court.
Key Differences: Flat vs Supination Serves
Flat serves in tennis generate maximum speed and minimal spin by striking the ball with the racquet face perpendicular to the ground, producing a fast, straight trajectory ideal for powerful first serves. Supination serves involve rotating the wrist outward during the swing, creating lateral spin that causes the ball to curve or slice, improving serve placement and creating difficult angles for the opponent. Key differences include speed and spin profile, with flat serves prioritizing velocity and supinated serves emphasizing controlled spin and strategic ball movement.
Biomechanics of the Flat Serve
The biomechanics of the flat tennis serve involve generating maximum racket head speed through explosive shoulder internal rotation, minimal pronation, and high ball toss placement to produce a direct, powerful trajectory. Unlike supination, which introduces a forearm rotation to add spin and control, the flat serve emphasizes a linear motion with limited wrist and forearm rotation to maximize speed and reduce spin. This technique requires optimal kinetic chain sequencing, starting from leg drive to shoulder rotation, ensuring efficient energy transfer for maximum serve velocity.
Biomechanics of the Supination Serve
The biomechanics of the supination tennis serve involve a distinct outward rotation of the forearm, creating enhanced racket head speed and increased topspin compared to the flat serve. Supination enables greater wrist flexion and pronation-supination torque, improving ball control and spin generation for aggressive yet consistent serves. In contrast, the flat serve relies primarily on maximum power and minimal spin, emphasizing shoulder and trunk rotation without extensive forearm supination.
Power and Speed Comparison
The flat tennis serve generates maximum power by minimizing spin and allowing the racket to strike the ball with a direct, linear motion, typically reaching speeds of 110-130 mph among professional players. Supination during the serve enhances racket head speed and pronation torque, contributing to greater racket acceleration and spin, but may slightly reduce raw speed compared to a purely flat serve. Power output in flat serves relies on optimal biomechanics for direct energy transfer, while supination balances speed with added ball control and spin effects.
Spin and Ball Trajectory Analysis
Flat serves generate minimal spin, resulting in a faster ball speed with a relatively straight and lower trajectory, making them effective for aggressive play and quick points. Supination in tennis serves involves outward rotation of the wrist, creating significant topspin or slice, which alters the ball's trajectory by increasing its arc and causing it to dip sharply upon landing. Spin variations from supination enhance control and deception, enabling players to manipulate ball bounce and placement more precisely compared to the flatter, speed-focused flat serves.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Serve
Flat tennis serves generate high speed and minimal spin, providing an advantage in overpowering opponents and finishing points quickly, but their low margin for error increases fault risk. Supination, involving wrist rotation to create topspin or slice, offers greater control and ball placement, reducing double faults and improving consistency during rallies, though it sacrifices some velocity. Choosing between flat and supinated serves depends on a player's style, with flat serves favoring aggressive attackers and supinated serves benefiting baseline players prioritizing precision.
Choosing the Right Serve for Your Game
Flat serves generate maximum speed and power by striking the ball with a firm, straight wrist motion, making them ideal for aggressive, fast-paced games and players seeking quick points. Supination serves involve a slight outward rotation of the wrist, producing topspin that enhances ball control and bounce, benefiting players who prioritize consistency and strategic placement. Choosing the right serve depends on balancing power and control according to playing style, physical ability, and match conditions to optimize performance on the court.
Flat (tennis serve) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com